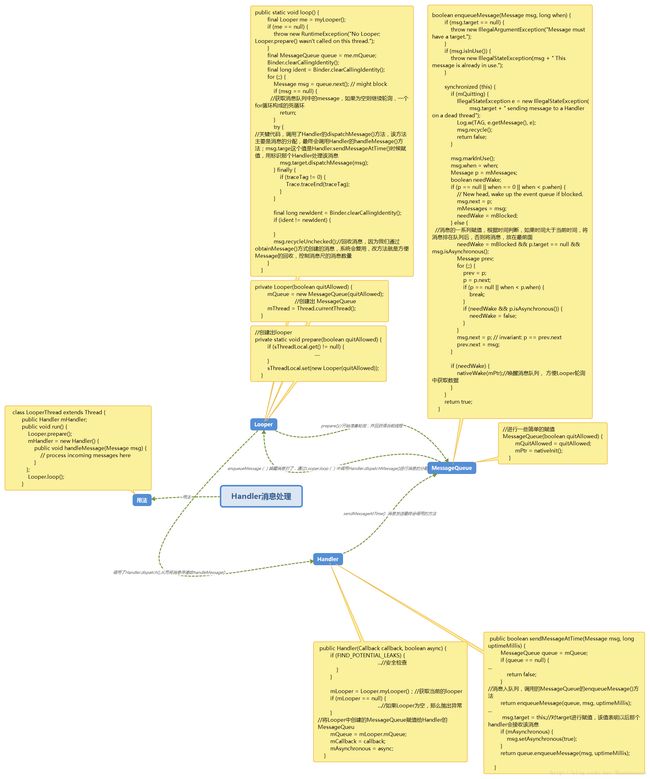
Handler源码分析,Handler,Looper,Message,MessageQueue
Android开发中我们常用到Handler,但是可能会有一些别的原因,没有去仔细分析源码,今天看了一下,在仅涉及的sdk源码中进行分析,未涉及ndk,因为源码并不是很多,所以建议大家可以自己去看一下,如有错误之处欢迎留言。。。
1.Handler常用的使用
class LooperThread extends Thread {
public Handler mHandler;
public void run() {
Looper.prepare();
mHandler = new Handler() {
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
// process incoming messages here
}
};
Looper.loop();
}
Activity中Looper的注册
attach()方法中会创建一个ActivityThread对象,
ActivityThread对象中的main方法户通过 Looper.prepareMainLooper()这个方法创建一个主线程的Looper。
public static void main(String[] args) { Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "ActivityThreadMain"); SamplingProfilerIntegration.start(); // CloseGuard defaults to true and can be quite spammy. We // disable it here, but selectively enable it later (via // StrictMode) on debug builds, but using DropBox, not logs. CloseGuard.setEnabled(false); Environment.initForCurrentUser(); // Set the reporter for event logging in libcore EventLogger.setReporter(new EventLoggingReporter()); // Make sure TrustedCertificateStore looks in the right place for CA certificates final File configDir = Environment.getUserConfigDirectory(UserHandle.myUserId()); TrustedCertificateStore.setDefaultUserDirectory(configDir); Process.setArgV0("" ); Looper.prepareMainLooper(); ActivityThread thread = new ActivityThread(); thread.attach(false); if (sMainThreadHandler == null) { sMainThreadHandler = thread.getHandler(); } if (false) { Looper.myLooper().setMessageLogging(new LogPrinter(Log.DEBUG, "ActivityThread")); } // End of event ActivityThreadMain. Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER); Looper.loop(); throw new RuntimeException("Main thread loop unexpectedly exited"); }
Handler解析_Handler重要方法解析
Callback(重要)用于非Handler类中的消息的接收,返回true代表无需进一步处理,也就是说Handler中的handleMessage()方法不会接收到消息
4)对消息延时处理,系统当前时间+延迟时间(毫秒数)SystemClock.uptimeMillis() + delayMillis
removeCallbacks
构造方法:主要是Looper,Callback,async的赋值
1)
public Handler() { this(null, false); }2)
public Handler(boolean async) { this(null, async); }3)
public Handler(Callback callback, boolean async) { //安全检查 if (FIND_POTENTIAL_LEAKS) { final Classextends Handler> klass = getClass(); if ((klass.isAnonymousClass() || klass.isMemberClass() || klass.isLocalClass()) && (klass.getModifiers() & Modifier.STATIC) == 0) { Log.w(TAG, "The following Handler class should be static or leaks might occur: " + klass.getCanonicalName()); } } //重点 各个参数的赋值 mLooper = Looper.myLooper(); if (mLooper == null) { throw new RuntimeException( "Can't create handler inside thread that has not called Looper.prepare()"); } mQueue = mLooper.mQueue; mCallback = callback; mAsynchronous = async; }4)
public Handler(Looper looper) { this(looper, null, false); }5)
public Handler(Looper looper, Callback callback) { this(looper, callback, false); }6)
public Handler(Looper looper, Callback callback, boolean async) { mLooper = looper; mQueue = looper.mQueue; mCallback = callback; mAsynchronous = async; }
用法:
public class A implements Callback{
public class A implements Callback{
public boolean handleMessage(Message msg){
return false;
}
}
public interface Callback { public boolean handleMessage(Message msg); }
如果Callback中的handleMessage的返回true,那么Handler中的handleMessage则不会收到消息了
obtainMessage,消息的创建的方式
1)
public final Message obtainMessage() { return Message.obtain(this); }
2)
public final Message obtainMessage(int what) { return Message.obtain(this, what); }3)
public final Message obtainMessage(int what, Object obj) { return Message.obtain(this, what, obj); }4)
public final Message obtainMessage(int what, int arg1, int arg2) { return Message.obtain(this, what, arg1, arg2); }5)
public final Message obtainMessage(int what, int arg1, int arg2, Object obj) { return Message.obtain(this, what, arg1, arg2, obj); }
Message obtain()
public static Message obtain(Handler h, int what, int arg1, int arg2, Object obj) { Message m = obtain(); m.target = h; m.what = what; m.arg1 = arg1; m.arg2 = arg2; m.obj = obj; return m; }
