【iOS学习】UITabBarController
alertView prompt
let alertView : UIAlertController = UIAlertController(title: "~~您已成功加入购物车耶耶~~", message: titleaddprice, preferredStyle: .alert)
let okaction : UIAlertAction = UIAlertAction(title: "嗯,本宝宝知道了~", style: .default, handler: nil)
alertView.addAction(okaction)
self .present(alertView, animated: true, completion: nil) //the left bar button item of navigation
self.navigationItem.leftBarButtonItem = UIBarButtonItem(title: "本月图书销量排行榜:",style: .plain ,target: self, action: nil)
//the right bar button item of navigation
self.navigationItem.rightBarButtonItem = UIBarButtonItem(title: "查看购物车",style: .plain ,target: self, action: #selector(callMe))
}
//show in shopping cart - jump to the shoppingcartviewcontroller
@objc fileprivate func callMe() {
let vc = UIStoryboard(name: "Main", bundle: nil).instantiateViewController(withIdentifier: "shoppingCart")
vc.navigationItem.title = self.navigationItem.rightBarButtonItem?.title
self.navigationController?.pushViewController(vc, animated: true)
}
UITabBarController
A container view controller that manages a radio-style selection interface, where the selection determines which child view controller to display.
On This Page
- Declaration
- Overview
- Topics
- Relationships
- See Also
Declaration
class UITabBarController : UIViewController
Overview
The tab bar interface displays tabs at the bottom of the window for selecting between the different modes and for displaying the views for that mode. This class is generally used as-is, but may also be subclassed.
Each tab of a tab bar controller interface is associated with a custom view controller. When the user selects a specific tab, the tab bar controller displays the root view of the corresponding view controller, replacing any previous views. (User taps always display the root view of the tab, regardless of which tab was previously selected. This is true even if the tab was already selected.) Because selecting a tab replaces the contents of the interface, the type of interface managed in each tab need not be similar in any way. In fact, tab bar interfaces are commonly used either to present different types of information or to present the same information using a completely different style of interface. Figure 1 shows the tab bar interface presented by the Clock app, each tab of which presents a type of time based information.
Figure 1
The tab bar interface in the Clock app
You should never access the tab bar view of a tab bar controller directly. To configure the tabs of a tab bar controller, you assign the view controllers that provide the root view for each tab to the viewControllers property. The order in which you specify the view controllers determines the order in which they appear in the tab bar. When setting this property, you should also assign a value to the selectedViewController property to indicate which view controller is selected initially. (You can also select view controllers by array index using the selectedIndex property.) When you embed the tab bar controller’s view (obtained using the inherited view property) in your app window, the tab bar controller automatically selects that view controller and displays its contents, resizing them as needed to fit the tab bar interface.
Tab bar items are configured through their corresponding view controller. To associate a tab bar item with a view controller, create a new instance of the UITabBarItem class, configure it appropriately for the view controller, and assign it to the view controller’s tabBarItemproperty. If you don't provide a custom tab bar item for your view controller, the view controller creates a default item containing no image and the text from the view controller’s titleproperty.
As the user interacts with a tab bar interface, the tab bar controller object sends notifications about the interactions to its delegate. The delegate can be any object you specify but must conform to the UITabBarControllerDelegate protocol. You can use the delegate to prevent specific tab bar items from being selected and to perform additional tasks when tabs are selected. You can also use the delegate to monitor changes to the tab bar that are made by the More navigation controller, which is described in more detail in The More Navigation Controller.
