MFC 创建和操作Excel2007 文件
目标:
生成一个excel文件,该文件可以使用office2007打开,也可以使用office2003打开,而不弹出提示;
实现数据写入自动换行,换列的操作;
实现写入实数、复数、字符串的操作;
实现在指定位置,指定范围写入的操作。
该程序在VS2005,VS2008,VS2010测试通过!
步骤:
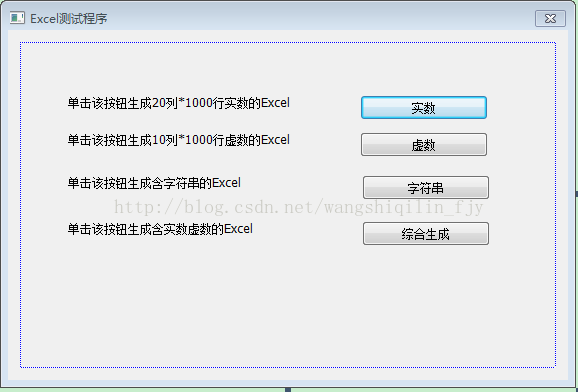
我们首先建立一个基于对话框的MFC程序,我将程序名命名为:GenenalCreateExcelFileDlg。然后打开界面,拖拽如图所示的四个static控件以及四个button控件。将界面更名为:“Excel测试程序”。其他界面的细节略过。
第一步:导入需要的库文件;
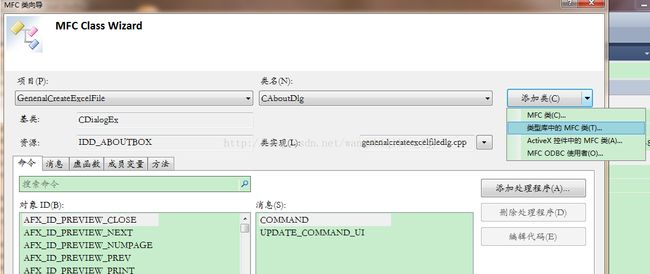
打开类向导,选择“类型库中的MFC类”如图:
 接着我们在打开的对话框中选择源:注册表,类型库为:Excel 12.0。选择的库文件如图所示
接着我们在打开的对话框中选择源:注册表,类型库为:Excel 12.0。选择的库文件如图所示
第二步:修改库文件中的部分语句,否则编译后讲弹出大量bug;
上述步骤完成后,编译一下发现很多bug,此时,注释掉,步骤一中添加的库文件的#import语句:“//#import "E:\\Program Files\\Office2007\\Office12\\EXCEL.EXE" no_namespace”,同时,将这些库文件中“DialogBox()”更改为“_DialogBox()”,以防止重名冲突。
第三步:设计思路:excel2003 的行共有:256列,65536行,2007 更是有:1048576行、16384列;我们需要往不同的行不同的列写入数据,手动指定的话,谁也受不了,但是,excel列的排序符合26进制,因此,一个小小的函数,就可以让输入换列,而行的规律就是简单的十进制,指定了列的话往该列的不同行写不是问题。因此程序中有一个inline函数。再者,生成excel一般的思维就是:生成一个空白文件,往该文件中写入不同的数据,然后保存到指定位置即可。程序中实现这些函数即可。
第四步:设计相关函数:
首先添加一个操作excel的类:CMyExcel。其头文件如下:
#include "CApplication.h"
#include "CRange.h"
#include "CWorkbook.h"
#include "CWorksheet.h"
#include "CWorkbooks.h"
#include "CWorksheets.h"
#include
using namespace std;
class CMyExcel
{
private:
//标记Excel对象的变量
CApplication m_app;
CWorkbooks m_books;
CWorkbook m_book;
CWorksheets m_sheets;
//标记excel中当前写入的标签页
CWorksheet m_sheet;
CRange m_range; //标记写入的范围
COleVariant m_covTrue,m_covFalse,m_coverOptional,m_filePath;
long m_rowCount; //标记Excel当前写入的列数
long m_sheetCount; //标记Excel使用了多少标签页的变量
long m_totalRow; //标记Excel总列数的变量
long m_totalCol; //标记Excel总行数的变量
char *m_colPst; //一个含有A-Z的数组
//列计数器
long m_matricImagCount;
//注释信息计数器,写完注释后写入数据
long m_comCount;
public:
CMyExcel();
virtual ~CMyExcel();
//string 字符串转换为CString
CString String2CString(const string& inStr);
//CString 字符串转换为string
string CString2String(const CString & inStr);
//打开文件用于读写
//输入:文件名,打开模式
//输出:文件打开状态
int openfile(const string& filepath ,int mode);
//写入实数组
//输入:文件名,待写入文件的内容指针,待写入的行,待写入的列
//输出:文件写入状态
int writeMatrix(const string &matName ,double *mateData,long row,long col);
//写入复数组
//输入文件名,待写入文件的内容实部指针,待写入文件的内容虚部指针,待写入的行,待写入的列
//输出:文件写入状态
int writeMatrix(const string &matName ,double *mateDataReal,double *mateDataImag,long row,long col);
//写入字符串
//在Excel的指定范围生成含有指定字符串的文件
int writeString(const string& str,int& col1,int& col2,int& row1,int& row2);
//一个计算当前数据输入列的函数(输入到指定列需要得到列的标题:A,AX等,而他们满足26进制)
