系统架构--分布式项目如何实现跨模块调用--初级了解
对于所有的有进取心的crud码农来说,如何完整部署一个项目,或者说一个分布式项目都是一个很有挑战性的任务。
在实际开发中,我们经常是在别人已经搭建好的项目中进行业务开发,完全不需要了解具体的搭建细节,这对于我们技术提升是一个巨大的阻碍。
所以这里我来聊一聊分布式项目搭建的一些细节问题,这里创建的项目
是按企业中实际开发的架构来作为依据,所以不会过于简洁的。。。。
注意:本文适合不了解分布式开发的小白,讲的会比较杂。
1.如何使各模块间可以互相调用
①首先,第一步是需要创建一个父项目(Maven创建,空项目就好)
②删除父项目中的src,并创建4个子项目,如下图

以上的四个子项目也是空项目,删除src目录
③上述的四个项目都有其功能,其中:
api模块
是用于后端各个模块之间互相提供接口调用,专业一点就是存放"feign接口"
common模块
是公共模块,主要存放的是一些规范和封装的一些基本功能,比如会封装一些方法如:获取当前访问项目的用户名和用户编号(我目前所做的模块就经常用到这个封装的方法,贼好用),或者是封装生成uuid的方法,所有模块生成主键id都是调用这个方法,形成规范等(可惜我目前的的项目没用上这个方法,直接用Mybatis-plus的IdWork.getId()方法,比这封装的方法好用)
该模块还可以用于存放依赖,所有依赖都可以放在common中。
service模块和web模块
可以当做是不同的功能模块吧,基本上每一个分布式后端项目都会有api和common模块,额,大概率还会有auth权限模块和getway网关模块,这里没有添加上这两个模块,无伤大雅。然后再搭配几个功能模块就组成了一个完整的分布式项目了。
④以上四个模块都是空模块,也就是作为一个存放实际模块的包,或者说是壳子。所以接下来就要在四个空模块中创建实际开发的模块了。如下图

⑤正常来说,有多少个业务模块,就要在api模块中创建多少个对应的模块,比如在这个项目中,service和web作为功能模块,他们下面分别有product和background业务模块,所以在api中就要创建对应的模块。
⑥模块创建完成了,接下来就是最最关键的pom.xml文件的处理了,这也是构建分布式项目的真正难点
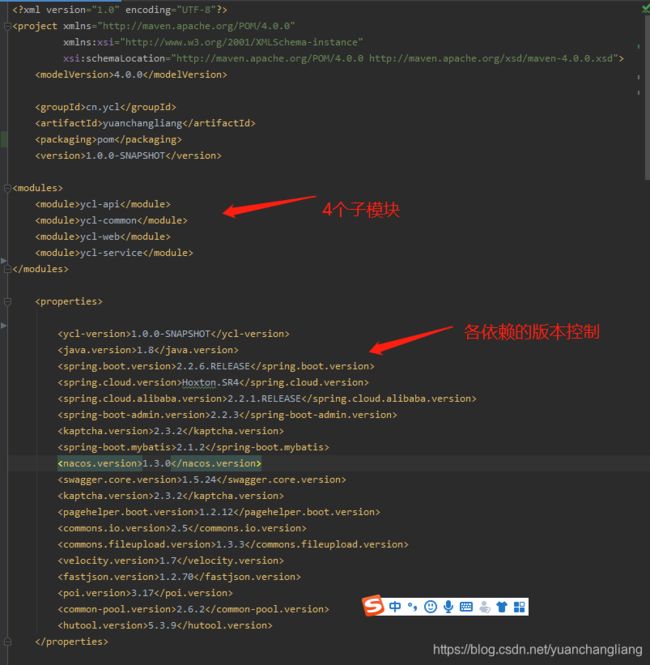
yuanchangliang模块是父项目,它的职责就是对所有依赖进行版本控制,防止出现各个模块间使用不同版本的相同依赖的情况,造成依赖冲突,pom.xml
文件如下:
由于pom文件太长了,大家应该不会去看,不够友好,我就分批次来讲吧,顺便讲解一下各个标签的作用
第一部分
以上图片中models标签,是用于表示该父模块有4个子模块
properties标签,则是用于在pom.xml中设置参数用的,我们可以看到每一行都标识着一个版本号,这里的内容要搭配下图一起看
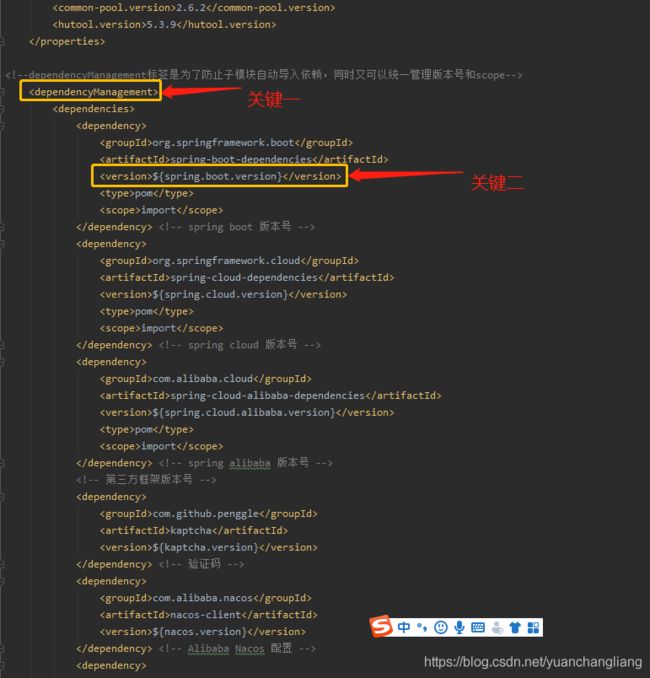
第二部分
我们先看图中的关键二,在每个依赖中,版本号都是用标识符代替(类似于mybatis中的占位符吧),再联系第一部分中的properties标签,就能够对依赖的版本进行集中控制了
关键一中,dependencyManagement标签的作用就是子项目中无法自动引入父项目的被dependencyManagement标签包裹的依赖,只能够主动引入,只不过不需要写版本号和scope了,这样就可以协助实现版本号管理了,如随便在子项目中找一个依赖
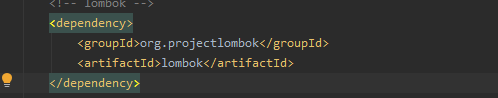
只需要groupId标签和artifactId标签
⑦接下来就是子项目的pom.xml文件中的依赖了,也是跨模块调用的关键了
在子模块中,都需要声明其父项目,也就是需要用到大家比较熟悉的parent标签
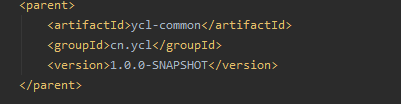
我们需要在除了yuanchangliang父项目外的所有其他模块中申明其父类,而parent标签的作用就是表示子类会完全继承父类中所有的,没有被dependencyManagement标签所包裹的依赖。
举个例子,我习惯把所有核心依赖放在common-core模块中(见上文中的项目架构图),如下为common-core模块中的pom文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<artifactId>ycl-common</artifactId>
<groupId>cn.ycl</groupId>
<version>1.0.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</parent>
<artifactId>ycl-common-core</artifactId>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeign</artifactId>
</dependency> <!-- SpringCloud Openfeign -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context-support</artifactId>
