锁屏View附着点源码解析
文章目录
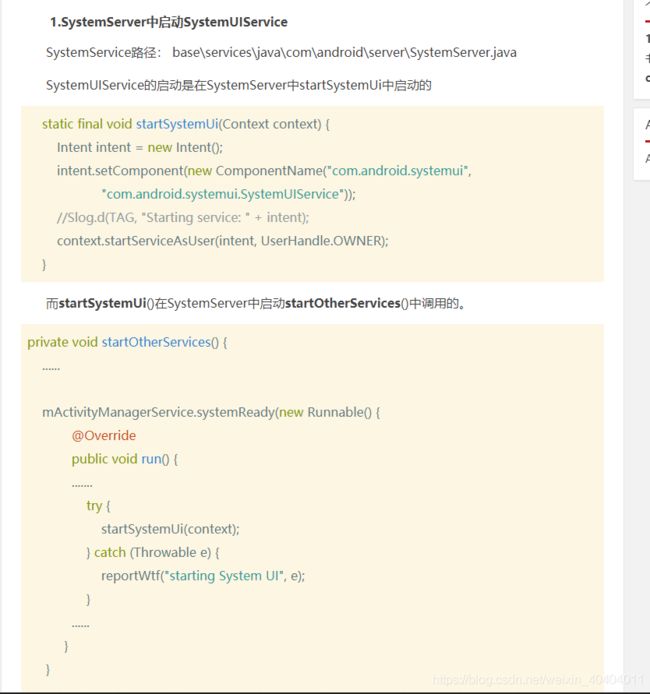
- 同样入口都是SystemService
- SystemUIService到SystemUIApplication启动"服务",实际上是初始化SystemUI类
- SystemBars关注这个类,是手机的状态栏
- 到PhoneStatusBar这里的start
- StatusBarKeyguardViewManager
- KeyguardBouncer,可以看到锁屏的View是建立在解锁的View上面而解锁的View又是建立在状态栏内
- 锁屏是建立在哪个Context上面的
参考链接
同样入口都是SystemService
SystemUIService到SystemUIApplication启动"服务",实际上是初始化SystemUI类
SystemBars关注这个类,是手机的状态栏
public class SystemBars extends SystemUI implements ServiceMonitor.Callbacks {
......
//start()方法是再启动中调用的额方法
@Override
public void start() {
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "start");
//这里会启动ServiceMonitor,并调用其的start(),重点看注释“如果没有远程服务,就会回调onNoService()方法”
mServiceMonitor = new ServiceMonitor(TAG, DEBUG,
mContext, Settings.Secure.BAR_SERVICE_COMPONENT, this);
mServiceMonitor.start(); // will call onNoService if no remote service is found
}
@Override
public void onNoService() {
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "onNoService");
createStatusBarFromConfig(); // fallback to using an in-process implementation
}
......
//第一次启动时,远程服务没有被启动,因此会回调onNoService()方法,然后调用createStatusBarFromConfig()方法,继续
private void createStatusBarFromConfig() {
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "createStatusBarFromConfig");
//根据xml中的配置,是一个应用包名路径,这里就是“com.android.systemui.statusbar.phone.PhoneStatusBar”
//然后根据包名路径并启动
final String clsName = mContext.getString(R.string.config_statusBarComponent);
if (clsName == null || clsName.length() == 0) {
throw andLog("No status bar component configured", null);
}
Class<?> cls = null;
try {
cls = mContext.getClassLoader().loadClass(clsName);
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw andLog("Error loading status bar component: " + clsName, t);
}
try {
mStatusBar = (BaseStatusBar) cls.newInstance();
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw andLog("Error creating status bar component: " + clsName, t);
}
mStatusBar.mContext = mContext;
mStatusBar.mComponents = mComponents;
//这里调用mStausBar就是“PhoneStatusBar”实例,并调用start()方法
mStatusBar.start();
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "started " + mStatusBar.getClass().getSimpleName());
}
}
到PhoneStatusBar这里的start
public class PhoneStatusBar extends BaseStatusBar implements DemoMode,
DragDownHelper.DragDownCallback, ActivityStarter, OnUnlockMethodChangedListener,
HeadsUpManager.OnHeadsUpChangedListener {
......
