参数赋值方式
1.属性驱动
public class LoginAction {
private String username;
private String password;
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
}
2.定义一个对象
public class LoginAction {
private User user;
public User getUser() {
return user;
}
public void setUser(User user) {
this.user = user;
}
}
3.模型驱动
public class LoginAction implements ModelDriven {
private User user=new User();
public User getModel() {
return user;
}
}
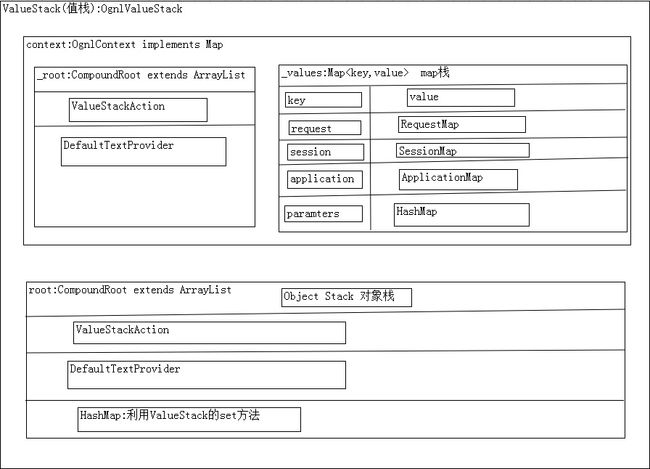
Value Stack
概念
ValueStack是一个接口
OgnlValueStack是ValueStack接口的默认实现类。
用途
可以作为一个数据中转站。
用于在前台-后台之间传递数据。
生命周期
ValueStack的生命周期随着request的创建而创建,随着request的销毁而销毁
在PrepareOperations类的createActionContext中创建,cleanupRequest中清理
/**
* Creates the action context and initializes the thread local
*/
public ActionContext createActionContext(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
ActionContext ctx;
Integer counter = 1;
Integer oldCounter = (Integer) request.getAttribute(CLEANUP_RECURSION_COUNTER);
if (oldCounter != null) {
counter = oldCounter + 1;
}
ActionContext oldContext = ActionContext.getContext();
if (oldContext != null) {
// detected existing context, so we are probably in a forward
ctx = new ActionContext(new HashMap(oldContext.getContextMap()));
} else {
//------创建ValueStack-------
ValueStack stack = dispatcher.getContainer().getInstance(ValueStackFactory.class).createValueStack();
stack.getContext().putAll(dispatcher.createContextMap(request, response, null, servletContext));
ctx = new ActionContext(stack.getContext());
}
request.setAttribute(CLEANUP_RECURSION_COUNTER, counter);
ActionContext.setContext(ctx);
return ctx;
}
结构
在OgnlValueStack中有两个至关重要的东西,简称“对象栈”和“Map栈”。
CompoundRoot root;
transient Map context;
对象栈的说明:1.处于对象栈中的对象,它的属性是可以直接访问的。2.如果在对象栈中有相同名称的属性,那么从栈顶开始查找,直到找到为止。3.一般情况下回显的数据应该放在对象栈中,这样效率比较高。4.用Ognl表达式访问对象栈,直接属性名称就可以了,不用加#。
map栈的说明:1.request,session,application都在map栈中。2.可以把一个对象放到map中。3.Ognl表达式访问map栈中的内容:如果一个对象在map中,那么就是#request.对象的key值.属性; 如果一个对象直接放入到map中,那么就是#对象的key值.属性。注意:把一个对象放到map栈中,你是不能直接访问这个对象的属性的。
ModelDriven
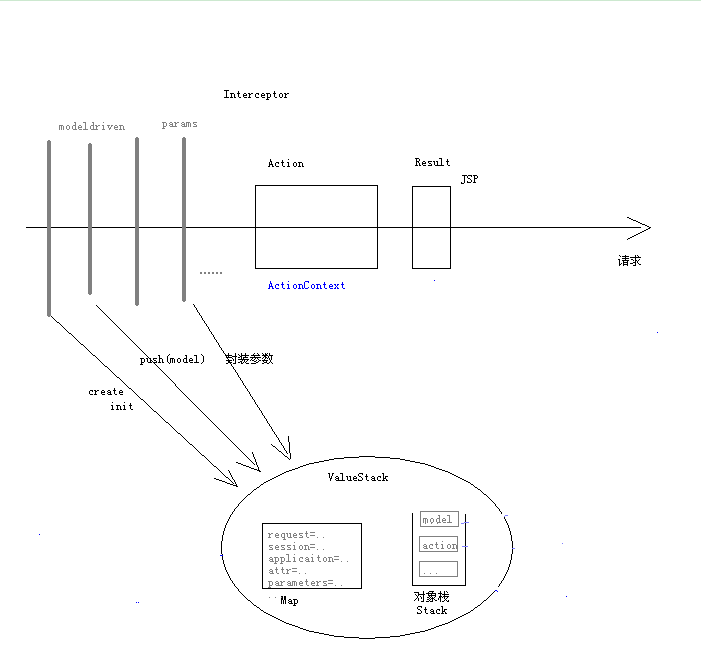
ModelDriven背后的机制就是ValueStack。界面通过username、password这样的名称,就能够被直接赋值给user对象。
那么,为什么user对象会在ValueStack中呢?它是什么时候被压入ValueStack的呢?
