Thread.join()方法源码分析
在JDK中Thread.join()的底层是调用了其中的
public final synchronized void join(long millis)这个方法的,看看此方法的源码作者的英文解释:
/**
* Waits at most {@code millis} milliseconds for this thread to
* die. A timeout of {@code 0} means to wait forever.
*
* This implementation uses a loop of {@code this.wait} calls
* conditioned on {@code this.isAlive}. As a thread terminates the
* {@code this.notifyAll} method is invoked. It is recommended that
* applications not use {@code wait}, {@code notify}, or
* {@code notifyAll} on {@code Thread} instances.
这段英文翻译过来就是让当前线程等待至多mills毫秒再接着执行。注意这段英文如果只看源码的注释很是晦涩难懂,但是如果我在原来注释的基础上加上几个被作者省略的内容后就变得好懂了。
改动后:
* Waits at most {@code millis} milliseconds for this thread to
* die. A timeout of {@code 0} means to wait forever unless some other
* thread stop the situation.
*
* This implementation uses a loop of {@code this.wait} calls
* conditioned on {@code this.isAlive}.
* As a thread terminates the {@code this.notifyAll} method is invoked. It is
* recommended that
* applications not use {@code wait}, {@code notify}, or
* {@code notifyAll} on {@code Thread} instances.
现在就好懂多了:当前线程会在原地等待至多 millis 毫秒,然后就会接着执行join()方法之后的代码。如果 millis 的值为0,则此线程(当前线程)会永远的等待下去直到另外的线程改变这个状态。
通过源码可知 Thread.join()方法内部实际的执行逻辑是Thread类的
public final synchronized void join(long millis)方法。这个方法依靠while循环去持续不断的对millis进行判断,底层还是使用了 wait():
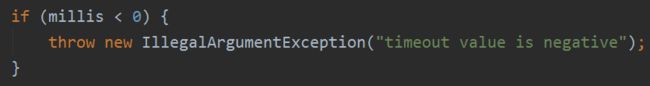
- 如果 millis 的值为负,直接抛异常;
- 如果 millis 值为0,则会判断当前线程是不是还在活跃状态,如果当前线程依然活跃就执行 wait(0),即让当前线程等待下去,直到有某个线程跳出来改变这个状态;
-
if (millis == 0) { while (isAlive()) { wait(0); } - 如果 millis 值为正数,会计算出当前线程会被耽搁的时间 delay,然后会在底层调用 wait(delay):
while (isAlive()) {
long delay = millis - now;
if (delay <= 0) {
break;
}
wait(delay);
now = System.currentTimeMillis() - base;
}换句话说就是 Thread.join() 的作用是让当前调用 Thread.join() 的线程的执行过程暂时中断等待被 join 的线程执行完毕再接着执行 剩下的代码。
下面是代码验证:
首先定义一个 ThreadB类,此类会在各个关键节点打印一些信息。
public class ThreadB extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("开始执行-->"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"的 run 方法");
for (int i=0;i<10;i++){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" for循环--> "+i);
try {
//System.out.println("线程-->"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"休眠1秒");
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("异常来自"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"的 run 方法");
}
}
System.out.println("线程-->"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+" 的 run 方法执行完毕");
}
}
定义 ThreadA 类,此类内部有一个 ThreadB 类型的属性:
public class ThreadA extends Thread {
ThreadB threadB;
private int num = 0;
public ThreadA(ThreadB threadB) {
this.threadB = threadB;
}
@Override
public void run() {
String threadName = Thread.currentThread().getName();
System.out.println("执行"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"的 run 方法");
try {
System.out.println("在线程A的 run 方法中 join 入了"+threadB.getName()+"线程的 run 方法");
threadB.join(3000);
System.out.println(threadName+" 的 run 方法执行完毕");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("异常来自于"+threadName+"线程的 run 方法");
}
}
}可以看到在 ThreadA 的run 方法内部调用了 ThreadB的 join() ,这个方法会让ThreadA 在此处暂停执行3秒,这3秒线程ThreadB没有停止,一直在执行;
主类:
public class PrimaryClass {
public static void main(String[] args) throws UnsupportedEncodingException, InterruptedException {
String threadName = Thread.currentThread().getName();
ThreadB threadB = new ThreadB();
ThreadA threadA = new ThreadA(threadB);
threadA.setName("线程A");
threadB.setName("线程B");
threadB.start();
System.out.println("主线程睡眠1秒");
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println("在主线程中调用了线程A的 start 方法");
threadA.start();
System.out.println("在主线程中调用了线程A的 join 方法");
threadA.join();
System.out.println("继续执行主线程的 run 方法内容");
System.out.println("主线程执行完毕");
}
}主类中又调用了 ThreadA.join()方法。
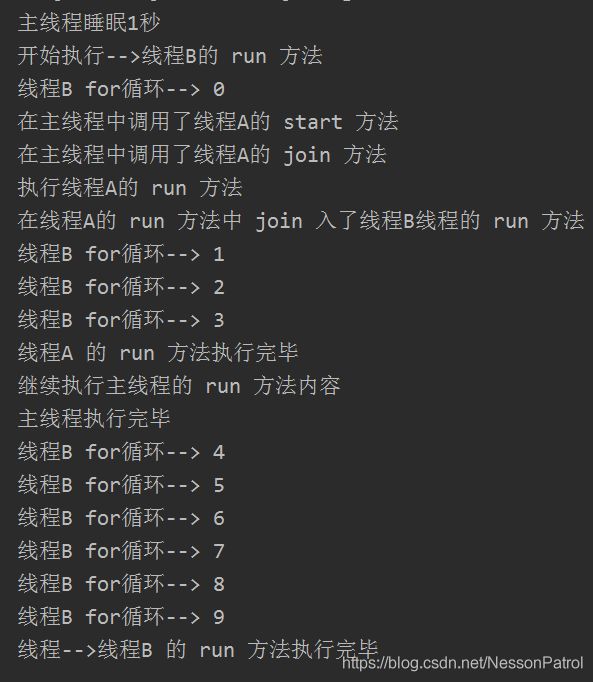
执行一下:
你如果感兴趣可以改一下 ThraedA.join()和ThreadB.join()方法内的参数值,参数不一样,执行的结果也会不一样。