python_文件操作open
有时候我们会把一些数据保存到一个文档中,等需要使用的时候,打开这个文档读取
文件打开:f = open(‘文件名.后缀’)
注意:文件打开使用完后一定要记得关闭文件,f.close()
1、open的使用
实例:在demo_01.py中打开文档demo123.txt并读取
1、open()&close()
#第一种方式
在f = open('demo123.txt')
# f 就是表示打开的文件
data = f.read() #data就是读取到的内容,是str类型
f.close()
print(data)
#第二种方式
print(open('demo123.txt').read())
f.close()
2、with语句:(自动关闭文件,不需要手动close)
#如果文档有中文时,加上参数 encoding='utf-8'
with open('demo123.txt', encoding='utf-8') as f:
print(f.read())
2、open()的参数
1、mode:打开方式
rb:以二进制方式打开一个文件只用于读取
r:只读
a:追加,文件不存在时创建并写入,存在时打开追加
w:写入,文件不存在时创建并写入,存在时覆盖旧的
ab:以二进制格式打开一个文件只用于追加
wb:以二进制格式打开一个文件只用于写入
2、encoding:
文档中有中文时,使用 encoding=‘utf-8’
3、读取
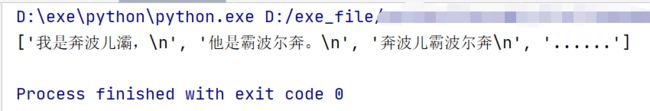
同一个包下有一个文档demo.txt,内容为:
我是奔波儿灞,
他是霸波尔奔。
奔波儿霸波尔奔
…
1、readline():
按行读取
with open('demo.txt', encoding='utf8') as f:
print(f.readline())
2、readlines():
多行读取
会将文档中的数据每一行存成一个字符串,再将所有的字符串存在一个列表中打印出来(换行符也会打印出来)
with open('demo.txt', encoding='utf8') as f:
print(f.readlines())
4、写入
1、write()
#先写入demo.txt文件
with open('demo.txt', mode='a', encoding='utf8') as f:
f.write("大王叫我来巡山呐。。。")
#读取demo.txt文件的内容并输出到屏幕上
with open('demo.txt', mode='r', encoding='utf8') as f:
print(f.read())
f = open('demo01.txt', 'w', encoding= 'utf8')
data = ['id, age, name\n', "1, 18, 'a1'\n", "2, 17, 'a2'" ]
f.writelines(data)
f.close()