GMS:Grid-based Motion Statistics 算法代码阅读
论文:GMS:Grid-based Motion Statistics for Fast,Ultra-robust Feature Correspondence
CVPR 2017
开源代码地址:https://github.com/JiawangBian/GMS-Feature-Matcher
对于论文具体内容的推导大家自己看论文,我这里仅对代码做一个简单的说明。
代码实现有是三种方式:C++、python、matlab。下面阅读C++实现方式:
首先打开src文件夹下的demo.cpp文件
int main()
{
#ifdef USE_GPU
int flag = cuda::getCudaEnabledDeviceCount();
if (flag != 0) { cuda::setDevice(0); }
#endif // USE_GPU
runImagePair();
return 0;
}如果定义了USE_GPU,可以利用GPU加速ORB特征匹配。主函数很简单,直接调用runImagePair函数。
void runImagePair() {
Mat img1 = imread("../data/01.jpg");
Mat img2 = imread("../data/02.jpg");
GmsMatch(img1, img2);
}该函数读取一对图像,然后调用GmsMatch函数。
void GmsMatch(Mat &img1, Mat &img2) {
vector kp1, kp2;
Mat d1, d2;
vector matches_all, matches_gms;
Ptr orb = ORB::create(10000);
orb->setFastThreshold(0);
orb->detectAndCompute(img1, Mat(), kp1, d1);
orb->detectAndCompute(img2, Mat(), kp2, d2);
#ifdef USE_GPU
GpuMat gd1(d1), gd2(d2);
Ptr matcher = cv::cuda::DescriptorMatcher::createBFMatcher(NORM_HAMMING);
matcher->match(gd1, gd2, matches_all);
#else
BFMatcher matcher(NORM_HAMMING);
matcher.match(d1, d2, matches_all);
#endif
// GMS filter
std::vector vbInliers;
gms_matcher gms(kp1, img1.size(), kp2, img2.size(), matches_all);
int num_inliers = gms.GetInlierMask(vbInliers, false, false);
cout << "Get total " << num_inliers << " matches." << endl;
// collect matches
for (size_t i = 0; i < vbInliers.size(); ++i)
{
if (vbInliers[i] == true)
{
matches_gms.push_back(matches_all[i]);
}
}
// draw matching
Mat show = DrawInlier(img1, img2, kp1, kp2, matches_gms, 1);
imshow("show", show);
waitKey();
} 这部分首先提取ORB特征点并计算描述子,然后BF暴力匹配。之后创建gms_matcher对象,调用GetInlierMask成员函数获取内点,将内点存入vbInliers。最后调用DrawInlier画出匹配的内点。
Mat DrawInlier(Mat &src1, Mat &src2, vector &kpt1, vector &kpt2, vector &inlier, int type) {
const int height = max(src1.rows, src2.rows);
const int width = src1.cols + src2.cols;
Mat output(height, width, CV_8UC3, Scalar(0, 0, 0));
src1.copyTo(output(Rect(0, 0, src1.cols, src1.rows)));
src2.copyTo(output(Rect(src1.cols, 0, src2.cols, src2.rows)));
if (type == 1)
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < inlier.size(); i++)
{
Point2f left = kpt1[inlier[i].queryIdx].pt;
Point2f right = (kpt2[inlier[i].trainIdx].pt + Point2f((float)src1.cols, 0.f));
line(output, left, right, Scalar(0, 255, 255));
}
}
else if (type == 2)
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < inlier.size(); i++)
{
Point2f left = kpt1[inlier[i].queryIdx].pt;
Point2f right = (kpt2[inlier[i].trainIdx].pt + Point2f((float)src1.cols, 0.f));
line(output, left, right, Scalar(255, 0, 0));
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < inlier.size(); i++)
{
Point2f left = kpt1[inlier[i].queryIdx].pt;
Point2f right = (kpt2[inlier[i].trainIdx].pt + Point2f((float)src1.cols, 0.f));
circle(output, left, 1, Scalar(0, 255, 255), 2);
circle(output, right, 1, Scalar(0, 255, 0), 2);
}
}
return output;
