牛客网暑期ACM多校训练营(第一场)A.Monotonic Matrix(非降路径和Lindström–Gessel–Viennot定理)
链接:https://www.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/139/A
来源:牛客网
题目描述
Count the number of n x m matrices A satisfying the following condition modulo (109+7).
* Ai, j ∈ {0, 1, 2} for all 1 ≤ i ≤ n, 1 ≤ j ≤ m.
* Ai, j ≤ Ai + 1, j for all 1 ≤ i < n, 1 ≤ j ≤ m.
* Ai, j ≤ Ai, j + 1 for all 1 ≤ i ≤ n, 1 ≤ j < m.
输入描述:
The input consists of several test cases and is terminated by end-of-file.
Each test case contains two integers n and m.
输出描述:
For each test case, print an integer which denotes the result.
示例1
输入
复制
1 2
2 2
1000 1000
输出
复制
6
20
540949876
备注:
* 1 ≤ n, m ≤ 103
* The number of test cases does not exceed 105.
题意
给你一个nxm的矩阵让你向其中填{0,1,2}三个数且满足 Ai,j⩽Ai+1,j A i , j ⩽ A i + 1 , j , Ai,j⩽Ai,j+1 A i , j ⩽ A i , j + 1 有几种填法
思路
填数的过程可以看作是一个沿着网格走的过程,我们先只考虑仅有0,1两个数字那么每一种填法都有一条沿着两者边界的路径,这个路径也满足只能往上和往右走,这就变成了典型的非降路径的问题了

非降路径问题转换为组合数可以认为总共有n+m总选择方案从中选择n种或m种及 Cnn+m C n + m n 或 Cmn+m C n + m m ,这道题的区别在于现在有两条路径一条是0和1的一条是1和2的即把矩阵分成3个区间
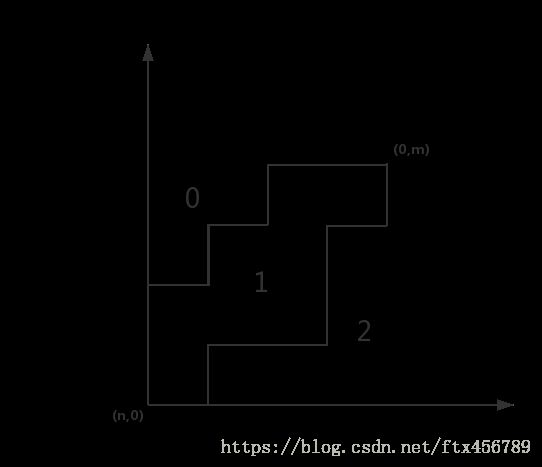
现在有两条可重合的路径
如果不考虑两条路径相交的情况的话,那么总的方法数就会变成 Cnn+m∗Cnn+m C n + m n ∗ C n + m n
下面是去重的方法
我们将其中的一条向左上平移使其变为 (n−1,−1)−>(−1,m−1) ( n − 1 , − 1 ) − > ( − 1 , m − 1 ) ,相对的我们要求解的就是这两条路径严格不相交的方案数
那么现在两条路径就是

根据 Lindström–Gessel–Viennot引理我们就可以求出n条严格不相交的路径的方案数
其中 ai a i 代表路径的起点 bi b i 代表路径的终点 e(ai,bj) e ( a i , b j ) 代表 ai a i 到 bj b j 的方案数,答案是这个行列式的值
我们现在只有两个点即
那么答案就是
e(ai,bj) e ( a i , b j ) 可以用非降路径的方法求出
#include 0] = 1;
for(int j=1;j<=i;j++)
{
C[i][j] = (C[i-1][j]+C[i-1][j-1])%mod;
}
}
}
int main()
{
get_C();
int n,m;
while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)!=EOF)
{
long long ans=(C[n+m][n]%mod*C[n+m][n]%mod-C[n+m][n+1]%mod*C[n+m][m+1]%mod)%mod;
printf("%lld\n",(ans+mod)%mod);
}
return 0;
}