Python字符串的常用方法(参考菜鸟教程)
首先需要:
import string
1.capitalize()
- 返回值首字母大写。
test1 = 'he cheated me!'
print(test1.capitalize())
print(test1)
运行结果:
He cheated me!
he cheated me!
输出两次的目的主要是验证该方法能否改变字符串本身,输出结果证明capitalize()方法不可以
2.count()
- 数括号里的字符串在字符串实例里出现了多少次。
- 通过改变括号里的参数可以设置搜索的范围。start=?, end=?
代码还同时引入了其他方法(字符串句子是根据需求随便编的)
test2 = 'I word word word time time we we I.'
print(test2.strip(string.punctuation)) # 去掉字符串中的标点符号
words = [word for word in test2.strip(string.punctuation).split()]
print(words)
words_set = set(words)
print(words_set)
word_count_dict = {single_word: test2.strip(string.punctuation).count(single_word) for single_word in words_set}
print(word_count_dict)
该代码完成了:
- test2.strip(string.punctuation)去掉句中左右两边的标点符号
- split()联合列表解析式将句子分割成单词,分割的标准是字符串中的空格
- set(words)将列表转换成集合,避免重复
- 最后利用集合解析式,和count()方法得到键为单词,值为该词在句中出现次数的字典
3.encode()和decode()
编码和解码字符串,对字符串编码后,得到bytes对象,对bytes解码后,得到字符串对象。
bytes的编码方式有UTF-8, GBK等等,需要选择编码的方式。
4.find()系列
find(str, beg=0, end=len(string))
在字符串string中找str的位置,beg和end指定搜索范围。“位置”指的是从0开始数
test2 = 'I word word word time time we we I.'
print(test2.find('I'))
输出结果:0
还有rfind()从右边开始找
5.is*****()系列
检测这个字符串里是否只有该种字符,如果是,返回True。
isalnum():都是字母或数字
isalpha():都是字母
isdigit():都是数字
islower():都是小写字母
isupper():都是大写字母
isspace()都是空格
istitle()是标题(title的意思是每个词首字母大写),而且title()方法即是将字符串的每个单词首字母大写,转化成标题的形式。
6.join()
str.join(sequence),把许多字符串用str分隔后连接在一起。
seq = ('I', 'love', 'you')
test3 = '~'
print(test3.join(seq))
输出:
![]()
7.max(str)和min(str)
找最大和最小的字母。使用方法:
str.max()
max(str) ✔
什么是最大的字母?小写的,在字母表顺序后面的。
8.replace()
替换。str.replace(old_str, new_str),备选参数:最大替换次数
# replace(),2指替换次数不超过两次
test2 = 'I word word word time time we we I.'
print(test2.replace('word', 'world', 2))
输出:
![]()
9.(l/r)just()系列
让字符串左/右对齐,并用某指定字符(默认空格)来填充字符串长度到要求长度。
(l/r)just(width),width:要求字符串长度。可选参数:指定填充字符
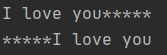
test4 = 'I love you'
print(test4.ljust(15, '*'))
print(test4.rjust(15, '*'))
10.strip()系列
lstrip(),rstrip(),strip()各自为:去掉左边,右边,左右两边指定字符(默认空格)
test5 = '****#*I love you*#****'
print(test5.lstrip('*'))
print(test5.rstrip('*'))
print(test5.strip('*'))
11.大小写转换系列
upper()
lower()
swapcase():把大写转小写,把小写转大写
12.translate()指定密码本翻译
一定要有的参数:密码本(两个字符串用str.maketrans()形成一一映射)
可选参数:需要删掉的字符列表
test6 = 'I hate you'
str1 = 'hateyou'
str2 = 'loveme '
password = str.maketrans(str1, str2)
print(test6.translate(password))
输出:
![]()
关于str.maketrans(),如果里面只有一个参数,那么它应该是字典,如果里面有2个参数,应该是长度相等的字符串,否则映射不了。
13.len()长度
这个不用说了。