} 这里有两种方式,第一种是只在对应特征点之间画直线,第二种是圈出每个特征点,然后在对应特征点之间画直线。
下面看一下includ文件夹下的gms_matcher.h文件。该文件定义了gms_matcher类。
class gms_matcher
{
public:
// OpenCV Keypoints & Correspond Image Size & Nearest Neighbor Matches
gms_matcher(const vector &vkp1, const Size size1, const vector &vkp2, const Size size2, const vector &vDMatches)
{
// Input initialize
NormalizePoints(vkp1, size1, mvP1);
NormalizePoints(vkp2, size2, mvP2);
mNumberMatches = vDMatches.size();
ConvertMatches(vDMatches, mvMatches);
// Grid initialize
mGridSizeLeft = Size(20, 20);
mGridNumberLeft = mGridSizeLeft.width * mGridSizeLeft.height;
// Initialize the neihbor of left grid
mGridNeighborLeft = Mat::zeros(mGridNumberLeft, 9, CV_32SC1);
InitalizeNiehbors(mGridNeighborLeft, mGridSizeLeft);
};
~gms_matcher() {};
private:
// Normalized Points
vector mvP1, mvP2;
// Matches
vector > mvMatches;
// Number of Matches
size_t mNumberMatches;
// Grid Size
Size mGridSizeLeft, mGridSizeRight;
int mGridNumberLeft;
int mGridNumberRight;
// x : left grid idx
// y : right grid idx
// value : how many matches from idx_left to idx_right
Mat mMotionStatistics;
//
vector mNumberPointsInPerCellLeft;
// Inldex : grid_idx_left
// Value : grid_idx_right
vector mCellPairs;
// Every Matches has a cell-pair
// first : grid_idx_left
// second : grid_idx_right
vector > mvMatchPairs;
// Inlier Mask for output
vector mvbInlierMask;
//
Mat mGridNeighborLeft;
Mat mGridNeighborRight;
public:
// Get Inlier Mask
// Return number of inliers
int GetInlierMask(vector &vbInliers, bool WithScale = false, bool WithRotation = false);
private:
// Normalize Key Points to Range(0 - 1)
void NormalizePoints(const vector &kp, const Size &size, vector &npts) {
const size_t numP = kp.size();
const int width = size.width;
const int height = size.height;
npts.resize(numP);
for (size_t i = 0; i < numP; i++)
{
npts[i].x = kp[i].pt.x / width;
npts[i].y = kp[i].pt.y / height;
}
}
// Convert OpenCV DMatch to Match (pair)
void ConvertMatches(const vector &vDMatches, vector > &vMatches) {
vMatches.resize(mNumberMatches);
for (size_t i = 0; i < mNumberMatches; i++)
{
vMatches[i] = pair(vDMatches[i].queryIdx, vDMatches[i].trainIdx);
}
}
int GetGridIndexLeft(const Point2f &pt, int type) {
int x = 0, y = 0;
if (type == 1) {
x = floor(pt.x * mGridSizeLeft.width);
y = floor(pt.y * mGridSizeLeft.height);
if (y >= mGridSizeLeft.height || x >= mGridSizeLeft.width){
return -1;
}
}
if (type == 2) {
x = floor(pt.x * mGridSizeLeft.width + 0.5);
y = floor(pt.y * mGridSizeLeft.height);
if (x >= mGridSizeLeft.width || x < 1) {
return -1;
}
}
if (type == 3) {
x = floor(pt.x * mGridSizeLeft.width);
y = floor(pt.y * mGridSizeLeft.height + 0.5);
if (y >= mGridSizeLeft.height || y < 1) {
return -1;
}
}
if (type == 4) {
x = floor(pt.x * mGridSizeLeft.width + 0.5);
y = floor(pt.y * mGridSizeLeft.height + 0.5);
if (y >= mGridSizeLeft.height || y < 1 || x >= mGridSizeLeft.width || x < 1) {