答案是:ModelDrivenInterceptor。
ModelDrivenInterceptor是缺省的拦截器链的一部分,当一个请求经过ModelDrivenInterceptor的时候,在这个拦截器中,会判断当前要调用的Action对象是否实现了ModelDriven接口,如果实现了这个接口,则调用getModel()方法,并把返回值(本例是返回user对象)压入ValueStack。
public String intercept(ActionInvocation invocation) throws Exception {
Object action = invocation.getAction();
if (action instanceof ModelDriven) {
ModelDriven modelDriven = (ModelDriven) action;
ValueStack stack = invocation.getStack();
Object model = modelDriven.getModel();
if (model != null) {
//放入栈中
stack.push(model);
}
if (refreshModelBeforeResult) {
invocation.addPreResultListener(new RefreshModelBeforeResult(modelDriven, model));
}
}
return invocation.invoke();
}
如何赋值
Struts2有个params拦截器(ParametersInterceptor),它是在调用你的LogonAction之前调用的,它会把request里面的参数(就是jsp页面上传递过来的那些值)取出来,去跟LogonAction里面的变量匹配,匹配到了就set进去,这里匹配是以setXXX方法为基准的。
比如jsp页面上有个userName参数,拦截器就去LogonAction里面找setUserName()方法,找到了就把userName参数的值传递到setUserName()方法里面,setUserName()方法再把值赋给LogonAction里面的userName变量(这个名字随便是什么都行,因为拦截器只认setUserName()方法)。
如果jsp页面上有个user.userName参数,拦截器就去LogonAction里面找setUser()方法,当然setUser()方法的参数就是一个User对象,所以拦截器会new一个User对象给这个setUser()方法,接着拦截器会到User对象中找setUserName()方法,并将user.userName参数的值传递给这个setUserName()方法。
流程图
赋值方法
(1)向map栈中存数据,即ValueStack中的context(OgnlContext)
ServletActionContext.getRequest().setAttribute("key","value");
ServletActionContext.getSession().put("key","value");通过request,session等向map中存储数据
ActionContext.getContext().put("key","value"); 直接向map栈中放数据,通过JSONResult返回json格式的数据时可以使用这种方式赋值
@Action(value = "json", results = {@Result(type = "json", params = {"root", "result"})})
public String queryFlowProject() {
JSONArray result = new JSONArray();
ServletActionContext.getContext().put("result", result);
return "success";
}
(2)向对象栈中存数据,即ValueStack中的root(CompoundRoot)对象
ValueStack valueStack = ActionContext.getContext().getValueStack();
valueStack.getRoot().add(new Object());先得到root,再把数据压入到root中,这中方式是放入到栈底.
ValueStack valueStack = ActionContext.getContext().getValueStack();
valueStack.getRoot().add(0,new Object());//这里0,表示压入栈顶.先得到root,利用add(index,Object)把一个对象压入到root中指定位置.
ValueStack valueStack = ActionContext.getContext().getValueStack();
valueStack.set("key","value");//先New一个Map,再调用push方法把Map放入到对象栈中,且放入栈顶.存放一个map到对象栈中
ValueStack valueStack = ActionContext.getContext().getValueStack();
valueStack.push(new Object());利用valueStack的push方法把一个对象直接压入栈顶