一、
Map是c++的一个标准容器,它提供了很好一对一的关系,在一些程序中建立一个map可以起到事半功倍的效果,总结了一些map基本简单实用的操作!
1. map构造函数;
mapmapstring; mapmapint;
mapmapstring; map< char ,string>mapchar;
mapmapchar; mapmapint;
如在打枚举中打印 “指定值对应的字符串”时,可是采用map的STL实现。
以前我们是这样打印信息出来的:
- static inline const char *
- VNET_TYPE_STRING(vnet_type_t type)
- {
- static VALUE_STRING_STRUCT g_type_string[] =
- {
- { VNET_TYPE_UNKOWN, "unkown1" },
- { VNET_TYPE_SOCKET, "socket" },
- { VNET_TYPE_RDP, "rdp" },
- { VNET_TYPE_PCOIP, "pcoip" },
- { VNET_TYPE_ICA, "ica" },
- { VNET_TYPE_XRED, "xred" },
- { 0, NULL },
- };
- return GetValueString(g_type_string, (ULONG)type);
- }
- static inline const TCHAR *
- GetValueString(VALUE_STRING_STRUCT *vsarray, ULONG value)
- {
- VALUE_STRING_STRUCT *tmp = vsarray;
-
- while ( tmp->string != NULL )
- {
- if ( tmp->value == value )
- {
- return tmp->string;
- }
- tmp++;
- }
- return _T("unkown");
- }
2. map添加数据;
map maplive;
1.maplive.insert(pair(102,"aclive"));
2.maplive.insert(map::value_type(321,"hai"));
3, maplive[112]="April";//map中最简单最常用的插入添加!
3,map中元素的查找:
find()函数返回一个迭代器指向键值为key的元素,如果没找到就返回指向map尾部的迭代器。
map::iterator l_it;;
l_it=maplive.find(112);
if(l_it==maplive.end())
cout<<"we do not find 112"< else cout<<"wo find 112"<
4,map中元素的删除:
如果删除112;
map::iterator l_it;;
l_it=maplive.find(112);
if(l_it==maplive.end())
cout<<"we do not find 112"< else maplive.erase(l_it); //delete 112;
5,map中 swap的用法:
Map中的swap不是一个容器中的元素交换,而是两个容器交换;
For example:
- #include
- #include
-
- using namespace std;
-
-
- int main( )
- {
- map <int, int> m1, m2, m3;
- map <int, int>::iterator m1_Iter;
-
- m1.insert ( pair <int, int> ( 1, 10 ) );
- m1.insert ( pair <int, int> ( 2, 20 ) );
- m1.insert ( pair <int, int> ( 3, 30 ) );
- m2.insert ( pair <int, int> ( 10, 100 ) );
- m2.insert ( pair <int, int> ( 20, 200 ) );
- m3.insert ( pair <int, int> ( 30, 300 ) );
-
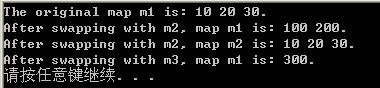
- cout << "The original map m1 is:";
- for ( m1_Iter = m1.begin( ); m1_Iter != m1.end( ); m1_Iter++ )
- cout << " " << m1_Iter->second;
- cout << "." << endl;
-
-
-
- m1.swap( m2 );
-
- cout << "After swapping with m2, map m1 is:";
- for ( m1_Iter = m1.begin( ); m1_Iter != m1.end( ); m1_Iter++ )
- cout << " " << m1_Iter -> second;
- cout << "." << endl;
- cout << "After swapping with m2, map m2 is:";
- for ( m1_Iter = m2.begin( ); m1_Iter != m2.end( ); m1_Iter++ )
- cout << " " << m1_Iter -> second;
- cout << "." << endl;
-
- swap( m1, m3 );
-
- cout << "After swapping with m3, map m1 is:";
- for ( m1_Iter = m1.begin( ); m1_Iter != m1.end( ); m1_Iter++ )
- cout << " " << m1_Iter -> second;
- cout << "." << endl;
-
- system("pause");
- }
运行结果是:
6.map的sort问题:
Map中的元素是自动按key升序排序,所以不能对map用sort函数:
For example:
- #include
- #include
-
- using namespace std;
-
-
- int main( )
- {
- map <int, int> m1;
- map <int, int>::iterator m1_Iter;
-
- m1.insert ( pair <int, int> ( 1, 20 ) );