</dependency> <!-- Spring Context Support -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-web</artifactId>
</dependency> <!-- Spring Web -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-pool2</artifactId>
</dependency> <!-- Apache Commons Pool2 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.pagehelper</groupId>
<artifactId>pagehelper-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency> <!-- Pagehelper -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.validation</groupId>
<artifactId>validation-api</artifactId>
</dependency> <!-- Java Validation -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
</dependency> <!-- Jackson -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
</dependency> <!-- Alibaba Fastjson -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-lang3</artifactId>
</dependency> <!-- Apache Lang3 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-io</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-io</artifactId>
</dependency> <!-- Commons Io -->
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-fileupload</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-fileupload</artifactId>
</dependency> <!-- Commons Fileupload -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId>
<artifactId>poi-ooxml</artifactId>
</dependency> <!-- excel工具 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
</dependency> <!-- Java Servlet -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.swagger</groupId>
<artifactId>swagger-annotations</artifactId>
</dependency> <!-- Swagger -->
<dependency>
<groupId>net.logstash.logback</groupId>
<artifactId>logstash-logback-encoder</artifactId>
<version>5.1</version>
</dependency>
<!-- mybatis-plus begin -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.2.0</version>
</dependency>
<!-- lombok -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- hutool -->
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.hutool</groupId>
<artifactId>hutool-all</artifactId>
<version>5.3.9</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<source>8</source>
<target>8</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
我们只需要在功能模块中引入common-core的依赖即可,功能模块是以下两个:
![]()
![]()
引入common-core的依赖(自定义的依赖)
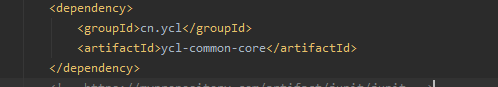
只需要引入该模块的依赖,
就可以跨模块调用common-core中的类和接口
所以就引出了实现跨模块调用的真相了,引入对应模块的依赖就可以实现跨模块调用了!!!