inline void rowName(CString &mRowName,const long& mCount )
{
if(mCount < 27 )
{
mRowName += m_colPst[mCount];
}
else
{
int i = mCount / 26;
int j = mCount %26;
mRowName += m_colPst[i];
mRowName += m_colPst[j];
}
}
}; 其实现文件如下:
#include"stdafx.h"
#include"MyExcel.h"
CMyExcel::CMyExcel():m_rowCount(1),m_sheetCount(1),m_totalCol(256),m_totalRow(65536),m_matricImagCount(1),m_comCount(1)
{
//获取系统的excel句柄
if(!m_app.CreateDispatch(TEXT("Excel.Application")))
{
AfxMessageBox(_T("Could not start Excel and get Application object !"));
return;
}
m_covTrue = COleVariant((short)TRUE);
m_covFalse = COleVariant((short)FALSE);
m_coverOptional = COleVariant((long)DISP_E_PARAMNOTFOUND,VT_ERROR);
m_books = m_app.get_Workbooks();
m_book = m_books.Add(m_coverOptional);
m_sheets = m_book.get_Sheets();
//m_colPst初始化为A-Z,其中下表为0的为一个无意义的占位符
m_colPst = new char[27];
m_colPst[0] = '#';
for(int i = 1;i<27;i++)
{
m_colPst[i]=64+i;
}
}
CMyExcel::~CMyExcel()
{
//在这里保存生成的excel
m_book.SaveAs(
m_filePath,
_variant_t((long)56),//该参数使得保存的时候使用兼容模式,避免了使用excel2003打开的时候弹出提示框
m_coverOptional,
m_coverOptional,
m_coverOptional,
m_coverOptional,
0,
m_coverOptional,
m_coverOptional,
m_coverOptional,
m_coverOptional,
m_coverOptional
);
//释放占用的excel资源
m_book.ReleaseDispatch();
m_books.ReleaseDispatch();
m_app.Quit();
m_app.DetachDispatch();
//将一些计数器变量复原
m_comCount = 1;
m_matricImagCount = 1;
}
CString CMyExcel::String2CString(const string& inStr)
{
int nLen = (int)inStr.length()+1;
int nwLen = MultiByteToWideChar(CP_ACP,0,inStr.c_str(),nLen,NULL,0);
TCHAR* lpszOut = new TCHAR[nwLen]; //最多1024字节
MultiByteToWideChar(CP_ACP,0,inStr.c_str(),nLen,lpszOut,nwLen);
CString outStr;
outStr += lpszOut;
delete []lpszOut;
lpszOut = NULL;
return outStr;
}
string CMyExcel::CString2String(const CString & inStr)
{
int nLength = 0;
//获取需要的字节数
nLength = WideCharToMultiByte(CP_ACP,NULL,inStr,-1,NULL,0,NULL,NULL);
//申请char存储空间
char *buffer = (char*)malloc(nLength);
//转换
WideCharToMultiByte(CP_ACP,NULL,inStr,-1,buffer,nLength,NULL,NULL);
string str(buffer);
//释放缓存区
free(buffer);
return str;
}
int CMyExcel::openfile(const string& filepath ,int mode)
{
if(m_books)
{
m_filePath = COleVariant(String2CString(filepath));
return 1;
}
else
return -1;
}
int CMyExcel::writeMatrix(const string &matName ,double *mateData,long row,long col)
{
m_sheet = m_sheets.get_Item(COleVariant((short)m_sheetCount));
//用于标记当前写入的是哪一列:A、B、C、......