The Views of a Tab Bar Controller
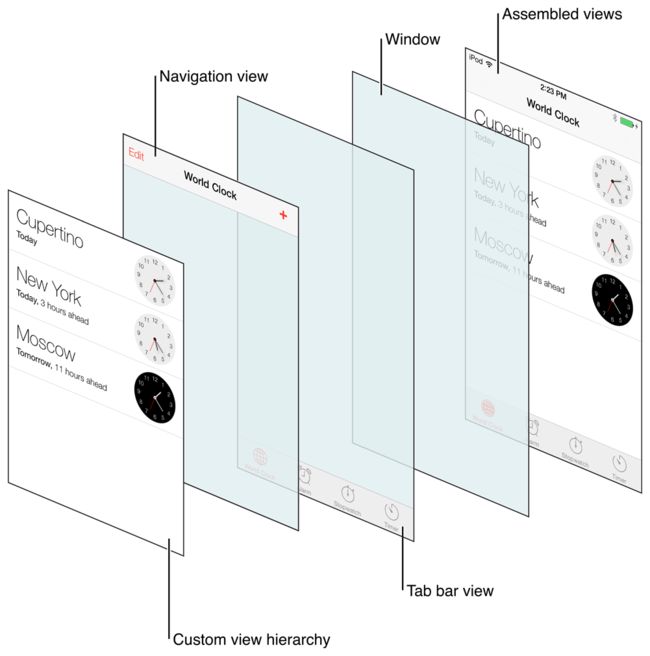
Because the UITabBarController class inherits from the UIViewController class, tab bar controllers have their own view that is accessible through the view property. The view for a tab bar controller is just a container for a tab bar view and the view containing your custom content. The tab bar view provides the selection controls for the user and consists of one or more tab bar items. Figure 2 shows how these views are assembled to present the overall tab bar interface. Although the items in the tab bar and toolbar views can change, the views that manage them do not. Only the custom content view changes to reflect the view controller for the currently selected tab.
Figure 2
The primary views of a tab bar controller
You can use navigation controllers or custom view controllers as the root view controller for a tab. If the root view controller is a navigation controller, the tab bar controller makes further adjustments to the size of the displayed navigation content so that it does not overlap the tab bar. Any views you display in a tab bar interface should therefore have their autoresizingMask property set to resize the view appropriately under any conditions.
The More Navigation Controller
The tab bar has limited space for displaying your custom items. If you add six or more custom view controllers to a tab bar controller, the tab bar controller displays only the first four items plus the standard More item on the tab bar. Tapping the More item brings up a standard interface for selecting the remaining items.
The interface for the standard More item includes an Edit button that allows the user to reconfigure the tab bar. By default, the user is allowed to rearrange all items on the tab bar. If you do not want the user to modify some items, though, you can remove the appropriate view controllers from the array in the customizableViewControllers property.
Note
Tab bar customization and the More interface are not available in tvOS.
State Preservation
In iOS 6 and later, if you assign a value to this view controller’s restorationIdentifierproperty, it preserves a reference to the view controller in the selected tab. At restore time, it uses the reference to select the tab with the same view controller.
When preserving a tab bar controller, assign unique restoration identifiers to the child view controllers you want to preserve. Omitting a restoration identifier from a child view controller causes that tab to return to its default configuration. Although the tab bar controller saves its tabs in the same order that they are listed in the viewControllers property, the save order is actually irrelevant. Your code is responsible for providing the new tab bar controller during the next launch cycle, so your code can adjust the order of the tabs as needed. The state preservation system restores the contents of each tab based on the assigned restoration identifier, not based on the position of the tab.
For more information about how state preservation and restoration works, see App Programming Guide for iOS.
Differences in tvOS
Tab bar controllers serve the same purpose in tvOS as in iOS, but provide slightly different user interface features:
-
The tab bar interface appears at the top of the window. When focus leaves the tab bar, the tab bar is hidden. Swiping up on the remote shows the tab bar again and focuses it. A user can also show and focus the tab bar by pressing the Menu button.
-
Swiping down from the tab bar moves focus into the content view; specifically, to the first focusable view that is visually below the selected tab. Swiping down behaves like a normal focus-changing gesture—that is, focus moves in the direction the user swiped. If nothing is focusable immediately below the selected tab, the closest focusable view is focused instead.
-
Pressing the Select button while a tab is focused moves focus into the content view. Because there is no direction associated with this change, focus moves to the view specified in the content view's
preferredFocusedViewproperty. -
Tab bar controllers in tvOS do not support customization. A tab bar controller displays only the number of view controllers from its
viewControllersarray that fit on the screen, and does not provide the More interface seen in iOS.