消息发送的方式(常用)
sendXXX系列
1)
public final boolean sendEmptyMessage(int what) { return sendEmptyMessageDelayed(what, 0); }2)
public final boolean sendEmptyMessageDelayed(int what, long delayMillis) { Message msg = Message.obtain(); msg.what = what; return sendMessageDelayed(msg, delayMillis); }
3)
public final boolean sendEmptyMessageDelayed(int what, long delayMillis) { Message msg = Message.obtain(); msg.what = what; return sendMessageDelayed(msg, delayMillis); }
public final boolean sendMessageDelayed(Message msg, long delayMillis) { if (delayMillis < 0) { delayMillis = 0; } return sendMessageAtTime(msg, SystemClock.uptimeMillis() + delayMillis); }
5)
public boolean sendMessageAtTime(Message msg, long uptimeMillis) { MessageQueue queue = mQueue; if (queue == null) { RuntimeException e = new RuntimeException( this + " sendMessageAtTime() called with no mQueue"); Log.w("Looper", e.getMessage(), e); return false; } return enqueueMessage(queue, msg, uptimeMillis); }enqueueMessage消息入队列,对message进行处理,调用MessageQueue 的enqueueMessage()方法,入队
private boolean enqueueMessage(MessageQueue queue, Message msg, long uptimeMillis) { msg.target = this; if (mAsynchronous) { msg.setAsynchronous(true); } return queue.enqueueMessage(msg, uptimeMillis); }MessageQueue 中的enqueueMessage()方法
boolean enqueueMessage(Message msg, long when) { if (msg.target == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Message must have a target."); } if (msg.isInUse()) { throw new IllegalStateException(msg + " This message is already in use."); } synchronized (this) { if (mQuitting) { IllegalStateException e = new IllegalStateException( msg.target + " sending message to a Handler on a dead thread"); Log.w(TAG, e.getMessage(), e); msg.recycle(); return false; } msg.markInUse(); msg.when = when; Message p = mMessages; boolean needWake; if (p == null || when == 0 || when < p.when) { // New head, wake up the event queue if blocked. msg.next = p; mMessages = msg; needWake = mBlocked; } else { // Inserted within the middle of the queue. Usually we don't have to wake // up the event queue unless there is a barrier at the head of the queue // and the message is the earliest asynchronous message in the queue. needWake = mBlocked && p.target == null && msg.isAsynchronous(); Message prev; for (;;) { prev = p; p = p.next; if (p == null || when < p.when) { break; } if (needWake && p.isAsynchronous()) { needWake = false; } } msg.next = p; // invariant: p == prev.next prev.next = msg; } // We can assume mPtr != 0 because mQuitting is false. if (needWake) { nativeWake(mPtr); } } return true; }postXXX系列 本质上还是调用的sendXXX系列中的方法
1)
public final boolean post(Runnable r) { return sendMessageDelayed(getPostMessage(r), 0); }2)
public final boolean postAtTime(Runnable r, long uptimeMillis) { return sendMessageAtTime(getPostMessage(r), uptimeMillis); }3)
public final boolean postAtTime(Runnable r, Object token, long uptimeMillis) { return sendMessageAtTime(getPostMessage(r, token), uptimeMillis); }4)
public final boolean postDelayed(Runnable r, long delayMillis) { return sendMessageDelayed(getPostMessage(r), delayMillis); }5)
public final boolean postAtFrontOfQueue(Runnable r) { return sendMessageAtFrontOfQueue(getPostMessage(r)); }6)
public final boolean sendMessageAtFrontOfQueue(Message msg) { MessageQueue queue = mQueue; if (queue == null) {//异常检查 RuntimeException e = new RuntimeException( this + " sendMessageAtTime() called with no mQueue"); Log.w("Looper", e.getMessage(), e); return false; } return enqueueMessage(queue, msg, 0);//调用 Handler的enqueueMessage()同sendMessage }getPostMessage(r) 创建message并且赋值callback
private static Message getPostMessage(Runnable r) { Message m = Message.obtain(); m.callback = r; return m; }dispatchMessage(重要),消息分配的关键方法,在Lopper中的loop方法中被调用
/** * Handle system messages here. */ public void dispatchMessage(Message msg) { if (msg.callback != null) {//msg.callback 是一个线程,如果不为空就运行 handleCallback(msg); } else { if (mCallback != null) { //判断Callback是否为空,非空就调用Callback的handleMessage方法处理, //mCallback.handleMessage(msg)返回true的话Handler自带的handleMessage //就不会收到消息,上面讲过 if (mCallback.handleMessage(msg)) { return; } } handleMessage(msg); } }
