Android开发,MapBox的使用及部分功能实现(二)----- draw、layer、以及一些杂的知识点
Android开发,MapBox的使用及部分功能实现(一)----- 初始化、标记、定位、styleurl
上一节,主要写了最基本的时候,这一篇准备写一写更深一点的内容
一些很杂的知识点
设置地图UI
就是修改地图上一些你不喜欢的东西,比如说左下角的logo,以及一个提示按钮,右上角的罗盘,地图可以调整角度,又可以旋转,太乱了这种
代码如下
UiSettings uiSettings = mMapboxMap.getUiSettings();
uiSettings.setCompassEnabled(false);//隐藏指南针
uiSettings.setLogoEnabled(false);//隐藏logo
uiSettings.setTiltGesturesEnabled(true);//设置是否可以调整地图倾斜角
uiSettings.setRotateGesturesEnabled(true);//设置是否可以旋转地图
uiSettings.setAttributionEnabled(false);//设置是否显示那个提示按钮很简单,注释都写好了
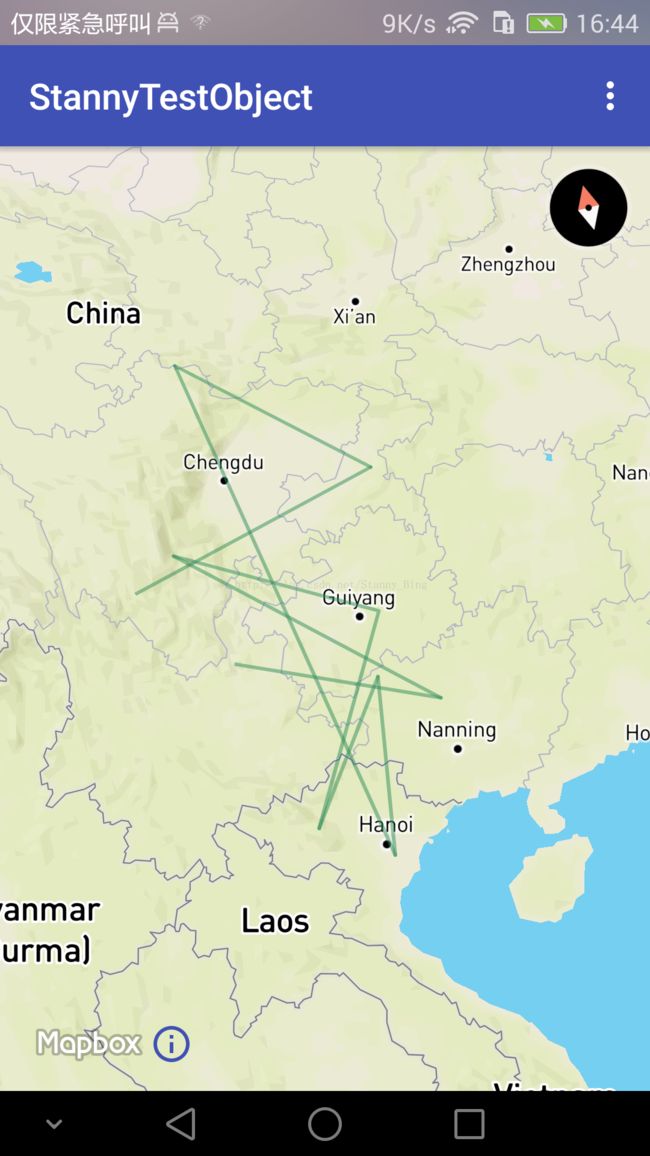
绘制线和面
绘制polyline
List polyline = new ArrayList<>();
polyline.add(new LatLng(26.1564854, 103.156741));
polyline.add(new LatLng(24.1255854, 108.254741));
polyline.add(new LatLng(29.1114854, 102.241741));
polyline.add(new LatLng(26.5764854, 107.272741));
polyline.add(new LatLng(21.7874854, 104.278741));
polyline.add(new LatLng(25.0044854, 106.782741));
polyline.add(new LatLng(20.7174854, 106.014741));
polyline.add(new LatLng(33.7684854, 103.520741));
polyline.add(new LatLng(30.1274854, 108.104741));
polyline.add(new LatLng(28.4174854, 101.000741));
mapboxMap.addPolyline(new PolylineOptions()
.addAll(polyline)
.color(ContextCompat.getColor(PolygonActivity.this, R.color.seagreen))
.alpha(0.5f)
.width(2));
return true; 颜色,透明度,宽度,这些就就不说了
绘制polygon
绘制polygon,也就是我们说的图斑
和polyline差不多
List polygon = new ArrayList<>();
polygon.add(new LatLng(26.1564854, 103.156741));
polygon.add(new LatLng(24.1255854, 108.254741));
polygon.add(new LatLng(29.1114854, 102.241741));
polygon.add(new LatLng(26.5764854, 107.272741));
polygon.add(new LatLng(21.7874854, 104.278741));
polygon.add(new LatLng(25.0044854, 106.782741));
polygon.add(new LatLng(20.7174854, 106.014741));
polygon.add(new LatLng(33.7684854, 103.520741));
polygon.add(new LatLng(30.1274854, 108.104741));
polygon.add(new LatLng(28.4174854, 101.000741));
mapboxMap.addPolygon(new PolygonOptions()
.addAll(polygon)
.fillColor(ContextCompat.getColor(PolygonActivity.this, R.color.blueviolet))
.alpha(0.5f)
.strokeColor(ContextCompat.getColor(PolygonActivity.this, R.color.steelblue))
); 有一些自己的方法,填充颜色,边界颜色,都很简单
需要注意一点,虽然我们设置了边界线颜色,但是,边界线不能设置宽度,所以很难看到边界线,除非两个颜色有很大的区别
根据geojson绘制
geojison,是一个geometry的点阵集合的一个json串,说白了,里面放了很多的点。
如下
{
"type": "FeatureCollection",
"features": [
{
"type": "Feature",
"properties": {
"name": "Crema to Council Crest"
},
"geometry": {
"type": "LineString",
"coordinates": [
...