@Override
public void start() {
......
super.start(); // calls createAndAddWindows(),在这里把状态栏的View加到WindowManager,初始化View,顶部状态栏,和底部导航栏
......
addNavigationBar();
// Lastly, call to the icon policy to install/update all the icons.
mIconPolicy = new PhoneStatusBarPolicy(mContext, mCastController, mHotspotController,
mUserInfoController, mBluetoothController);
mIconPolicy.setCurrentUserSetup(mUserSetup);
......
startKeyguard(); //启动屏锁
......
}
......
@Override
public void createAndAddWindows() {
addStatusBarWindow();
}
private void addStatusBarWindow() {
makeStatusBarView();//*-这里先生成View
mStatusBarWindowManager = new StatusBarWindowManager(mContext);
mRemoteInputController = new RemoteInputController(mStatusBarWindowManager,
mHeadsUpManager);
//由这里就可知,无论是锁屏View、导航栏View、通知栏View都是基于这个状态栏ViewGroup
//这样就避免了多个Window层级不好管理,转向好管理的ViewGroup
mStatusBarWindowManager.add(mStatusBarWindow, getStatusBarHeight());//*-在这里加入WindowManager
}
/**
* Adds the status bar view to the window manager.
*
* @param statusBarView The view to add.
* @param barHeight The height of the status bar in collapsed state.
*/
public void add(View statusBarView, int barHeight) {
// Now that the status bar window encompasses the sliding panel and its
// translucent backdrop, the entire thing is made TRANSLUCENT and is
// hardware-accelerated.
mLp = new WindowManager.LayoutParams(
ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT,
barHeight,
WindowManager.LayoutParams.TYPE_STATUS_BAR,
WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_NOT_FOCUSABLE
| WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_TOUCHABLE_WHEN_WAKING
| WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_SPLIT_TOUCH
| WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_WATCH_OUTSIDE_TOUCH
| WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_DRAWS_SYSTEM_BAR_BACKGROUNDS,
PixelFormat.TRANSLUCENT);
mLp.flags |= WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_HARDWARE_ACCELERATED;
mLp.gravity = Gravity.TOP;
mLp.softInputMode = WindowManager.LayoutParams.SOFT_INPUT_ADJUST_RESIZE;
mLp.setTitle("StatusBar");
mLp.packageName = mContext.getPackageName();
mStatusBarView = statusBarView;
mBarHeight = barHeight;
mWindowManager.addView(mStatusBarView, mLp);
mLpChanged = new WindowManager.LayoutParams();
mLpChanged.copyFrom(mLp);
}
//接下来看看锁屏View是怎么出现的
protected void startKeyguard() {
Trace.beginSection("PhoneStatusBar#startKeyguard");
//关注这个类
KeyguardViewMediator keyguardViewMediator = getComponent(KeyguardViewMediator.class);
mFingerprintUnlockController = new FingerprintUnlockController(mContext,
mStatusBarWindowManager, mDozeScrimController, keyguardViewMediator,
mScrimController, this);
//关注这个类
mStatusBarKeyguardViewManager = keyguardViewMediator.registerStatusBar(this,
getBouncerContainer(), mStatusBarWindowManager, mScrimController,
mFingerprintUnlockController);
mKeyguardIndicationController.setStatusBarKeyguardViewManager(
mStatusBarKeyguardViewManager);
mFingerprintUnlockController.setStatusBarKeyguardViewManager(mStatusBarKeyguardViewManager);
mIconPolicy.setStatusBarKeyguardViewManager(mStatusBarKeyguardViewManager);
mRemoteInputController.addCallback(mStatusBarKeyguardViewManager);
mRemoteInputController.addCallback(new RemoteInputController.Callback() {
@Override
public void onRemoteInputSent(Entry entry) {
if (FORCE_REMOTE_INPUT_HISTORY && mKeysKeptForRemoteInput.contains(entry.key)) {
removeNotification(entry.key, null);
} else if (mRemoteInputEntriesToRemoveOnCollapse.contains(entry)) {
// We're currently holding onto this notification, but from the apps point of
// view it is already canceled, so we'll need to cancel it on the apps behalf
// after sending - unless the app posts an update in the mean time, so wait a
// bit.
