leetcode柱子题目总结
装水问题(左右指针)
Given n non-negative integers a1, a2, ..., an , where each represents a point at coordinate (i, ai). n vertical lines are drawn such that the two endpoints of line i is at (i, ai) and (i, 0). Find two lines, which together with x-axis forms a container, such that the container contains the most water.
Note: You may not slant the container and n is at least 2.
![]()
The above vertical lines are represented by array [1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7]. In this case, the max area of water (blue section) the container can contain is 49.
Example:
Input: [1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7]
Output: 49即最大为7和7之间作为容器:7*7=49
思路:
这道只是让求最大的一个的装水量,我们需要定义i和j两个指针分别指向数组的左右两端,然后两个指针向中间搜索,每移动一次算一个值和结果比较取较大的,容器装水量的算法是找出左右两个边缘中较小的那个乘以两边缘的距离
复杂度:
时间复杂度O(n),这里我写出来的是O(n*n),每个节点往前找,其实没有意义,两个边界之间较小的那个就是容器的高,与之间的高度无关,容器的高*宽度即得到容量
class Solution {
public:
int maxArea(vector& height) {
if(height.size() < 2) return 0;
int i=0,j=height.size()-1,max_area=0;
while(i < j){
if(height[i]
接雨水
给定 n 个非负整数表示每个宽度为 1 的柱子的高度图,计算按此排列的柱子,下雨之后能接多少雨水。
上面是由数组 [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1] 表示的高度图,在这种情况下,可以接 6 个单位的雨水(蓝色部分表示雨水)。 感谢 Marcos 贡献此图。
![]()
示例:
输入: [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1]
输出: 6
class Solution {
public:
int trap(vector& height) {
int n = height.size();
if(n < 3) return 0;
// 保存左侧最大值
vector dp_lh(n, 0);
int max_h = height[0],res = 0;
for(int i = 1;i < n;i++){
dp_lh[i] = max_h;
max_h = max(max_h,height[i]);
}
max_h = height[n-1];
for(int i = n-2;i >= 0;i--){
if(min(dp_lh[i], max_h) > height[i])
res += min(dp_lh[i], max_h) - height[i];
max_h = max(max_h,height[i]);
}
return res;
}
};
柱状图中最大矩形
Given n non-negative integers representing the histogram's bar height where the width of each bar is 1, find the area of largest rectangle in the histogram.
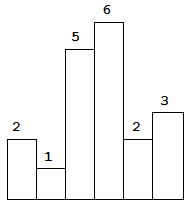
Above is a histogram where width of each bar is 1, given height =[2,1,5,6,2,3].
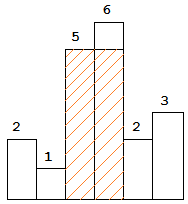
The largest rectangle is shown in the shaded area, which has area = 10 unit.
Example:
Input: [2,1,5,6,2,3] Output: 10
思路:
这题我真的除了暴力破解没啥思路,下面这种方法是参考网上写的剪枝
遍历数组,每找到一个局部峰值(而不是每次都往前查找,这里做了剪枝,因为局部峰值已经是局部最高点,所以往前计算获得的面积是局部最大的,我们比较的是每次的局部峰值处算出的面积到底哪次最大),然后向前遍历所有的值,算出共同的矩形面积,每次对比保留最大值
算出共同的矩形面积不要在heights[i+1]
class Solution {
public:
int largestRectangleArea(vector& heights) {
if(heights.empty()) return 0;
int max_rec = heights[0];
for(int i = 0;i < heights.size();i++){
// 递增时或者没有到末尾时
if(i+1 < heights.size() && heights[i] <= heights[i+1]){
continue;
}
// 计算矩阵大小
int min_h = INT_MAX;
for(int j = i;j >= 0;j--){
min_h = min(min_h,heights[j]);
int cur = min_h*(i-j+1);
max_rec = max(max_rec,cur);
}
}
return max_rec;
}
};
思路:使用单调栈做,时间为O(N),每个节点进栈一次,出栈一次,2n
class Solution {
public:
int largestRectangleArea(vector& heights) {
if(heights.empty()) return 0;
int max_rec = heights[0],i = 0;
// 维护一个单调递增的栈
stack s;
// 在高度数组(不是栈)最后面加上一个0,这样原先的最后一个板子也可以被处理
// 0肯定比任何的heights都小,所以0放在heights最后,一定会计算最后一块板到前面板子的面积
heights.push_back(0);
while(i < heights.size()){
if(s.empty() || heights[s.top()] < heights[i]){
s.push(i); // 栈内存放i
i++;
}
else{
int cur = s.top();s.pop();
max_rec = max(max_rec,heights[cur]*(s.empty()? i: (i-s.top()-1)));
}
}
return max_rec;
}
};