private static void handleCallback(Message message) { message.callback.run(); }移除方法: 本质上调用的Message.Queue中的removeXXX()方法
removeCallbacks
/** * Remove any pending posts of Runnable r that are in the message queue. */ public final void removeCallbacks(Runnable r) { mQueue.removeMessages(this, r, null); } /** * Remove any pending posts of Runnable r with Object * token that are in the message queue. If token is null, * all callbacks will be removed. */ public final void removeCallbacks(Runnable r, Object token) { mQueue.removeMessages(this, r, token); }removeMessages
/** * Remove any pending posts of messages with code 'what' that are in the * message queue. */ public final void removeMessages(int what) { mQueue.removeMessages(this, what, null); } /** * Remove any pending posts of messages with code 'what' and whose obj is * 'object' that are in the message queue. If object is null, * all messages will be removed. */ public final void removeMessages(int what, Object object) { mQueue.removeMessages(this, what, object); }Handler解析_Looper重要方法解析
官方用法
* class LooperThread extends Thread { * public Handler mHandler; * * public void run() { * Looper.prepare(); * * mHandler = new Handler() { * public void handleMessage(Message msg) { * // process incoming messages here * } * }; * * Looper.loop(); * }
Looper.prepare();主要的作用通过是ThreadLocal这个类进行判断,创建Looper
private static void prepare(boolean quitAllowed) { if (sThreadLocal.get() != null) { throw new RuntimeException("Only one Looper may be created per thread"); } sThreadLocal.set(new Looper(quitAllowed)); }
Looper中创建MessageQueue
private Looper(boolean quitAllowed) { mQueue = new MessageQueue(quitAllowed); mThread = Thread.currentThread(); }关键步骤Looper的轮询,Loop.loop();
/** * Run the message queue in this thread. Be sure to call * {@link #quit()} to end the loop. */ public static void loop() { final Looper me = myLooper(); if (me == null) { throw new RuntimeException("No Looper; Looper.prepare() wasn't called on this thread."); } final MessageQueue queue = me.mQueue; // Make sure the identity of this thread is that of the local process, // and keep track of what that identity token actually is. Binder.clearCallingIdentity(); final long ident = Binder.clearCallingIdentity(); for (;;) { Message msg = queue.next(); // might block if (msg == null) { // No message indicates that the message queue is quitting. return; } // This must be in a local variable, in case a UI event sets the logger final Printer logging = me.mLogging; if (logging != null) { logging.println(">>>>> Dispatching to " + msg.target + " " + msg.callback + ": " + msg.what); } final long traceTag = me.mTraceTag; if (traceTag != 0 && Trace.isTagEnabled(traceTag)) { Trace.traceBegin(traceTag, msg.target.getTraceName(msg)); } try { msg.target.dispatchMessage(msg); } finally { if (traceTag != 0) { Trace.traceEnd(traceTag); } } if (logging != null) { logging.println("<<<<< Finished to " + msg.target + " " + msg.callback); } // Make sure that during the course of dispatching the // identity of the thread wasn't corrupted. final long newIdent = Binder.clearCallingIdentity(); if (ident != newIdent) { Log.wtf(TAG, "Thread identity changed from 0x" + Long.toHexString(ident) + " to 0x" + Long.toHexString(newIdent) + " while dispatching to " + msg.target.getClass().getName() + " " + msg.callback + " what=" + msg.what); } msg.recycleUnchecked(); } }Looper的退出
/** * Quits the looper. ** Causes the {@link #loop} method to terminate without processing any * more messages in the message queue. *
* Any attempt to post messages to the queue after the looper is asked to quit will fail. * For example, the {@link Handler#sendMessage(Message)} method will return false. *
* Using this method may be unsafe because some messages may not be delivered * before the looper terminates. Consider using {@link #quitSafely} instead to ensure * that all pending work is completed in an orderly manner. * * * @see #quitSafely */ public void quit() { mQueue.quit(false); }