mHandler.postDelayed(() -> {
if (mRemoteInputEntriesToRemoveOnCollapse.remove(entry)) {
removeNotification(entry.key, null);
}
}, REMOTE_INPUT_KEPT_ENTRY_AUTO_CANCEL_DELAY);
}
}
});
mKeyguardViewMediatorCallback = keyguardViewMediator.getViewMediatorCallback();
mLightStatusBarController.setFingerprintUnlockController(mFingerprintUnlockController);
Trace.endSection();
}
}
StatusBarKeyguardViewManager
public void registerStatusBar(PhoneStatusBar phoneStatusBar,
ViewGroup container, StatusBarWindowManager statusBarWindowManager,
ScrimController scrimController,
FingerprintUnlockController fingerprintUnlockController) {
mPhoneStatusBar = phoneStatusBar;
//注意这个ViewGroup,就是状态栏
mContainer = container;
mStatusBarWindowManager = statusBarWindowManager;
mScrimController = scrimController;
mFingerprintUnlockController = fingerprintUnlockController;
//他把这个ViewGroup继续传递给解锁界面
mBouncer = SystemUIFactory.getInstance().createKeyguardBouncer(mContext,
mViewMediatorCallback, mLockPatternUtils, mStatusBarWindowManager, container);
}
KeyguardBouncer,可以看到锁屏的View是建立在解锁的View上面而解锁的View又是建立在状态栏内
protected void inflateView() {
removeView();
mRoot = (ViewGroup) LayoutInflater.from(mContext).inflate(R.layout.keyguard_bouncer, null);
mKeyguardView = (KeyguardHostView) mRoot.findViewById(R.id.keyguard_host_view);
mKeyguardView.setLockPatternUtils(mLockPatternUtils);
mKeyguardView.setViewMediatorCallback(mCallback);
mContainer.addView(mRoot, mContainer.getChildCount());
mRoot.setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE);
}
锁屏是建立在哪个Context上面的
回顾锁屏启动流程图,从KeyguardService开始,在开启这个服务的时候onCreate方法中获取了一个SystemUIApplication,这个Application是个关键
@Override
public void onCreate() {
((SystemUIApplication) getApplication()).startServicesIfNeeded();
mKeyguardViewMediator =
((SystemUIApplication) getApplication()).getComponent(KeyguardViewMediator.class);
}
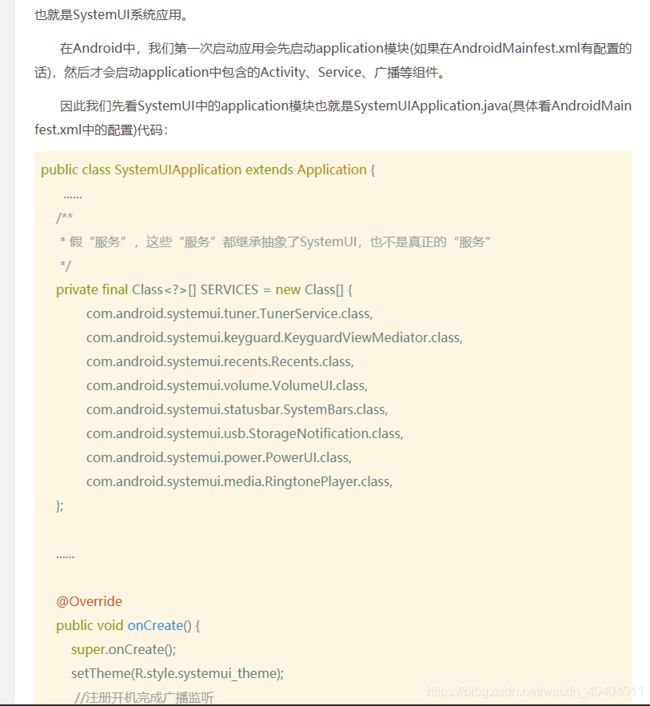
SystemUIApplication
//这里是指与SystemUI有关的类数组
private final Class<?>[] SERVICES = new Class[] {
com.android.systemui.tuner.TunerService.class,
com.android.systemui.keyguard.KeyguardViewMediator.class,
com.android.systemui.recents.Recents.class,
com.android.systemui.volume.VolumeUI.class,
Divider.class,
com.android.systemui.statusbar.SystemBars.class,
com.android.systemui.usb.StorageNotification.class,
com.android.systemui.power.PowerUI.class,
com.android.systemui.media.RingtonePlayer.class,
com.android.systemui.keyboard.KeyboardUI.class,
com.android.systemui.tv.pip.PipUI.class,
com.android.systemui.shortcut.ShortcutKeyDispatcher.class,
com.android.systemui.VendorServices.class
};
/**
* Hold a reference on the stuff we start.