原来依赖还可以自定义?是的。
⑧实际项目中是如何调用其他模块的接口的?
(ps,我刚开始工作的时候,对接口特别迷茫?啥叫提供接口啊?啥叫feign接口啊?我该怎么提供接口给其他模块的后端开发人员使用啊?完全是三脸懵逼)
调用其他模块的接口都是统一通过api模块的,项目中的功能模块,在api模块中,都会有对应的api模块用于提供feign接口
举个例子:ycl-web-background模块中的申报合同接口,如下:
/**
* 申报合同
* @param info 前端填写的申报数据
* @return 请求的url返回值
*/
@PreAuthorize("@ss.hasPermi('contract:contract:declareContract')")
@Log(title = "合同--申报合同", businessType = BusinessType.INSERT)
@PostMapping("/declareContract")
public R<Object> declare(@RequestBody String info) {
return contractInfoServiceImpl.declareContract(info);
}
额,可能大家不太了解@PreAuthorize注解和@Log注解,其中PreAuthorize是用于给前端的页面权限(如果我不给他配权限,前端页面甚至无法看到申报合同的按钮),@Log注解是用于记录操作日志,是我们项目自定义的日志注解
把无用的注解去掉,就是我们熟悉的controller了,看
@PostMapping("/declareContract")
public R<Object> declare(@RequestBody String info) {
return contractInfoServiceImpl.declareContract(info);
}
ycl-service-product功能模块中,需要调用ycl-web-background模块中的申报合同接口,肯定是不能直接调用的,必须通过api中的feign接口。
然后我们在ycl-api-background模块,中的RemotePriceService文件中提供接口,目录如下
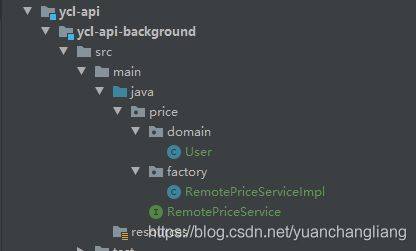
RemotePriceService中代码如下:
/**
* 合同接口
* @author ycl
*/
@FeignClient(
contextId = "remoteContractService",
value = ServiceNameConstants.SYSTEM_EXTEND,
fallbackFactory = RemoteContractFallbackFactory.class
)
public interface RemoteContractService {
/**
* 申报合同
*
* @param info 前端填写的申报数据
* @return 请求的url返回值
*/
@PostMapping("/contract/declareContract")
public R<Object> declare(@RequestBody String info);
}
RemotePriceService的实现类RemotePriceServiceImpl代码如下:
/**
*
* @author ycl
*/
public class RemoteContractFallbackFactory implements FallbackFactory<RemoteContractService> {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(RemoteContractFallbackFactory.class);
@Override
public RemoteContractService create(Throwable throwable) {
log.error("合同接口服务调用失败:{}", throwable.getMessage());
return new RemoteContractService(){
/**
* 申报合同
*
* @param info 前端填写的申报数据
* @return 请求的url返回值
*/
@Override
public R<Object> declare(String info) {
return null;
}
}
以上就是提供接口的过程了,接下来是ycl-service-product功能模块调用接口
ycl-service-product功能模块调用只需要两步:
①在pom中引入ycl-api-background依赖(添加方式见上文)
②在页面中注入RemotePriceService接口,如:
@AutoWired
RemotePriceService remotePriceService ;
然后调用申报合同接口:
remotePriceService .declare();
这样就是规范的跨模块调用接口了
总结:所以接口就是一个controller而已,不过是给其他模块调用的时候叫接口而已,至于为什么叫feign接口,因为在api模块中必须要有feign依赖而已,是通过feign实现的,如在RemotePriceService中的
@FeignClient(
contextId = "remoteContractService",
value = ServiceNameConstants.SYSTEM_EXTEND,
fallbackFactory = RemoteContractFallbackFactory.class
)
就这样了,写的不好,思路还是有点乱,将就着看吧,可以给我建议,但是别骂我,谢谢
-----我是“道祖且长”,一个在互联网苟且偷生的Java程序员