return -1;
}
}
return x + y * mGridSizeLeft.width;
}
int GetGridIndexRight(const Point2f &pt) {
int x = floor(pt.x * mGridSizeRight.width);
int y = floor(pt.y * mGridSizeRight.height);
return x + y * mGridSizeRight.width;
}
// Assign Matches to Cell Pairs
void AssignMatchPairs(int GridType);
// Verify Cell Pairs
void VerifyCellPairs(int RotationType);
// Get Neighbor 9
vector GetNB9(const int idx, const Size& GridSize) {
vector NB9(9, -1);
int idx_x = idx % GridSize.width;
int idx_y = idx / GridSize.width;
for (int yi = -1; yi <= 1; yi++)
{
for (int xi = -1; xi <= 1; xi++)
{
int idx_xx = idx_x + xi;
int idx_yy = idx_y + yi;
if (idx_xx < 0 || idx_xx >= GridSize.width || idx_yy < 0 || idx_yy >= GridSize.height)
continue;
NB9[xi + 4 + yi * 3] = idx_xx + idx_yy * GridSize.width;
}
}
return NB9;
}
void InitalizeNiehbors(Mat &neighbor, const Size& GridSize) {
for (int i = 0; i < neighbor.rows; i++)
{
vector NB9 = GetNB9(i, GridSize);
int *data = neighbor.ptr(i);
memcpy(data, &NB9[0], sizeof(int) * 9);
}
}
void SetScale(int Scale) {
// Set Scale
mGridSizeRight.width = mGridSizeLeft.width * mScaleRatios[Scale];
mGridSizeRight.height = mGridSizeLeft.height * mScaleRatios[Scale];
mGridNumberRight = mGridSizeRight.width * mGridSizeRight.height;
// Initialize the neihbor of right grid
mGridNeighborRight = Mat::zeros(mGridNumberRight, 9, CV_32SC1);
InitalizeNiehbors(mGridNeighborRight, mGridSizeRight);
}
// Run
int run(int RotationType);
}; 构造函数首先对输入图像初始化,归一化特征点位置(0~1之间)、得到匹配特征点对的数量。然后将DMatch类型转化成int类型。设置网格数量为20X20,初始化mGridNeighborLeft变量,其行数是左图网格数,列数为9,每一行都存储了每个网格周围九个网格的信息。
接下来看一下GetInlierMask函数:
int gms_matcher::GetInlierMask(vector &vbInliers, bool WithScale, bool WithRotation) {
int max_inlier = 0;
if (!WithScale && !WithRotation)
{
SetScale(0);
max_inlier = run(1);
vbInliers = mvbInlierMask;
return max_inlier;
}
if (WithRotation && WithScale)
{
for (int Scale = 0; Scale < 5; Scale++)
{
SetScale(Scale);
for (int RotationType = 1; RotationType <= 8; RotationType++)
{
int num_inlier = run(RotationType);
if (num_inlier > max_inlier)
{
vbInliers = mvbInlierMask;
max_inlier = num_inlier;
}
}
}
return max_inlier;
}
if (WithRotation && !WithScale)
{
SetScale(0);
for (int RotationType = 1; RotationType <= 8; RotationType++)
{
int num_inlier = run(RotationType);
if (num_inlier > max_inlier)
{
vbInliers = mvbInlierMask;
max_inlier = num_inlier;
}
}
return max_inlier;
}
if (!WithRotation && WithScale)
{
for (int Scale = 0; Scale < 5; Scale++)
{
SetScale(Scale);
int num_inlier = run(1);
if (num_inlier > max_inlier)
{
vbInliers = mvbInlierMask;
max_inlier = num_inlier;
}
}
return max_inlier;
}
return max_inlier;
}
const int mRotationPatterns[8][9] = {
1,2,3,
4,5,6,
7,8,9,
4,1,2,
7,5,3,
8,9,6,
7,4,1,
8,5,2,
9,6,3,
8,7,4,
9,5,1,
6,3,2,
9,8,7,
6,5,4,
3,2,1,
6,9,8,
3,5,7,
2,1,4,
3,6,9,
2,5,8,
1,4,7,
2,3,6,
1,5,9,
4,7,8
}; 可以设置是否具有尺度和旋转,如果设置尺度,则右图网格尺寸按照左图网格进行缩放。如果设置旋转,则检测内点时遍历八种旋转的情况(详见mRotationPatterns)。直接来看不带尺度不旋转的情况:调用run函数获取内点。