/** * Quits the looper safely. ** Causes the {@link #loop} method to terminate as soon as all remaining messages * in the message queue that are already due to be delivered have been handled. * However pending delayed messages with due times in the future will not be * delivered before the loop terminates. *
* Any attempt to post messages to the queue after the looper is asked to quit will fail. * For example, the {@link Handler#sendMessage(Message)} method will return false. * */ public void quitSafely() { mQueue.quit(true); }
Handler解析_Message重要方法解析
Message final修饰 Message的链表结构,并非是通过类似 LinkedList形成的数据结构,而是同内部的next变量作为指引下一个Message的指针,来获取下一个Message消息
public final class Message implements Parcelable创建方式:
1)通过handler的obtainMessage()方法创建,本质上调用的Message的obtainMessage()方法
2)
通过Message的obtainMessage()方法
构造方法 (空实现)
/** Constructor (but the preferred way to get a Message is to call {@link #obtain() Message.obtain()}). */ public Message() { }常用的变量 what arg1 arg2 obj 用于判断区分message以及携带数据
/** * User-defined message code so that the recipient can identify * what this message is about. Each {@link Handler} has its own name-space * for message codes, so you do not need to worry about yours conflicting * with other handlers. */ public int what; /** * arg1 and arg2 are lower-cost alternatives to using * {@link #setData(Bundle) setData()} if you only need to store a * few integer values. */ public int arg1; /** * arg1 and arg2 are lower-cost alternatives to using * {@link #setData(Bundle) setData()} if you only need to store a * few integer values. */ public int arg2; /** * An arbitrary object to send to the recipient. When using * {@link Messenger} to send the message across processes this can only * be non-null if it contains a Parcelable of a framework class (not one * implemented by the application). For other data transfer use * {@link #setData}. * * Note that Parcelable objects here are not supported prior to * the {@link android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES#FROYO} release. */ public Object obj;target 用于判断handler的来源,通过该值调用dispatchMessage()方法分配数据 callback
// sometimes we store linked lists of these things
/*package*/ Message next;
/*package*/ Handler target; /*package*/ Runnable callback; // sometimes we store linked lists of these things /*package*/ Message next;
Handler解析_MessageQueue重要方法解析
MessageQueue与其说是消息队列,更不如说会用于操作message的一个类
构造方法:quitAllowed(消息是否允许退出)
MessageQueue(boolean quitAllowed) { mQuitAllowed = quitAllowed; mPtr = nativeInit(); }重要方法:该类中有多个native方法
enqueueMessage消息的入队列,通过Handler中的sendMessage()方法调用
boolean enqueueMessage(Message msg, long when) { if (msg.target == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Message must have a target."); } if (msg.isInUse()) { throw new IllegalStateException(msg + " This message is already in use."); } synchronized (this) { if (mQuitting) { IllegalStateException e = new IllegalStateException( msg.target + " sending message to a Handler on a dead thread"); Log.w(TAG, e.getMessage(), e); msg.recycle(); return false; } msg.markInUse(); msg.when = when; Message p = mMessages; boolean needWake; if (p == null || when == 0 || when < p.when) { // New head, wake up the event queue if blocked. msg.next = p; mMessages = msg; needWake = mBlocked; } else { // Inserted within the middle of the queue. Usually we don't have to wake // up the event queue unless there is a barrier at the head of the queue // and the message is the earliest asynchronous message in the queue. needWake = mBlocked && p.target == null && msg.isAsynchronous(); Message prev; for (;;) { prev = p; p = p.next; if (p == null || when < p.when) { break; } if (needWake && p.isAsynchronous()) { needWake = false; } } msg.next = p; // invariant: p == prev.next prev.next = msg;//新消息的赋值,并且唤醒消息队列,进行消息的提取 } // We can assume mPtr != 0 because mQuitting is false. if (needWake) { nativeWake(mPtr); } } return true; }
next()方法 Loop.loop()方法会调用
先暂时这些吧
public static void loop() {
for (;;) { ...
