回溯专题
这期刷leetcode上所有的回溯专题
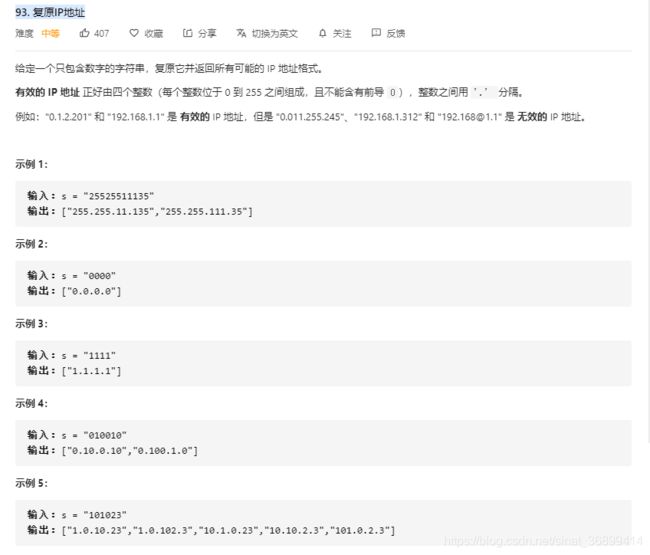
93. 复原IP地址
这题先不考虑一些剪枝类问题,只是单纯考虑AC,我们设置的两个参数,一个index表示索引到哪个字符串下标了,另一个strs双端队列放入表示合法的字符串(0-255)
class Solution {
List<String> res = new ArrayList<>();
public List<String> restoreIpAddresses(String s) {
if(s.equals("")) return res;
helper(s,0,new LinkedList<>());
return res;
}
public void helper(String s, int index, Deque<String> strs){
if(index > s.length()) return; // 已经越界了
if(strs.size() == 4 && index == s.length()){
// 表示已经访问到最后一个字符串,并且队列中已经有了4个合法字符串
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
for(String str: strs)
sb.append(str).append(".");
String keywordStr = sb.deleteCharAt(sb.length() - 1).toString(); // 去掉最后一个 .
res.add(keywordStr);
return;
}
if(strs.size() > 4) return;
for(int i = 1; i<4 && index+i <=s.length(); i++){
// 每个合法字符串组成最多由3个char
String p = s.substring(index,index+i);
if(p.charAt(0) == '0' && p.length() > 1) return; // 检查以0开头的字符串
if(Integer.parseInt(p) >= 0 && Integer.parseInt(p) < 256){
strs.offerLast(p);
helper(s,index+i,strs);
strs.pollLast(); // 这一步一定要还原
}
}
}
}
这里的思路和上题差不多,但是坑比较多,我太菜的原因,先看代码:
class Solution {
public List<List<String>> partition(String s) {
List<List<String>> res = new ArrayList<>();
if(s.length() == 0) return res;
helper(s,0,new ArrayList<>(),res);
return res;
}
public boolean isPalindrome(String str){
int start = 0;
int end = str.length()-1;
while(end > start){
if(str.charAt(start) != str.charAt(end)) return false;
end--;
start++;
}
return true;
}
public void helper(String s, int index, List<String> r, List<List<String>> res){
if(index == s.length()) {
res.add(new ArrayList<>(r)); // 这里不能直接res.add(r),否则r改变后,res里面随之改变
return;
}
for(int i = 1; i+index<=s.length(); i++){
String choose = s.substring(index,index+i);
if(isPalindrome(choose)){
r.add(choose);
helper(s,index+i,r,res);
r.remove(r.size()-1);
}
else continue; // 坑二
}
return;
}
坑一: List列表的删除会影响到已经加到res里面的列表
坑二:该位置之前写的return,直接影响到数组后面元素的添加,比如说 aba,我添加到ab时显示的是非回文字符,return之后就没有继续下去考虑aba的情况,所以此处用continue
排列问题,这类问题在面试中会常问到
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) {
if(nums.length == 0) return res;
Map<Integer,Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); // 记录哪些元素已经放进去,不能重复放进去
for(int i : nums)
map.put(i,1);
helper(nums, new LinkedList<>(),0,map);
return res;
}
public void helper(int []num, Deque<Integer> t, int index, Map<Integer,Integer> map){
if(index == num.length){
res.add(new ArrayList<>(t));
return ;
}
for(int i = 0; i < num.length; i++){
if(map.get(num[i]) != null){
map.remove(num[i]);
t.offerLast(num[i]);
helper(num,t,index+1,map);
map.remove(num[i]);
t.pollLast();
map.put(num[i],1);
}
}
return;
}
}
组合问题
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> combine(int n, int k) {
if(k > n || n == 0 || k == 0) return res;
helper(n,k,0,new ArrayList<>());
return res;
}
public void helper(int n, int k, int index, List<Integer>list){
if(list.size() == k){
res.add(new ArrayList<>(list));
return;
}
for(int i = index; i<n; i++){
list.add(i+1);
helper(n,k,i+1,list); // i+1 表示用过的元素,后面不用了,这里不能用index+1
list.remove(list.size()-1);
}
return;
}
}
全套组合总和问题
组合总和 I
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) {
if(candidates.length == 0) return res;
helper(candidates,target,new ArrayList<>(),0,0);
