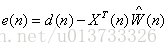机器学习第5章第2节 : LMS算法
- LMS算法-逻辑或运算
- 思路
- 代码
- 运行结果
- LMS算法-二值分类
- 思路
- 代码
- 运行结果
LMS算法-逻辑或运算
思路
LMS算法全称为
least mean square算法,中文名叫最小均方算法.在ANN领域,均方误差是指样本预测输出值与实际输出值只差的平方的期望值,记为MSE.设observed为样本真值,predicted为预测值,计算公式如下:
LMS的算法策略是使均方误差最小,该算法运行在一个线性神经元上,使用的是批量修正算法,其误差信号为:
最后,生成权值调整方案,公式如下:
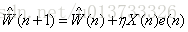
在上面的公式中,η代表学习率,该值越小,LMS算法执行的越精确,但同时算法的收敛速度越慢.
代码
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Thu Dec 7 14:06:09 2017
@author: Oscar
LMS算法实现逻辑或运算
"""
import numpy as np
#学习速率
learn_speed = 0.1
#偏置
b = 1
#学习的数据
x = np.array([
[1,1,1],
[1,1,0],
[1,0,1],
[1,0,0]
])
#期望输出,对应的是学习数据的真假
d = np.array([1,1,1,0])
#权值
weight = np.array([b,0,0])
#最小误差信号值
min_error_signal = 0.005
#最大学习次数
max_try_count = 20
#感知函数
def sgn(v):
if v > 0:
return 1
else:
return 0
#拿到感知器的返回值
def get_sgn(current_weight,current_x):
#当前权值矩阵转置后与当前的学习的数据进行矩阵相乘,得到一个实数,然后调用sgn函数得到感知器的返回值
return sgn(np.dot(current_weight.T,current_x))
#获取误差信号
def get_error_signal(current_weight,current_x,current_d):
return current_d - get_sgn(current_weight,current_x)
#权值更新
def update_weight(old_weight,current_d,current_x,learn_speed):
current_error_signal = get_error_signal(old_weight,current_x,current_d)
return (old_weight + learn_speed * current_error_signal * current_x,current_error_signal)
#当前重复的次数
current_count = 0
while True:
error_signal = 0
i = 0
for xn in x:
weight , current_error_signal = update_weight(weight,d[i],xn,learn_speed)
i += 1
#pow() 方法返回 xy(x的y次方) 的值。
error_signal += pow(current_error_signal,2)
error_signal /= float(i)
current_count += 1
print("第",current_count,"次调整后的权值为:",weight," 误差信号值为:",error_signal)
#当当前的误差信号值精度小于最小的误差信号值精度的时候
#或者当调整次数大于最大的调整次数的时候
#跳出循环
if error_signal < min_error_signal or current_count > max_try_count : break
#训练完成,开始检验
for xn in x:
print("当前数据:",xn,",当前分类:",xn[1],"与",xn[2],"进行逻辑或运算,被分类为:",get_sgn(weight,xn))运行结果
第 1 次调整后的权值为: [ 0.9 0. 0. ] 误差信号值为: 0.25
第 2 次调整后的权值为: [ 0.8 0. 0. ] 误差信号值为: 0.25
第 3 次调整后的权值为: [ 0.7 0. 0. ] 误差信号值为: 0.25
第 4 次调整后的权值为: [ 0.6 0. 0. ] 误差信号值为: 0.25
第 5 次调整后的权值为: [ 0.5 0. 0. ] 误差信号值为: 0.25
第 6 次调整后的权值为: [ 0.4 0. 0. ] 误差信号值为: 0.25
第 7 次调整后的权值为: [ 0.3 0. 0. ] 误差信号值为: 0.25
第 8 次调整后的权值为: [ 0.2 0. 0. ] 误差信号值为: 0.25
第 9 次调整后的权值为: [ 0.1 0. 0. ] 误差信号值为: 0.25
第 10 次调整后的权值为: [ 1.38777878e-16 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00] 误差信号值为: 0.25
第 11 次调整后的权值为: [-0.1 0. 0. ] 误差信号值为: 0.25
第 12 次调整后的权值为: [-0.1 0.1 0.1] 误差信号值为: 0.5
第 13 次调整后的权值为: [-0.1 0.1 0.1] 误差信号值为: 0.0
当前数据: [1 1 1] ,当前分类: 1 与 1 进行逻辑或运算,被分类为: 1
当前数据: [1 1 0] ,当前分类: 1 与 0 进行逻辑或运算,被分类为: 1
当前数据: [1 0 1] ,当前分类: 0 与 1 进行逻辑或运算,被分类为: 1
当前数据: [1 0 0] ,当前分类: 0 与 0 进行逻辑或运算,被分类为: 0LMS算法-二值分类
思路
应用LMS算法实现比逻辑或更复杂的算法,比如:在输入矩阵中,如果x向量的整除结果为6,则表示一类,输出为1;如果整除结果为3,则表示另一类,输出为-1.
