标号法求解单源最短路径
1. 问题描述
给定一个图结构,包含n个点,e条边,求解源点 s 到汇点 t 的最短路径及长度,以及源点 s 到前1000个点的最短路径长度。
数据文件"union.txt",格式为:
start_id,end_id,weight,start_x,start_y,end_x,end_y
1,101043,540,567.988263,99.564119,567.988263,100.104119
......
2. 算法策略
算法模拟了标号法的求解过程。首先有一个优先队列,队列种中的元素为(点号,权值),初始状态把源点(权值为0)入队,然后不断进行BFS,从优先队列里取出权值最小的元素(如果访问过则重新取下一个元素),访问该元素,标记位置1,对其相邻的结点进行“松弛”,更新它们的当前权值,更新它们的距离数组dist和路径数组path,并将它们全部入队,进行下一轮操作,从队列中取元素......队列为空时路径求解完成。
需要注意的是,某个结点可能会多次入队,可能会被多次松弛,但只会被访问一次(由标记数组决定)。
由dist数组和path数组可得到源点 s 到任意一点 t 的最短路径及长度。求解完成后,dist数组本身即更新为最短路径长度。由于path[i]是i的前驱结点,可间接得到路径。
3. 优化操作
因为涉及大量数据的 I/O,为加快读写速度,使用C语法进行 I/O操作,而不用
4. 代码实现
#include "stdio.h"
#include "windows.h"
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
#define MAXN 195234 //0 1 ... 195233
#define MAXW 0x3f3f3f3f //最大权重
typedef struct WNode{
int id;
int cur_w;
bool operator<(const WNode& n)const{
return cur_w>n.cur_w;
}
WNode(int id,int cur_w):id(id),cur_w(cur_w){}
}WNode;
//Graph[i]中存放的是 与i号结点相邻的 结点们的编号j以及对应权重w, Graph[i]={pair,...}
vector > Graph[MAXN];
bool visit[MAXN];
int path[MAXN];
int dist[MAXN];
int s,t; //源点,汇点
clock_t start,finish;
//读入文件进行初始化
bool Initialize(){
printf("Input the starting point: ");
scanf("%d",&s);
printf("Input the ending point: ");
scanf("%d",&t);
printf("\nInputing data...\n");
start=clock();
FILE* fp=fopen("union.txt","r");
if(fp==NULL){
printf("File open error./n");
return -1;
}
int sid,tid,w;
double sx,sy,tx,ty;
fscanf(fp,"%*[^\n]%*c");//跳过第一行
while(true){
fscanf(fp,"%d,%d,%d,%lf,%lf,%lf,%lf",&sid,&tid,&w,&sx,&sy,&tx,&ty);
Graph[sid].push_back(make_pair(tid,w));
//printf("%d %d %d\n",sid,tid,w);
if(sid%1000==0){
printf("\r[%.2f%%]",sid/195233.0*100);
fflush(stdout);
}
if(sid==195233){
printf("\r[%.2f%%]",sid/195233.0*100);
finish=clock();
printf("\nData input successfully.\n");
printf("Total time is %.2fs\n.",(double)(finish-start)/CLOCKS_PER_SEC);
break;
}
}
fclose(fp);
return true;
}
//求解最短路径
void ShortestPath(int s){
printf("\nSolving shortest path...\n");
start=clock();
memset(path,0,sizeof(path));
memset(visit,0,sizeof(visit));
memset(dist,MAXW,sizeof(dist));
priority_queue qu;
qu.push(WNode(s,0));
path[s]=0;
dist[s]=0;
int sumvisit=0;//记录进度
while(!qu.empty()){
WNode cur=qu.top();
qu.pop();
if(visit[cur.id])continue;
visit[cur.id]=1;
sumvisit++;
if(sumvisit%500==0){
printf("\r[%.2f%%]",sumvisit/195233.0*100);
fflush(stdout);
}
for(int i=0;i tmp=Graph[cur.id][i];
if(!visit[tmp.first]){ //将未访问过的入队
qu.push(WNode(tmp.first,tmp.second+cur.cur_w));
}
if(tmp.second+cur.cur_w < dist[tmp.first]){ //松弛
dist[tmp.first]=tmp.second+cur.cur_w;
path[tmp.first]=cur.id;
}
}
}
printf("\r[100.00%%]\n");
printf("Path solved successfully.\n");
finish=clock();
printf("Total time is %.2fs.\n",(double)(finish-start)/CLOCKS_PER_SEC);
}
//显示路径,反向输出
void DispPath(int t){
printf("\nPath from %d to %d:\n",s,t);
printf("Shortest path length is %d.\n\n",dist[t]);
stack tmps;
int j=t;
while(j>0){
tmps.push(j);
j=path[j];
}
while(tmps.size()>1){
printf("%d->",tmps.top());
tmps.pop();
}
printf("%d\n",tmps.top()); //不输出最后一个箭头
tmps.pop();
}
//将源点 s 与前 10000 个点的最短距离输出到文件
void ToFile(){
FILE* fp;
char str[20];
itoa(s,str,10);
strcat(str,".txt");//生成文件名
fp=fopen(str,"w");
fprintf(fp,"start_id,end_id,dist\n");
for(int i=1;i<=10000;i++){
if(dist[i]!=0x3f3f3f3f)
fprintf(fp,"%d,%d,%d\n",s,i,dist[i]);
else
fprintf(fp,"%d,%d,NaN\n",s,i);
}
fclose(fp);
}
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
Initialize();
ShortestPath(s);
ToFile();
DispPath(t);
return 0;
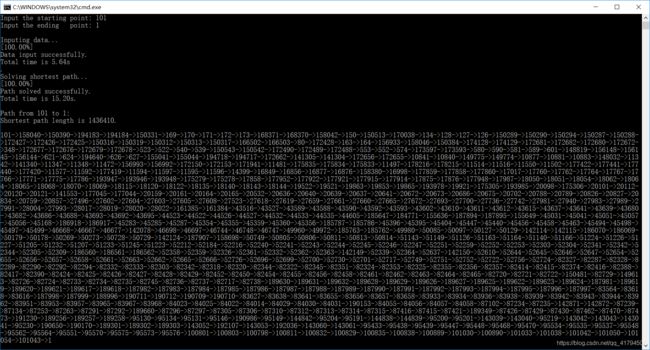
} 5. 运行结果
(1)最短路径(101->1):
(2)源点到前10000个点的距离:
start_id,end_id,dist
101,1,1436410
101,2,1302440
101,3,1334756
101,4,1334893
101,5,1293080
......