字符串Hash例题详解
Catalogue
- 1.Codeforces 898F Restoring the Expression
- 2.Codeforces 961F k-substrings
- 3.Codeforces 985F Isomorphic Strings
- 4.friends
1.Codeforces 898F Restoring the Expression

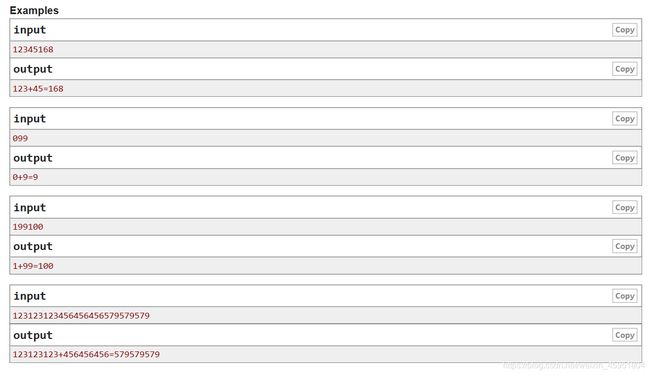
题目大意:给定一个字符串,将其划分成三个部分,使其满足一个加法等式。
设计思路:在这里首先我们考虑假定和为 n \;n\; n位数,那么两个加数的位数肯定都不会超过 n \;n\; n,并且其中一个加数一定是 n \;n\; n位或者 n − 1 \;n-1\; n−1位。这样我们先求出整个字符串的 H a s h \;Hash\; Hash函数,这里 b a s e \;base\; base取 10 \;10\; 10便于加法计算,然后枚举等号的位置,判断三个字符串的关系。
Solution:
#include2.Codeforces 961F k-substrings


题目大意:给定一个字符串,对于它的所有子串 k − s u b s t r i n g s \;k-substrings\; k−substrings,问其前缀和后缀相同的最大长度,且长度必须为奇数,如果不存在则为 − 1 \;-1\; −1。 k − s u b s t r i n g s \;k-substrings\; k−substrings是这样定义的:对于每个字符串,每次在开头和结尾删去 i \;i\; i个字符后得到的字符串。
设计思路:对于这道题目,我们考虑用字符串 H a s h \;Hash\; Hash来解决。先考虑朴素的枚举思想,即对于一个子串,从大到小枚举所有奇数前缀和后缀,然后根据Hash值来判断二者是否相等,复杂度在最坏情况下会达到 O ( n 2 ) \;O(n^2)\; O(n2),即使 4 s \;4s\; 4s也不够解决。观察字符串的特点,当在计算 i \;i\; i的最大公共前缀和后缀时,由于每次子串是两头向中间收缩,所以有这样一个结果,即 r e s [ i ] − 2 ≤ r e s [ i + 1 ] \;res[i]-2≤res[i+1]\; res[i]−2≤res[i+1],观察下图所示:

在计算出第 i \;i\; i位开始的子串的最大长度,紧接着计算 i + 1 \;i+1\; i+1位的长度,首先去掉首字符和尾字符,由于之前我们已经得到两部分子串长度相同,所以对于 i + 1 \;i+1\; i+1开始的子串的结果至少为上一次结果-2。也就是说对于上一次的前缀和后缀,去掉它们首字符和尾字符,中间部分一定是相同的,所以有 r e s [ i ] − 2 ≤ r e s [ i + 1 ] \;res[i]-2≤res[i+1]\; res[i]−2≤res[i+1],简单移项后就有 r e s [ i ] ≤ r e s [ i + 1 ] + 2 \;res[i]≤res[i+1]+2\; res[i]≤res[i+1]+2,问题恰好为求最大值,根据这个等式可以得到较长子串一定不会较短子串的结果+2,所以从中间开始枚举,然后对每个子串从上一次的结果开始,逐次-2,判断 H a s h \;Hash\; Hash值是否相等。
Solution:
#include3.Codeforces 985F Isomorphic Strings