代码
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Thu Dec 7 15:17:13 2017
@author: Oscar
使用LMS算法实现在输入矩阵中,如果x向量的整除结果为6,则表示一类,输出为1;
如果整除结果为3,则表示另一类,输出为-1.
"""
import numpy as np
#学习速率
learn_speed = 0.1
#偏置
b = 1
#学习的数据
x = np.array([
[1,1,6], #1
[1,2,12], #1
[1,3,9], #-1
[1,8,24] #-1
])
#测试数据
test_data1 = np.array([1,9,27]) #-1
test_data2 = np.array([1,11,66])#1
#期望输出,对应的是学习数据的真假
d = np.array([1,1,-1,-1])
#权值
weight = np.array([b,0,0])
#最小误差信号值
min_error_signal = 0.005
#最大学习次数
max_try_count = 20
#感知函数
def sgn(v):
if v > 0:
return 1
else:
return -1
#拿到感知器的返回值
def get_sgn(current_weight,current_x):
#当前权值矩阵转置后与当前的学习的数据进行矩阵相乘,得到一个实数,然后调用sgn函数得到感知器的返回值
return sgn(np.dot(current_weight.T,current_x))
#获取误差信号值
def get_error_signal(current_weight,current_x,current_d):
return current_d - get_sgn(current_weight,current_x)
#权值更新
def update_weight(old_weight,current_d,current_x,learn_speed):
current_error_signal = get_error_signal(old_weight,current_x,current_d)
return (old_weight + learn_speed * current_error_signal * current_x,current_error_signal)
#当前重复的次数
current_count = 0
while True:
error_signal = 0
i = 0
for xn in x:
weight , current_error_signal = update_weight(weight,d[i],xn,learn_speed)
i += 1
#pow() 方法返回 xy(x的y次方) 的值。
error_signal += pow(current_error_signal,2)
error_signal /= float(i)
current_count += 1
print("第",current_count,"次调整后的权值为:",weight," 误差信号值为:",error_signal)
#当当前的误差信号值精度小于最小的误差信号值精度的时候
#或者当调整次数大于最大的调整次数的时候
#跳出循环
if abs(error_signal) < min_error_signal or current_count > max_try_count : break
#训练完成,开始检验
for xn in x:
print("当前数据:",xn,",当前分类:",xn[1],"与",xn[2],"进行分类,被分类为:",get_sgn(weight,xn))
#开始测试
print("测试数据为:",test_data1,",被分类为:",get_sgn(weight,test_data1))
print("测试数据为:",test_data2,",被分类为:",get_sgn(weight,test_data2))运行结果
第 1 次调整后的权值为: [ 0.8 -0.6 -1.8] 误差信号值为: 1.0
第 2 次调整后的权值为: [ 1.00000000e+00 -6.00000000e-01 4.44089210e-16] 误差信号值为: 3.0
第 3 次调整后的权值为: [ 0.8 -2.4 -4.2] 误差信号值为: 3.0
第 4 次调整后的权值为: [ 1.2 -1.8 -0.6] 误差信号值为: 2.0
第 5 次调整后的权值为: [ 1.2 -2.2 -1.2] 误差信号值为: 2.0
第 6 次调整后的权值为: [ 1.4 -2.2 0.6] 误差信号值为: 3.0
第 7 次调整后的权值为: [ 1.2 -2.8 -1.2] 误差信号值为: 1.0
第 8 次调整后的权值为: [ 1.4 -2.8 0.6] 误差信号值为: 3.0
第 9 次调整后的权值为: [ 1.4 -2.8 0.6] 误差信号值为: 0.0
当前数据: [1 1 6] ,当前分类: 1 与 6 进行分类,被分类为: 1
当前数据: [ 1 2 12] ,当前分类: 2 与 12 进行分类,被分类为: 1
当前数据: [1 3 9] ,当前分类: 3 与 9 进行分类,被分类为: -1
当前数据: [ 1 8 24] ,当前分类: 8 与 24 进行分类,被分类为: -1
测试数据为: [ 1 9 27] ,被分类为: -1
测试数据为: [ 1 11 66] ,被分类为: 1