C++中STL容器之集合——Set/multiset
文章目录
- 1.简单介绍
- 2.set成员函数
- 3.set自定义比较函数以及存储结构体
- 4.集合操作
1.简单介绍
set跟vector差不多,它跟vector的区别就是,set里面的元素是有序的且唯一的,只要你往set里添加元素,它就会自动排序,而且,如果你添加的元素set里面本来就存在,那么这次添加操作就不执行。set类包含在头文件#included中。
而multiset允许元素重复,即
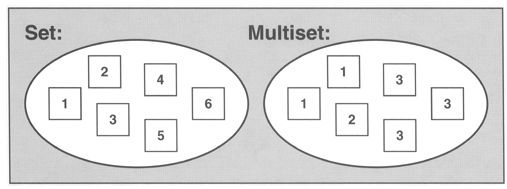
与multiset、map和multimap等关联容器一样,底层通过 红黑树 实现,所以通常情况下,其复杂度都可以看成是一个比较完美的 平衡二叉树看待,近似于 O ( l o g n ) O(logn) O(logn)。
复杂度
考虑到底层用红黑树实现,所以各个操作的复杂度
| 操作 | 复杂度 |
|---|---|
| 插入insert() | O(logn) |
| 删除erase() | O(logn) |
| 查找find() | O(logn) |
简单示例:
#include输出结果:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
c++ hello to welcome
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
c++ everyone hello to welcome
请按任意键继续. . .
set注意事项:
1)不能直接改变元素值,因为那样会打乱原本正确的顺序,要改变元素值必须先删除旧元素,则插入新元素
2) 不提供直接存取元素的任何操作函数,只能通过迭代器进行间接存取,而且从迭代器角度来看,元素值是常数
3) 元素比较动作只能用于型别相同的容器(即元素和排序准则必须相同)
2.set成员函数
| 操作 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| begin() | 返回指向第一个元素的迭代器 |
| clear() | 清除所有元素 |
| count() | 返回某个值元素的个数 |
| empty() | 判断集合是否为空 |
| end() | 返回指向最后一个元素的迭代器 |
| equal_range() | 返回集合中与给定值相等的上下限的两个迭代器 |
| c.erase(num) | 删除元素num或者迭代器,返回下一个元素的迭代器 |
| find() | 返回一个指向被查找到元素的迭代器,若失败则返回end() |
| get_allocator() | 返回集合的分配器 |
| insert() | 在集合中插入元素 |
| lower_bound() | 返回指向大于(或等于)某值的第一个元素的迭代器 |
| key_comp() | 返回一个用于元素间值比较的函数 |
| rbegin() | 返回指向集合中最后一个元素的反向迭代器 |
| rend() | 返回指向集合中第一个元素的反向迭代器 |
| size() | 集合中元素的数目 |
| swap() | 交换两个集合变量 |
| upper_bound() | 返回大于某个值元素的迭代器 |
| value_comp() | 返回一个用于比较元素间的值的函数 |
示例代码:
#include输出结果:
print1 s1:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
print2 s2:5 6 7 8 9 10
print3 s2 max num:10
print4 s2.size():6
8 在s2中的地址 003D30F8:
1 isn't in s2
erase num 6 success
交换s1和s2后,s2:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
请按任意键继续. . .
3.set自定义比较函数以及存储结构体
如果set的类型是个结构体,我们需要定义重载函数:
set 容器模版需要3个泛型参数,如下:
template ,
class Alloc = alloc>
class set {
...
};
其中,
第一个是元素类型,必选;
第二个指定元素比较方式,缺省为 Less, 即使用 < 符号比较;
第三个指定空间分配对象,一般使用默认类型。
因此:
(1) 如果第2个泛型参数你使用默认值的话,你的自定义元素类型需要重载 < 运算操作;
(2) 如果你第2个泛型参数不使用默认值的话,则比较对象必须具有 operator() 操作,即:
bool operator()(const T &a, const T &b)*
示例代码:
我们定义一个学生的结构体,包括姓名name,年龄age,性别sex等数据,且按照name为主关键字,age为次关键字进行升序排序。
#include4.集合操作
在数学上,集合包含交、并、补的操作,在STL中也实现了相应的操作,包含下列几个函数
| 操作 | 函数 |
|---|---|
| 集合交 | set_intersection() |
| 集合并 | set_uinion() |
| 集合补 | set_difference() |
这几个函数的参数都一样,以集合的交为例:
set_union(A.begin(), A.end(), B.begin(), B.end(), inserter(C,C.begin()));
// 前四个参数依次是第一个集合A的头尾。第二个集合B的头尾
// 第五个参数是将A和B操作后结果存入C中
set_union()函数的原型如下:
template<class InputIterator1, class InputIterator2, class OutputIterator>
OutputIterator set_union(
InputIterator1_First1 ,
InputIterator1_Last1 ,
InputIterator2_First2 ,
InputIterator2_Last2 ,
OutputIterator_Result
);
实现源码如下:
template<class InputIterator1,class InputIterator2,class OutputIterator>
OutputIterator set_intersection(InputIterator1 first1,InputIterator1 last1,InputIterator2 first2,InputIterator2 last2,OutputIterator result)
{
while (first1!=last1 && first2!=last2) //若均未到达尾端,则进行以下操作
{
//在两个区间内分别移动迭代器。若二者值相同用result记录该值,移动first1,first2和result
//若first1较小,则移动first1,其他不动
//若first2较小,则移动first2,其他不动
if (*first1<*first2)
first1++;
else if (*first2<*first1)
first2++;
else
{
*result=*first1;
first1++;
first2++;
result++;
}
}
return result;
}
例题示例
UVA 12096 The SetStack Computer
题目大意


本题的集合是集合的集合,为了方便,为每一个不同的集合分配一个ID,并将其存储在一个向量中,压栈出栈用其ID代替
#include代码中用到的其他STL中的容器可以翻阅之前的博客查看,不过第一次应该也能看得懂。