题目大意:给定一个字符串,然后每次截取两端相等长度的子串,问这两个子串是否同构。(同构就是两个字符对应位置只有一一映射的关系,即不能多对一也不能一对多)
设计思路:如果简单采取一一映射的方法,对每次询问子串遍历,那么复杂度肯定也是无法满足需求。由于这里的问题是对于两个字符串而言,它们能否构成同构,而字符串 H a s h \;Hash\; Hash的思想是将字符串映射为一个尽可能唯一的整数,通过比较两个整数来判断两个字符串是否相等,而这里两个字符串相等的关系不是仅仅的对应字符相等,而是要满足同构这种特殊相等关系,所以这时候不再对字符串进行 H a s h \;Hash\; Hash,而对每个字符的位置 H a s h \;Hash\; Hash,然后通过 H a s h \;Hash\; Hash值判断是否同构。
如何理解对位置 H a s h \;Hash\; Hash是这个问题的难点,首先要知道 H a s h \;Hash\; Hash函数有一种类似前缀和的性质,每一位字符 H a s h \;Hash\; Hash值是在上一位的结果基础上乘以进制再加上本位字符的数值大小。现在考虑两个字符串是否同构,那么来看如下一个例子;
比如对于字符串 a b c a b b a c d b c c \;abcabbacdbcc\; abcabbacdbcc,选取它的两个子串如 b c a b b \;bcabb\; bcabb和 c d b c c \;cdbcc\; cdbcc,肉眼可以直观看出这两个字符串是同构的,那么如何用计算机来判断呢?在这个例子中 f ( b ) = c , f ( c ) = d , f ( a ) = b \;f(b)=c\;,\;f(c)=d,f(a)=b\; f(b)=c,f(c)=d,f(a)=b,也就是说,每个字母和另一个有对应关系,有了这个想法,我们考虑将原字符串映射为26个01串,每个01串表示一个字母,该位置为这个字符为1其余为0,那么上述例子中就可以转化为100100100000, 010011000100, 001000010011, 000000001000…这时候问题就转化了,对于 f ( b ) = c \;f(b)=c\; f(b)=c,在 b \;b\; b转化的01串中,对应位置的子串为10011,在 c \;c\; c转化的01串中,对应位置的子串为10011,这两个转化的子串是完全一致的,也就是说,对于 b \;b\; b和 c \;c\; c,满足一一映射的关系,因为如果子串比如是…a…a…和…c…c…c…,那么对应的01串是…010…010…和…010…010…010…,这两个字符串一定是不相等的。所以判断两个字符串是否同构,只需要得到这两个字符串每个每个字母的 H a s h \;Hash\; Hash,然后判断两个字符串的26个字母是否都存在一一对应的关系。
Solution:
#include4.friends
题目大意:给定一个字符串,从中删除任一字符后得到的字符串能够分为两个相同的子串,如果不可能输出"NOT POSSIBLE",存在唯一解输出这个字符串,存在多解输出“NOT UNIQUE”。
设计思路:首先对于长度为偶数的字符串一定是不存在解的,删除一个字符后剩下的字符串不能分为两个等长的字符串。然后对于奇数长度的字符串,只需要枚举删除每一位字符后剩下的字符串分为两部分是否相等,如果相等则保存它的 H a s h \;Hash\; Hash值,用于下次再存在解时判重。同时可以进一步优化,当枚举的字符位于前 n 2 \;\frac{n}{2}\; 2n时,拆分的其中一个字符串一定是原字符串的后 n 2 \;\frac{n}{2}\; 2n位,同样枚举到后一半的字符时其中一个字符串一定是原字符串的前 n 2 \;\frac{n}{2}\; 2n位,预处理这两个值避免每次枚举时重复计算。( p s : \;ps:\; ps:这道题卡了 1 e 9 + 7 1e9+7 1e9+7和 1 e 9 + 9 1e9+9 1e9+9,所以模数要放大一些)
Solution:
#include有时间再更新啦 完结撒花!