int gms_matcher::run(int RotationType) {
mvbInlierMask.assign(mNumberMatches, false);
// Initialize Motion Statisctics
mMotionStatistics = Mat::zeros(mGridNumberLeft, mGridNumberRight, CV_32SC1);
mvMatchPairs.assign(mNumberMatches, pair(0, 0));
for (int GridType = 1; GridType <= 4; GridType++)
{
// initialize
mMotionStatistics.setTo(0);
mCellPairs.assign(mGridNumberLeft, -1);
mNumberPointsInPerCellLeft.assign(mGridNumberLeft, 0);
AssignMatchPairs(GridType);
VerifyCellPairs(RotationType);
// Mark inliers
for (size_t i = 0; i < mNumberMatches; i++)
{
if (mvMatchPairs[i].first >= 0) {
if (mCellPairs[mvMatchPairs[i].first] == mvMatchPairs[i].second)
{
mvbInlierMask[i] = true;
}
}
}
}
int num_inlier = sum(mvbInlierMask)[0];
return num_inlier;
} mMotionStatistics行数为左图网格数,列数为右图网格数,可以看成坐标(a,b),a,b分别代表左图和右图网格的index,每一个坐标内存储的是a,b这两个区域内匹配的特征点数。由于特征点有可能正好落在网格边缘上,因此会对网格的长宽进行调整,论文里说进行三次迭代,代码中for循环是迭代了4次。for循环内主要有AssignMatchPairs与VerifyCellPairs这两个函数。
void gms_matcher::AssignMatchPairs(int GridType) {
for (size_t i = 0; i < mNumberMatches; i++)
{
Point2f &lp = mvP1[mvMatches[i].first];
Point2f &rp = mvP2[mvMatches[i].second];
int lgidx = mvMatchPairs[i].first = GetGridIndexLeft(lp, GridType);
int rgidx = -1;
if (GridType == 1)
{
rgidx = mvMatchPairs[i].second = GetGridIndexRight(rp);
}
else
{
rgidx = mvMatchPairs[i].second;
}
if (lgidx < 0 || rgidx < 0) continue;
mMotionStatistics.at(lgidx, rgidx)++;
mNumberPointsInPerCellLeft[lgidx]++;
}
}
void gms_matcher::VerifyCellPairs(int RotationType) {
const int *CurrentRP = mRotationPatterns[RotationType - 1];
for (int i = 0; i < mGridNumberLeft; i++)
{
if (sum(mMotionStatistics.row(i))[0] == 0)
{
mCellPairs[i] = -1;
continue;
}
int max_number = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < mGridNumberRight; j++)
{
int *value = mMotionStatistics.ptr(i);
if (value[j] > max_number)
{
mCellPairs[i] = j;
max_number = value[j];
}
}
int idx_grid_rt = mCellPairs[i];
const int *NB9_lt = mGridNeighborLeft.ptr(i);
const int *NB9_rt = mGridNeighborRight.ptr(idx_grid_rt);
int score = 0;
double thresh = 0;
int numpair = 0;
for (size_t j = 0; j < 9; j++)
{
int ll = NB9_lt[j];
int rr = NB9_rt[CurrentRP[j] - 1];
if (ll == -1 || rr == -1) continue;
score += mMotionStatistics.at(ll, rr);
thresh += mNumberPointsInPerCellLeft[ll];
numpair++;
}
thresh = THRESH_FACTOR * sqrt(thresh / numpair);
if (score < thresh)
mCellPairs[i] = -2;
}
} AssignMatchPairs函数遍历每一对特征点,获取它们在左图和右图的index,存入到mMotionStatistics相应的位置(a,b)。左图特征点mNumberPointsInPerCellLeft每次相应位置加一。
VerifyCellPairs函数寻找每一个左网格在又网格中对应匹配特征点数量最多的那一对网格(a,b),假设这一对网格看到的是同一位置。然后分别累计a周围9个网格与b周围9个网格匹配的特征点数,计算阈值,根据阈值判断真假匹配。
回到run函数的for循环,遍历每一对匹配特征点,当mCellPairs变量内网格a对应的匹配网格是网格b的时候才认为是内点。run函数最后返回内点数。
对于内点的判断有两次:一次是判断(a,b)这对网格是否为真匹配,如果是真匹配,a网格对应的特征点在b网格中才认为是内点(有可能a内的匹配点在右图的其他位置网格内)。
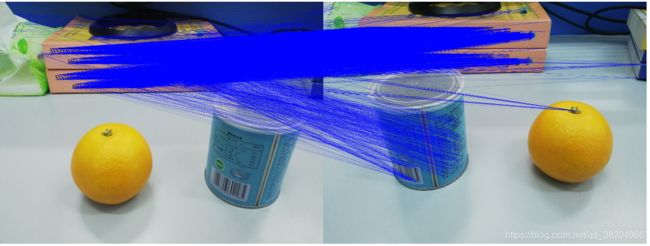
最后附上代码测试结果:
可见,ORB方法提取的特征,有较多的错误匹配,GMS筛选后可有效降低错误匹配数量。