[
106.70717,
29.49798
],
[
106.70713,
29.4984
],
[
106.70774,
29.49893
]
]
}
}
]
}
这个文件,我存在的assets中,命名为example.geojson
private class DrawGeoJson extends AsyncTask> {
@Override
protected List doInBackground(Void... voids) {
List points = new ArrayList<>();
try {
//加载geojson文件
InputStream inputStream = getAssets().open("example.geojson");
BufferedReader rd = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(inputStream));
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
int cp;
while ((cp = rd.read()) != -1) {
sb.append(((char) cp));
}
inputStream.close();
//转换成json
JSONObject json = new JSONObject(sb.toString());
JSONArray features = json.getJSONArray("features");
JSONObject feature = features.getJSONObject(0);
JSONObject geometry = feature.getJSONObject("geometry");
if (geometry != null) {
String type = geometry.getString("type");
if (!TextUtils.isEmpty(type) && type.equalsIgnoreCase("LineString")) {
JSONArray coords = geometry.getJSONArray("coordinates");
for (int lc = 0; lc < coords.length(); lc++) {
JSONArray coord = coords.getJSONArray(lc);
LatLng latlng = new LatLng(coord.getDouble(1), coord.getDouble(0));
points.add(latlng);
}
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return points;
}
@Override
protected void onPostExecute(List latLngs) {
super.onPostExecute(latLngs);
if (latLngs.size() > 0) {
mapboxMap.addPolyline(new PolylineOptions()
.addAll(latLngs)
.color(Color.parseColor("#3bb2d0"))
.width(2));
}
}
} 这里采用了异步的操作去执行,官方demo就是这样的,然而,听了我刚刚的解释,你应该能想到,这样其实并不需要!这只是一种比较好的方法,而不是必须的方法,如果你想,你放到主线程里面去也行,new一个Thread也没问题。代码不多说,很简单的。图都懒得放了,就和画polyline是一样的。
layer的绘制
layer即图层,这里主要讲一讲图层的绘制,请注意,这里面的坑不是一般的多,多到你想用就得重写很多工具类才行的地步。
SymbolLayer
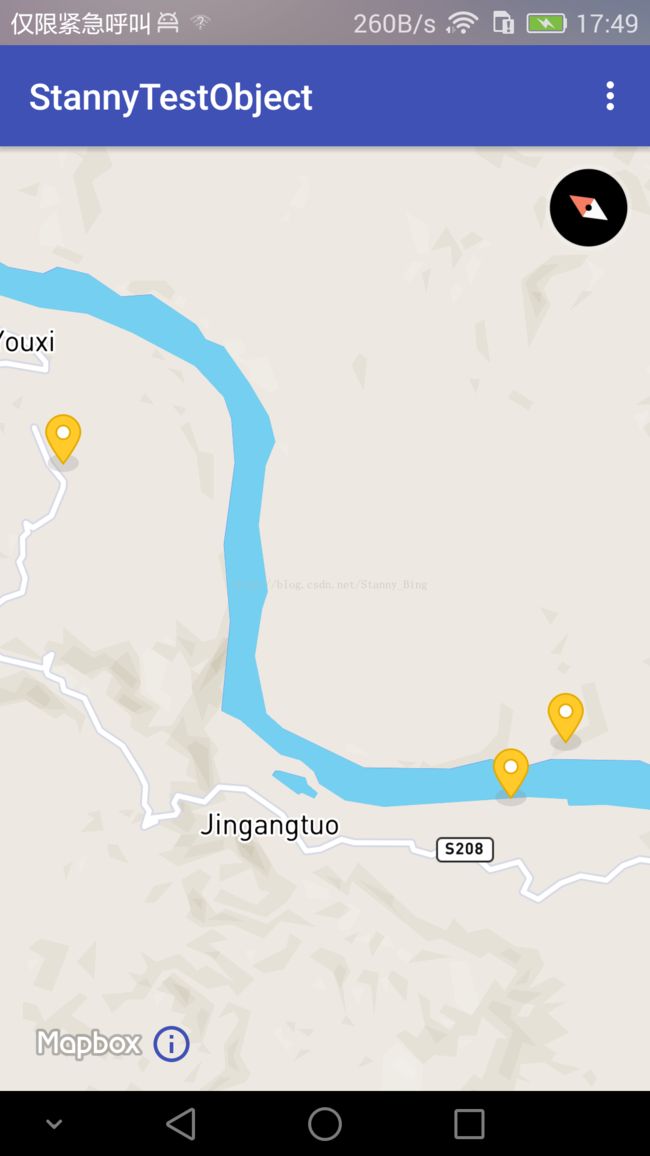
SymbolLayer,就是标记型的layer
如下
看着和前面的Marker很像是不是,但是并不一样,前面的是一个Marker,这里是一个Layer,只是我用的图标是这样的,同时,如果一个地方出现多个Symbol,当地图比例尺变大时,两个接近的会变成一个Layer,这个做过地图的都知道,比如下面这种
可以看到,现在只有两个图标了,右边的那一个其实代表了两个。
好,看代码
List featureList = new ArrayList<>();
featureList.add(Feature.fromGeometry(
Point.fromCoordinates(
Position.fromCoordinates(106.124621, 29.123654))));
featureList.add(Feature.fromGeometry(
Point.fromCoordinates(
Position.fromCoordinates(106.135491, 29.121623))));
featureList.add(Feature.fromGeometry(
Point.fromCoordinates(
Position.fromCoordinates(106.130192, 29.193052))));
FeatureCollection featureCollection = FeatureCollection.fromFeatures(featureList);