Message msg = queue.next();
...}
}
Message next() { // Return here if the message loop has already quit and been disposed. // This can happen if the application tries to restart a looper after quit // which is not supported. final long ptr = mPtr; if (ptr == 0) { return null; } int pendingIdleHandlerCount = -1; // -1 only during first iteration int nextPollTimeoutMillis = 0; for (;;) { if (nextPollTimeoutMillis != 0) { Binder.flushPendingCommands(); } nativePollOnce(ptr, nextPollTimeoutMillis); synchronized (this) { // Try to retrieve the next message. Return if found. final long now = SystemClock.uptimeMillis(); Message prevMsg = null; Message msg = mMessages; if (msg != null && msg.target == null) { // Stalled by a barrier. Find the next asynchronous message in the queue. do { prevMsg = msg; msg = msg.next; } while (msg != null && !msg.isAsynchronous()); } if (msg != null) { if (now < msg.when) { // Next message is not ready. Set a timeout to wake up when it is ready. nextPollTimeoutMillis = (int) Math.min(msg.when - now, Integer.MAX_VALUE); } else { // Got a message. mBlocked = false; if (prevMsg != null) { prevMsg.next = msg.next; } else { mMessages = msg.next; }//对消息判断如果是消息还没有发生那么就放在消息队列的后面,如果已经超时了,就提前放在消息的队 //列的前面 msg.next = null; if (DEBUG) Log.v(TAG, "Returning message: " + msg); msg.markInUse(); return msg; } } else { // No more messages. nextPollTimeoutMillis = -1; } // Process the quit message now that all pending messages have been handled. if (mQuitting) { dispose(); return null; } // If first time idle, then get the number of idlers to run. // Idle handles only run if the queue is empty or if the first message // in the queue (possibly a barrier) is due to be handled in the future. if (pendingIdleHandlerCount < 0 && (mMessages == null || now < mMessages.when)) { pendingIdleHandlerCount = mIdleHandlers.size(); } if (pendingIdleHandlerCount <= 0) { // No idle handlers to run. Loop and wait some more. mBlocked = true; continue; } if (mPendingIdleHandlers == null) { mPendingIdleHandlers = new IdleHandler[Math.max(pendingIdleHandlerCount, 4)]; } mPendingIdleHandlers = mIdleHandlers.toArray(mPendingIdleHandlers); } // Run the idle handlers. // We only ever reach this code block during the first iteration. for (int i = 0; i < pendingIdleHandlerCount; i++) { final IdleHandler idler = mPendingIdleHandlers[i]; mPendingIdleHandlers[i] = null; // release the reference to the handler boolean keep = false; try { keep = idler.queueIdle(); } catch (Throwable t) { Log.wtf(TAG, "IdleHandler threw exception", t); } if (!keep) { synchronized (this) { mIdleHandlers.remove(idler); } } } // Reset the idle handler count to 0 so we do not run them again. pendingIdleHandlerCount = 0; // While calling an idle handler, a new message could have been delivered // so go back and look again for a pending message without waiting. nextPollTimeoutMillis = 0; } }