OpenCV Java 实现票据、纸张的四边形边缘检测与提取、摆正
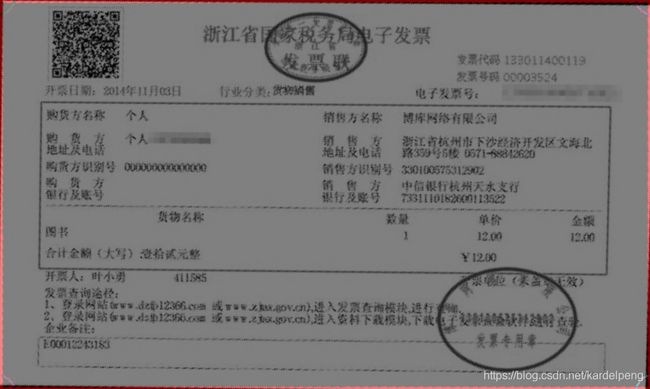
最近公司让研究用opencv来做发票的提取摆正,简单的说就是如下图所示
原图:
结果:
说说过程吧,网上找了很多范例,也试了很多。很多贴的代码都不全,要么就不是用java来实现的,下面是实现如上功能的具体java代码:
public static void main(String[] args) {
logger.info("测试票据、纸张的四边形边缘检测与提取、摆正程序开始....");
//这个必须配置,否则会报错
System.loadLibrary(Core.NATIVE_LIBRARY_NAME);
Mat img = Imgcodecs.imread("D:\\orc\\7.jpg");
if(img.empty()){
logger.info("读取的图片信息为空");
return;
}
Mat greyImg = img.clone();
//1.彩色转灰色
Imgproc.cvtColor(img, greyImg, Imgproc.COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
createImage(greyImg, "D:\\orc\\huise.jpg");
Mat gaussianBlurImg = greyImg.clone();
// 2.高斯滤波,降噪
Imgproc.GaussianBlur(greyImg, gaussianBlurImg, new Size(3,3),2,2);
createImage(gaussianBlurImg, "D:\\orc\\jiangzao.jpg");
Mat cannyImg = gaussianBlurImg.clone();
// 3.Canny边缘检测
Imgproc.Canny(gaussianBlurImg, cannyImg, 20, 60, 3, false);
createImage(cannyImg, "D:\\orc\\bianyuanjiance.jpg");
// 4.膨胀,连接边缘
Mat dilateImg = cannyImg.clone();
Imgproc.dilate(cannyImg, dilateImg, new Mat(), new Point(-1, -1), 2, 1, new Scalar(1));
createImage(dilateImg, "D:\\orc\\bianyuanjiance2.jpg");
//5.对边缘检测的结果图再进行轮廓提取
List contours = new ArrayList<>();
List drawContours = new ArrayList<>();
Mat hierarchy = new Mat();
Imgproc.findContours(dilateImg, contours, hierarchy, RETR_EXTERNAL, CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE);
Mat linePic = Mat.zeros(dilateImg.rows(), dilateImg.cols(), CvType.CV_8UC3);
//6.找出轮廓对应凸包的四边形拟合
List squares = new ArrayList<>();
List hulls = new ArrayList<>();
MatOfInt hull = new MatOfInt();
MatOfPoint2f approx = new MatOfPoint2f();
approx.convertTo(approx, CvType.CV_32F);
for (int i = 0; i < contours.size(); i++) {
MatOfPoint contour = contours.get(i);
// 边框的凸包
Imgproc.convexHull(contour, hull);
// 用凸包计算出新的轮廓点
Point[] contourPoints = contour.toArray();
int[] indices = hull.toArray();
List newPoints = new ArrayList<>();
for (int index : indices) {
newPoints.add(contourPoints[index]);
}
MatOfPoint2f contourHull = new MatOfPoint2f();
contourHull.fromList(newPoints);
// 多边形拟合凸包边框(此时的拟合的精度较低)
Imgproc.approxPolyDP(contourHull, approx, Imgproc.arcLength(contourHull, true)*0.02, true);
MatOfPoint mat = new MatOfPoint();
mat.fromArray(approx.toArray());
drawContours.add(mat);
// 筛选出面积大于某一阈值的,且四边形的各个角度都接近直角的凸四边形
MatOfPoint approxf1 = new MatOfPoint();
approx.convertTo(approxf1, CvType.CV_32S);
if (approx.rows() == 4 && Math.abs(Imgproc.contourArea(approx)) > 40000 &&
Imgproc.isContourConvex(approxf1)) {
double maxCosine = 0;
for (int j = 2; j < 5; j++) {
double cosine = Math.abs(getAngle(approxf1.toArray()[j%4], approxf1.toArray()[j-2], approxf1.toArray()[j-1]));
maxCosine = Math.max(maxCosine, cosine);
}
// 角度大概72度
if (maxCosine < 0.3) {
MatOfPoint tmp = new MatOfPoint();
contourHull.convertTo(tmp, CvType.CV_32S);
squares.add(approxf1);
hulls.add(tmp);
}
}
}
//这里是把提取出来的轮廓通过不同颜色的线描述出来,具体效果可以自己去看
Random r = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < drawContours.size(); i++) {
Imgproc.drawContours(linePic, drawContours, i, new Scalar(r.nextInt(255),r.nextInt(255), r.nextInt(255)));
}
createImage(linePic, "D:\\orc\\drawContours1.jpg");
//7.找出最大的矩形
int index = findLargestSquare(squares);
MatOfPoint largest_square = squares.get(index);
Mat polyPic = Mat.zeros(img.size(), CvType.CV_8UC3);
Imgproc.drawContours(polyPic, squares, index, new Scalar(0, 0,255), 2);
createImage(polyPic, "D:\\orc\\drawContours2.jpg");
//存储矩形的四个凸点
hull = new MatOfInt();