- m1.insert ( pair <int, int> ( 4, 40 ) );
- m1.insert ( pair <int, int> ( 3, 60 ) );
- m1.insert ( pair <int, int> ( 2, 50 ) );
- m1.insert ( pair <int, int> ( 6, 40 ) );
- m1.insert ( pair <int, int> ( 7, 30 ) );
-
- cout << "The original map m1 is:"<
- for ( m1_Iter = m1.begin( ); m1_Iter != m1.end( ); m1_Iter++ )
- cout << m1_Iter->first<<" "<second<
-
- }

7, map的基本操作函数:
C++ Maps是一种关联式容器,包含“关键字/值”对
begin() 返回指向map头部的迭代器
clear() 删除所有元素
count() 返回指定元素出现的次数
empty() 如果map为空则返回true
end() 返回指向map末尾的迭代器
equal_range() 返回特殊条目的迭代器对
erase() 删除一个元素
find() 查找一个元素
get_allocator() 返回map的配置器
insert() 插入元素
key_comp() 返回比较元素key的函数
lower_bound() 返回键值>=给定元素的第一个位置
max_size() 返回可以容纳的最大元素个数
rbegin() 返回一个指向map尾部的逆向迭代器
rend() 返回一个指向map头部的逆向迭代器
size() 返回map中元素的个数
swap() 交换两个map
upper_bound() 返回键值>给定元素的第一个位置
value_comp() 返回比较元素value的函数
二、C++中map用法
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- #include
- #include
- #include
- using namespace std;
-
-
- int main()
- {
- map<const char*,int> m;
- m["a"]=1;
- m["b"]=6;
- m["c"]=9;
- map<const char*,int>::iterator it;
- it=m.begin();
- const char* c =it->first;
- cout<<"first element is :"<
- int i = m["c"];
- while(it!=m.end()){
- cout << it->first<<";"<second<
- ++it;
- }
- cout <<"m[\"c\"]="<
- cout <<"sizeof m:"<
- cout <<"erase m[\"c\"](1:succ 0:failed):"<"c")<
- cout <<"erase m[\"c\"]:"<"c")<
- cout <<"sizeof m:"<
- cout<<"m[c]="<"c"]<
- cout<<"sizeof m :"<
-
- system("pause");
- return 0;
-
- }
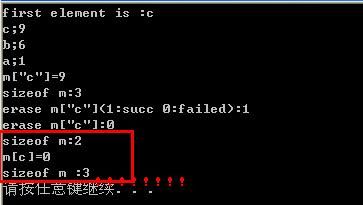
请注意上面打感叹号的地方,map的大小因此调用了“cout<<"m[c]="<
三、multimap 的使用方法
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- #include
- #include
- #include
-
-
-
-
-
- struct student{
- char* name;
- int age;
- char* city;
- char* phone;
- };
-
- int main()
- {
- using namespace std;
-
- student s[]={
- {"童进",23,"武汉","XXX"},
- {"老大",23,"武汉","XXX"},
- {"饺子",23,"武汉","XXX"},
- {"王老虎",23,"武汉","XXX"},
- {"周润发",23,"武汉","XXX"},
- {"周星星",23,"武汉","XXX"}
- };
- pair<int,student> p1(4,s[0]);
- pair<int,student> p2(2,s[1]);
- pair<int,student> p3(3,s[2]);
- pair<int,student> p4(4,s[3]);
- pair<int,student> p5(5,s[4]);
- pair<int,student> p6(6,s[5]);
- multimap<int,student> a;
- a.insert(p1);
- a.insert(p2);
- a.insert(p3);
- a.insert(p4);
- a.insert(p5);
- a.insert(p6);
- typedef multimap<int,student>::iterator int_multimap;
- pair p = a.equal_range(4);
- int_multimap i = a.find(4);
- cout<<"班上key值为"<< i->first<<"的学生有:"<"名,"<<" 他们是:"<
- for(int_multimap k = p.first; k != p.second; k++)
- {
- cout<second.name<
- }
- cout<<"删除重复键值的同学"<
- a.erase(i);
- cout<<"现在班上总人数为:"<". 人员如下:"<
- for(multimap<int,student>::iterator j=a.begin(); j != a.end(); j++)
- {
- cout<<"The name: "<second.name<<" "<<"age: "<second.age<<" "
- <<"city: "<second.city<<" "<<"phone: "<second.phone<
- }
-
- return 0;
- }
感谢博主: http://blog.csdn.net/chenyujing1234/article/details/8193172
![]()
![]()
![]()