算法之分治法解决平面最近点对问题
问题描述:
给定平面上n个点,找其中的一对点,使得在n个点的所有点对中,该点对的距离最小。严格地说,最接近点对可能多于1对。为了简单起见,这里只限于找其中的一对。
思路:
设S中的点为平面上的点,它们都有2个坐标值x和y。为了将平面上点集S线性分割为大小大致相等的2个子集S1和S2,我们选取一垂直线l:x=m来作为分割直线。其中m为S中各点x坐标的中位数。由此将S分割为S1={p∈S|px≤m}和S2={p∈S|px>m}。从而使S1和S2分别位于直线l的左侧和右侧,且S=S1∪S2 。
由于m是S中各点x坐标值的中位数,因此S1和S2中的点数大致相等。递归地在S1和S2上解最接近点对问题,我们分别得到S1和S2中的最小距离d1和d2。现设d=min(d1,d2)。若S的最接近点对(p,q)之间的距离d(p,q)
P1中所有点与P2中所有点构成的点对均为最接近点对的候选者。在最坏情况下有n2/4对这样的候选者。但是P1和P2中的点具有以下的稀疏性质,它使我们不必检查所有这n^2/4对候选者。考虑P1中任意一点p,它若与P2中的点q构成最接近点对的候选者,则必有d(p,q)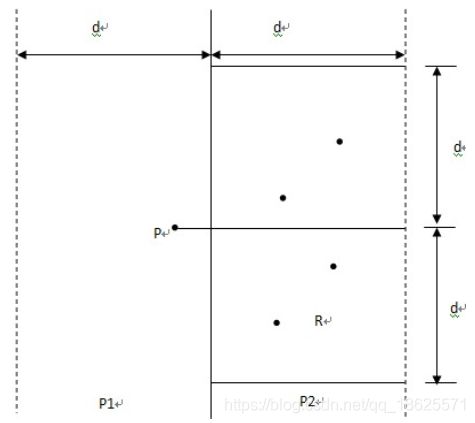
因此,若将P1和P2中所有S的点按其y坐标排好序,则对P1中所有点p,对排好序的点列作一次扫描,就可以找出所有最接近点对的候选者,对P1中每一点最多只要检查P2中排好序的相继6个点。
//用类PointX和PointY表示依x坐标和y坐标排好序的点
class PointX {
public:
int operator<=(PointX a)const
{ return (x<=a.x); }
int ID; //点编号
float x,y; //点坐标
};
class PointY {
public:
int operator<=(PointY a)const
{ return(y<=a.y); }
int p; //同一点在数组x中的坐标
float x,y; //点坐标
};
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
const int M=50;
float Random();
template
float dis(const Type&u,const Type&v);
bool Cpair2(PointX X[], int n,PointX& a,PointX& b, float& d);
void closest(PointX X[],PointY Y[],PointY Z[], int l, int r,PointX& a,PointX& b,float& d);
template
void Copy(Type a[],Type b[], int left,int right);
template
void Merge(Type c[],Type d[],int l,int m,int r);
template
void MergeSort(Type a[],Type b[],int left,int right);
int main()
{
srand((unsigned)time(0));
int length;
cout<<"请输入点对数:";
cin>>length;
PointX X[M];
cout<<"随机生成的二维点对为:"<
inline float dis(const Type& u,const Type& v)
{
float dx=u.x-v.x;
float dy=u.y-v.y;
return sqrt(dx*dx+dy*dy);
}
bool Cpair2(PointX X[], int n,PointX& a,PointX& b,float& d)
{
if(n<2) return false;
PointX* tmpX = new PointX[n];
MergeSort(X,tmpX,0,n-1);
PointY* Y=new PointY[n];
for(int i=0;im) Z[g++]=Y[i];
else Z[f++]=Y[i];
}
closest(X,Z,Y,l,m,a,b,d);
float dr;
PointX ar,br;
closest(X,Z,Y,m+1,r,ar,br,dr);
if(dr
void Merge(Type c[],Type d[],int l,int m,int r)
{
int i = l,j = m + 1,k = l;
while((i<=m)&&(j<=r))
{
if(c[i]<=c[j])
{
d[k++] = c[i++];
}
else
{
d[k++] = c[j++];
}
}
if(i>m)
{
for(int q=j; q<=r; q++)
{
d[k++] = c[q];
}
}
else
{
for(int q=i; q<=m; q++)
{
d[k++] = c[q];
}
}
}
template
void MergeSort(Type a[],Type b[],int left,int right)
{
if(left
void Copy(Type a[],Type b[], int left,int right)
{
for(int i=left;i<=right;i++)
a[i]=b[i];
}