Imgproc.convexHull(largest_square, hull, false);
List hullList = hull.toList();
List polyContoursList = largest_square.toList();
List hullPointList = new ArrayList<>();
List lastHullPointList = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i = 0; i < hullList.size();i++){
Imgproc.circle(polyPic, polyContoursList.get(hullList.get(i)), 10, new Scalar(r.nextInt(255),r.nextInt(255), r.nextInt(255), 3));
hullPointList.add(polyContoursList.get(hullList.get(i)));
System.out.println(hullList.get(i));
}
Core.addWeighted(polyPic, 0.5, img, 0.5, 0, img);
createImage(img, "D:\\orc\\addWeighted.jpg");
for(int i = 0; i < hullPointList.size(); i++){
lastHullPointList.add(hullPointList.get(i));
}
//dstPoints储存的是变换后各点的坐标,依次为左上,右上,右下, 左下
//srcPoints储存的是上面得到的四个角的坐标
Point[] dstPoints = {new Point(0,0), new Point(img.cols(),0), new Point(img.cols(),img.rows()), new Point(0,img.rows())};
Point[] srcPoints = new Point[4];
boolean sorted = false;
int n = 4;
//对四个点进行排序 分出左上 右上 右下 左下
while (!sorted){
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++){
sorted = true;
if (lastHullPointList.get(i-1).x > lastHullPointList.get(i).x){
Point tempp1 = lastHullPointList.get(i);
Point tempp2 = lastHullPointList.get(i-1);
lastHullPointList.set(i, tempp2);
lastHullPointList.set(i-1, tempp1);
sorted = false;
}
}
n--;
}
//即先对四个点的x坐标进行冒泡排序分出左右,再根据两对坐标的y值比较分出上下
if (lastHullPointList.get(0).y < lastHullPointList.get(1).y){
srcPoints[0] = lastHullPointList.get(0);
srcPoints[3] = lastHullPointList.get(1);
}else{
srcPoints[0] = lastHullPointList.get(1);
srcPoints[3] = lastHullPointList.get(0);
}
if (lastHullPointList.get(2).y < lastHullPointList.get(3).y){
srcPoints[1] = lastHullPointList.get(2);
srcPoints[2] = lastHullPointList.get(3);
}else{
srcPoints[1] = lastHullPointList.get(3);
srcPoints[2] = lastHullPointList.get(2);
}
List listSrcs = java.util.Arrays.asList(srcPoints[0], srcPoints[1], srcPoints[2], srcPoints[3]);
Mat srcPointsMat = Converters.vector_Point_to_Mat(listSrcs, CvType.CV_32F);
List dstSrcs = java.util.Arrays.asList(dstPoints[0], dstPoints[1], dstPoints[2], dstPoints[3]);
Mat dstPointsMat = Converters.vector_Point_to_Mat(dstSrcs, CvType.CV_32F);
//参数分别为输入输出图像、变换矩阵、大小。
//坐标变换后就得到了我们要的最终图像。
Mat transMat = Imgproc.getPerspectiveTransform(srcPointsMat, dstPointsMat); //得到变换矩阵
Mat outPic = new Mat();
Imgproc.warpPerspective(img, outPic, transMat, img.size());
createImage(outPic, "D:\\orc\\outPic.jpg");
logger.info("测试票据、纸张的四边形边缘检测与提取、摆正程序结束....");
}
// 根据三个点计算中间那个点的夹角 pt1 pt0 pt2
private static double getAngle(Point pt1, Point pt2, Point pt0)
{
double dx1 = pt1.x - pt0.x;
double dy1 = pt1.y - pt0.y;
double dx2 = pt2.x - pt0.x;
double dy2 = pt2.y - pt0.y;
return (dx1*dx2 + dy1*dy2)/Math.sqrt((dx1*dx1 + dy1*dy1)*(dx2*dx2 + dy2*dy2) + 1e-10);
}
// 找到最大的正方形轮廓
private static int findLargestSquare(List squares) {
if (squares.size() == 0)
return -1;
int max_width = 0;
int max_height = 0;
int max_square_idx = 0;
int currentIndex = 0;
for (MatOfPoint square : squares) {
Rect rectangle = Imgproc.boundingRect(square);
if (rectangle.width >= max_width && rectangle.height >= max_height) {
max_width = rectangle.width;
max_height = rectangle.height;
max_square_idx = currentIndex;
}
currentIndex++;
}
return max_square_idx;
}
/**
* 创建一张图片到指定位置
* @param mat
* @param fileName
*/
public static void createImage(Mat mat, String fileName) {
Mat dst = mat.clone();
Imgcodecs.imwrite(fileName, dst);
}
代码是经过本机测试的,使用如上图片是没有问题的,这里只是提供了一种大体思路,本文参考了:https://www.cnblogs.com/josephkim/p/8319069.html