Source source = new GeoJsonSource("marker-source", featureCollection);
mapboxMap.addSource(source); 不过大体上还是明白的,就是根据坐标构建feature,再将feature列表构造成一个FeatureCollection对象,这其实就是一个Feature集合的对象,他没有更多的方法,就是一个实体类,源代码如下
package com.mapbox.services.commons.geojson;
import com.mapbox.services.commons.geojson.BaseFeatureCollection;
import com.mapbox.services.commons.geojson.Feature;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
public class FeatureCollection extends BaseFeatureCollection {
private final List features;
protected FeatureCollection(List features) {
this.features = features;
}
public List getFeatures() {
return this.features;
}
public static FeatureCollection fromFeatures(List features) {
return new FeatureCollection(features);
}
public static FeatureCollection fromFeatures(Feature[] features) {
return new FeatureCollection(Arrays.asList(features));
}
} 然后,将其构造成一个资源类型Source,前面是资源id,后面是资源集
然后就添加到mapboxmap
//添加一个图标到地图上,以备随时使用
Bitmap icon = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(), R.mipmap.yellow_marker);
mapboxMap.addImage("my-marker", icon);
//设置layer id,并绑定资源
SymbolLayer markers = new SymbolLayer("marker-layer", "marker-source")
.withProperties(PropertyFactory.iconImage("my-marker"));//从配置里面找到刚刚存入的图标
mapboxMap.addLayer(markers);然后我们创建了一个Bitmap对象,作为图片资源添加到mapboxmap中,请注意,这个addImage并不是说直接就把图片添加到地图上了,而是暂时放到了mapboxmap中,然后下次要使用的时候可以直接拿出来用,下面,设置layer id ,并将资源进行绑定,这里的marker-source就是我们刚刚创建的资源名称,我也不知道为什么不直接把资源拿来用,非要先添加,再使用。
好,下面就是坑了
Positon,fromCoordinates(106.124621, 29.123654),和LatLng是相反的!
LatLng是(Latitude,Longitude)
但是,我们看源代码
public static Position fromCoordinates(double longitude, double latitude, double altitude) {
return new Position(longitude, latitude, altitude);
}
public static Position fromCoordinates(double longitude, double latitude) {
return new Position(longitude, latitude, 0.0D / 0.0);
}然后是第二个坑,比如我这个demo,我可能会重复添加一次这个layer,这是就会报错了
对,不能重复添加已存在的source
也就是说,在此之前,你必须得先移除所有的source,那想到这,你可能会想了,很简单,removeAllSource,然而并没有这个方法,mapboxmap.clear,然而这个方法移除不掉clear,好,可能你就会想到遍历,删除咯
for (Source source : mapboxMap.getSources()) {
mapboxMap.removeSource(source);
}
private List addSource = new ArrayList<>();
for (Source source : addSource) {
mapboxMap.removeSource(source);
}可以想到,Layer也不能这么搞
是的,Layer也没有removeAllLayer,clear也清除不掉
要一次性移除所有的Layer,就只能选择遍历,而且!和Souce一样,mapboxMap,getLayers得到的Layer不仅仅是你添加的Layer,事实上,这里可以得到一百多个Layer,所以如果你移除所有,你将看到一片漆黑,啥都没有
方法和上面一样,建立集合,添加进去addLayer.add(marker);,遍历集合。