return res;
}
public void helper(int [] candidates, int target, List<Integer> list, int sum, int index){
if(sum == target){
res.add(new ArrayList<>(list));
return;
}
if(sum > target) return;
for(int i = index; i < candidates.length; i++){
list.add(candidates[i]);
sum += candidates[i];
helper(candidates,target,list,sum, i);
sum -= candidates[i];
list.remove(list.size()-1);
}
return;
}
}
组合总和这个,这个必须消化,这是一个模板了:组合总和 II
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2(int[] candidates, int target) {
Arrays.sort(candidates);
if(candidates.length == 0) return res;
helper(candidates,target,new ArrayList<>(),0,0);
return res;
}
public void helper(int [] candidates, int target, List<Integer> list, int sum, int index){
if(sum == target){
res.add(new ArrayList<>(list));
return;
}
if(sum > target) return;
for(int i = index; i < candidates.length; i++){
if(i > index && candidates[i] == candidates[i-1]) continue;
list.add(candidates[i]);
sum += candidates[i];
helper(candidates,target,list,sum, i+1);
sum -= candidates[i];
list.remove(list.size()-1);
}
return;
}
}
继续延伸到 组合总和 III,将组合问题贯彻到底
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum3(int k, int n) {
if(k == 0 || n < 1) return res;
helper(k,n,new ArrayList<>(),0,1);
return res;
}
public void helper(int k, int n, List<Integer> list, int sum, int index){
if(k == list.size() && sum == n){
res.add(new ArrayList<>(list));
return;
}
if(sum > n) return;
if(index > 9) return;
for(int i = index; i<=9; i++){
sum += i;
list.add(i);
helper(k,n,list,sum,i+1);
sum -= i;
list.remove(list.size()-1);
}
return;
}
}
组合问题 IV(超时了,需要剪枝)
class Solution {
int res = 0;
public int combinationSum4(int[] nums, int target) {
if(nums.length == 0) return res;
helper(nums, target, 0);
return res;
}
public void helper(int []nums, int target, int sum){
if(sum == target){
res += 1;
return;
}
if(sum > target) return;
for(int i = 0; i<nums.length; i++){
sum += nums[i];
if(sum > target) return;
helper(nums,target,sum);
sum -= nums[i];
}
return;
}
}
357. 计算各个位数不同的数字个数

这道题目,我看题解大部分都是用动态规划做的,但是由于是回溯专题,强行用回溯做了 ,结果可想而知:
![]()
class Solution {
int res = 0;
public int countNumbersWithUniqueDigits(int n) {
if(n == 0) return 1;
if(n == 1) return 10;
helper(n, new ArrayList<>());
return res;
}
public void helper(int n, List<Integer> list){
if(list.size() > 1 && list.get(0) == 0) return;
if(list.size() > n) return;
if(list.size() > 0){
res += 1; // 这里有一个坑,习惯性在后面写个return; 结果直接不考虑后面的情况,只输出一位数的情况
}
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++){
if(list.contains(i)) continue;
list.add(i);
helper(n, list);
list.remove(list.size()-1);
}
return;
}
}
子集 II
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> subsetsWithDup(int[] nums) {
if(nums.length == 0) return res;
helper(nums, 0, new ArrayList<>(),new HashMap<>());
return res;
}
public void helper(int[] nums, int index, List<Integer> list, HashMap<List<Integer>,Integer> map){
if(index > nums.length) return;
if(list.size() > nums.length) return;
List<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<>(list);
Collections.sort(temp);
if(map.get(temp) == null){
res.add(new ArrayList<>(temp));
map.put(temp,0);
}
for(int i = index; i<nums.length; i++){
list.add(nums[i]);
helper(nums, i+1, list, map);
list.remove(list.size()-1);
}
return;
}
}