HDU2454 图的基本性质
Degree Sequence of Graph G
Time Limit: 5000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 1123 Accepted Submission(s): 437
Problem Description
Wang Haiyang is a strong and optimistic Chinese youngster. Although born and brought up in the northern inland city Harbin, he has deep love and yearns for the boundless oceans. After graduation, he came to a coastal city and got a job in a marine transportation company. There, he held a position as a navigator in a freighter and began his new life.
The cargo vessel, Wang Haiyang worked on, sails among 6 ports between which exist 9 routes. At the first sight of his navigation chart, the 6 ports and 9 routes on it reminded him of Graph Theory that he studied in class at university. In the way that Leonhard Euler solved The Seven Bridges of Knoigsberg, Wang Haiyang regarded the navigation chart as a graph of Graph Theory. He considered the 6 ports as 6 nodes and 9 routes as 9 edges of the graph. The graph is illustrated as below.
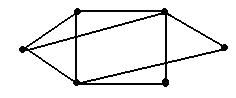
According to Graph Theory, the number of edges related to a node is defined as Degree number of this node.
Wang Haiyang looked at the graph and thought, If arranged, the Degree numbers of all nodes of graph G can form such a sequence: 4, 4, 3,3,2,2, which is called the degree sequence of the graph. Of course, the degree sequence of any simple graph (according to Graph Theory, a graph without any parallel edge or ring is a simple graph) is a non-negative integer sequence?
Wang Haiyang is a thoughtful person and tends to think deeply over any scientific problem that grabs his interest. So as usual, he also gave this problem further thought, As we know, any a simple graph always corresponds with a non-negative integer sequence. But whether a non-negative integer sequence always corresponds with the degree sequence of a simple graph? That is, if given a non-negative integer sequence, are we sure that we can draw a simple graph according to it.?
Let's put forward such a definition: provided that a non-negative integer sequence is the degree sequence of a graph without any parallel edge or ring, that is, a simple graph, the sequence is draw-possible, otherwise, non-draw-possible. Now the problem faced with Wang Haiyang is how to test whether a non-negative integer sequence is draw-possible or not. Since Wang Haiyang hasn't studied Algorithm Design course, it is difficult for him to solve such a problem. Can you help him?
The cargo vessel, Wang Haiyang worked on, sails among 6 ports between which exist 9 routes. At the first sight of his navigation chart, the 6 ports and 9 routes on it reminded him of Graph Theory that he studied in class at university. In the way that Leonhard Euler solved The Seven Bridges of Knoigsberg, Wang Haiyang regarded the navigation chart as a graph of Graph Theory. He considered the 6 ports as 6 nodes and 9 routes as 9 edges of the graph. The graph is illustrated as below.

According to Graph Theory, the number of edges related to a node is defined as Degree number of this node.
Wang Haiyang looked at the graph and thought, If arranged, the Degree numbers of all nodes of graph G can form such a sequence: 4, 4, 3,3,2,2, which is called the degree sequence of the graph. Of course, the degree sequence of any simple graph (according to Graph Theory, a graph without any parallel edge or ring is a simple graph) is a non-negative integer sequence?
Wang Haiyang is a thoughtful person and tends to think deeply over any scientific problem that grabs his interest. So as usual, he also gave this problem further thought, As we know, any a simple graph always corresponds with a non-negative integer sequence. But whether a non-negative integer sequence always corresponds with the degree sequence of a simple graph? That is, if given a non-negative integer sequence, are we sure that we can draw a simple graph according to it.?
Let's put forward such a definition: provided that a non-negative integer sequence is the degree sequence of a graph without any parallel edge or ring, that is, a simple graph, the sequence is draw-possible, otherwise, non-draw-possible. Now the problem faced with Wang Haiyang is how to test whether a non-negative integer sequence is draw-possible or not. Since Wang Haiyang hasn't studied Algorithm Design course, it is difficult for him to solve such a problem. Can you help him?
Input
The first line of input contains an integer T, indicates the number of test cases. In each case, there are n+1 numbers; first is an integer n (n<1000), which indicates there are n integers in the sequence; then follow n integers, which indicate the numbers of the degree sequence.
Output
For each case, the answer should be "yes"or "no" indicating this case is "draw-possible" or "non-draw-possible"
Sample Input
2 6 4 4 3 3 2 2 4 2 1 1 1
Sample Output
yes no
Source
2008 Asia Regional Harbin
Recommend
gaojie
题解:上课老师说给出结点的度 能否判断这个图是否为简单图 然后说了这道题 回来顺便给A了 首先能构成简单图 各个节点的度
相加是偶数 然后利用贪心不断对数组存储的度更新 比如 4 4 3 3 2 2 a[0]=4,利用性质更新 a[1]-1=3, a[2]-1=2,a[3]-1=2,a[4]-1=1, 最
后a[0]=0;再次排序 如果数组出现负数 那么直接跳出循环 证明不是简单图 如果a[0]=0 证明数组里都为0 此时可以判断是简单图
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int cmp(int a ,int b)
{
return a>b;
}
int main()
{
int t,n,a[1001];
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--)
{
memset(a,0,sizeof(a));
int sum=0;
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=0; i