*/
private final SystemUI[] mServices = new SystemUI[SERVICES.length];//SystemUI集合
private boolean mServicesStarted;
private boolean mBootCompleted;
private final Map<Class<?>, Object> mComponents = new HashMap<>();//注意这个HashMap
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
// Set the application theme that is inherited by all services. Note that setting the
// application theme in the manifest does only work for activities. Keep this in sync with
// the theme set there.
setTheme(R.style.systemui_theme);
//这个Application在onCreate的时候把自己的Context传递给了SystemUIFactory,可以说是所有继承了SystemUI的Context的由来
SystemUIFactory.createFromConfig(this);
if (Process.myUserHandle().equals(UserHandle.SYSTEM)) {
IntentFilter filter = new IntentFilter(Intent.ACTION_BOOT_COMPLETED);
filter.setPriority(IntentFilter.SYSTEM_HIGH_PRIORITY);
registerReceiver(new BroadcastReceiver() {
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
if (mBootCompleted) return;
if (DEBUG) Log.v(TAG, "BOOT_COMPLETED received");
unregisterReceiver(this);
mBootCompleted = true;
if (mServicesStarted) {
final int N = mServices.length;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
mServices[i].onBootCompleted();
}
}
}
}, filter);
} else {
// For a secondary user, boot-completed will never be called because it has already
// been broadcasted on startup for the primary SystemUI process. Instead, for
// components which require the SystemUI component to be initialized per-user, we
// start those components now for the current non-system user.
startServicesIfNeeded(SERVICES_PER_USER);
}
}
private void startServicesIfNeeded(Class<?>[] services) {
if (mServicesStarted) {
return;
}
if (!mBootCompleted) {
// check to see if maybe it was already completed long before we began
// see ActivityManagerService.finishBooting()
if ("1".equals(SystemProperties.get("sys.boot_completed"))) {
mBootCompleted = true;
if (DEBUG) Log.v(TAG, "BOOT_COMPLETED was already sent");
}
}
Log.v(TAG, "Starting SystemUI services for user " +
Process.myUserHandle().getIdentifier() + ".");
final int N = services.length;
for (int i=0; i<N; i++) {
Class<?> cl = services[i];
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "loading: " + cl);
try {
//刚刚那个HashMap中的Object在这里统统实例化
Object newService = SystemUIFactory.getInstance().createInstance(cl);
mServices[i] = (SystemUI) ((newService == null) ? cl.newInstance() : newService);
} catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
} catch (InstantiationException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
}
//并且获取了Context
mServices[i].mContext = this;
mServices[i].mComponents = mComponents;
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "running: " + mServices[i]);
mServices[i].start();
if (mBootCompleted) {
mServices[i].onBootCompleted();
}
}
mServicesStarted = true;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T getComponent(Class<T> interfaceType) {
//这就是Service调用的方法,通过类名得到一个已经实例化好了的类,带有Context
return (T) mComponents.get(interfaceType);
}
由于KeyguardService中创建的KeyguardViewMediator得到了解释,现在看KeyguardViewMediator这个类是怎么传递Context的
private void setupLocked() {
mStatusBarKeyguardViewManager =
SystemUIFactory.getInstance().createStatusBarKeyguardViewManager(mContext,
mViewMediatorCallback, mLockPatternUtils);
}
StatusBarKeyguardViewManager,构造方法中得到了Context
public StatusBarKeyguardViewManager(Context context, ViewMediatorCallback callback,
LockPatternUtils lockPatternUtils) {
mContext = context;
mViewMediatorCallback = callback;
mLockPatternUtils = lockPatternUtils;
}
public void registerStatusBar(PhoneStatusBar phoneStatusBar,
ViewGroup container, StatusBarWindowManager statusBarWindowManager,
ScrimController scrimController,
FingerprintUnlockController fingerprintUnlockController) {
mPhoneStatusBar = phoneStatusBar;
mContainer = container;
mStatusBarWindowManager = statusBarWindowManager;
mScrimController = scrimController;
mFingerprintUnlockController = fingerprintUnlockController;
//流程图中的解锁界面同理
mBouncer = SystemUIFactory.getInstance().createKeyguardBouncer(mContext,
mViewMediatorCallback, mLockPatternUtils, mStatusBarWindowManager, container);
}
KeyguardHostView,注意这个类的说明,这是最基本的锁屏View
/**
* Base class for keyguard view. {@link #reset} is where you should
* reset the state of your view. Use the {@link KeyguardViewCallback} via
* {@link #getCallback()} to send information back (such as poking the wake lock,
* or finishing the keyguard).
*
* Handles intercepting of media keys that still work when the keyguard is
* showing.
*/
锁屏的View布局
![]()