long matrixCt = 0;
//指定当前写入的行:需要先写入一些注释信息(m_comcount计数),然后在写入数据,因此将他们赋值即可
m_rowCount = m_comCount;
//标记当前列标题的变量:比如说(A,AX,BX等)
CString locPst(_T(""));
//标记保存位置的变量
CString position0(_T(""));
CString locPstReal(_T(""));
//超过列数就不继续
if(m_matricImagCount > m_totalCol)
{
return -1;
}
matrixCt = m_matricImagCount++;
CString mRow(_T("row="));
CString mCol(_T("col="));
CString temp;
temp.Format(_T("%ld"),row);
mRow = mRow + temp;
temp.Empty();
temp.Format(_T("%ld"),col);
mCol = mCol + temp;
rowName(locPst,matrixCt);
position0 = locPst;
temp.Empty();
temp.Format(_T("%ld"),m_rowCount++);
position0+=temp;
CString myMatName(matName.c_str());
m_range = m_sheet.get_Range(COleVariant(position0),COleVariant(position0));
m_range.put_Value2(_variant_t(myMatName));
position0 = locPst;
temp.Empty();
temp.Format(_T("%ld"),m_rowCount++);
position0+=temp;
m_range = m_sheet.get_Range(COleVariant(position0),COleVariant(position0));
m_range.put_Value2(COleVariant(TEXT("----")));
//数据写入文件
for(long iRow = 0;iRow < row;iRow++)
{
locPstReal.Empty();
long tmpCol = matrixCt++;
rowName(locPstReal, tmpCol);
position0 = locPstReal;
long rowCount = m_rowCount;
for(long icol = 0;icol m_totalRow)
{
break;
}
}
}
m_comCount = 1;
return 1;
}
int CMyExcel::writeMatrix(const string &matName ,double *mateDataReal,
double *mateDataImag,long row,long col)
{
m_sheet = m_sheets.get_Item(COleVariant((short)m_sheetCount));
//用于标记当前写入的是哪一列:A、B、C、......
long matrixCt = 0;
//指定当前写入的行:需要先写入一些注释信息(m_comcount计数),然后在写入数据,因此将他们赋值即可
m_rowCount = m_comCount;
//标记当前列标题的变量:比如说(A,AX,BX等)
CString locPstReal(_T(""));
CString locPstImge(_T(""));
//标记写入位置的变量:实数部分、虚数部分
CString colReal(_T(""));
CString colImge(_T(""));
//描述信息
CString mRow(_T("row = "));
CString mCol(_T("col = "));
CString temp;
temp.Format(_T("%ld"),row);
mRow = mRow + temp;
temp.Empty();
temp.Format(_T("%ld"),col);
mCol = mCol + temp;
//超过列数就不继续写
if(m_matricImagCount > m_totalCol)
{
return -1;
}
matrixCt = m_matricImagCount;
m_matricImagCount += (row * 2);
rowName(locPstReal, matrixCt);
colReal = locPstReal;
temp.Empty();
temp.Format(_T("%ld"),m_rowCount++);
colReal += temp;
CString myMatName(matName.c_str());
m_range = m_sheet.get_Range(COleVariant(colReal),COleVariant(colReal));
m_range.put_Value2(_variant_t(myMatName));
colReal = locPstReal;
temp.Empty();
temp.Format(_T("%ld"),m_rowCount++);
colReal+=temp;
m_range = m_sheet.get_Range(COleVariant(colReal),COleVariant(colReal));
m_range.put_Value2(COleVariant(TEXT("--------")));
//数据写入文件
for(long iRow = 0;iRow < row;iRow++)
{
locPstReal.Empty();
locPstImge.Empty();
long tmpCol = matrixCt;
rowName(locPstReal, tmpCol);
rowName(locPstImge, tmpCol+1);
matrixCt += 2;
colReal = locPstReal;
colImge = locPstImge;
long rowCount = m_rowCount;
for(long icol = 0;icol m_totalRow)
{
break;
}
}
}
m_comCount = 1;
return 1;
}
int CMyExcel::writeString(const string& str,int& col1,int& row1,int& col2,int& row2)
{
m_sheet = m_sheets.get_Item(COleVariant((short)m_sheetCount));
//获取矩形框走上角写入位置:E3
CString locPst11(_T(""));
rowName(locPst11,row1);
CString temp11(_T(""));
CString position11(_T(""));
position11= locPst11;
temp11.Format(_T("%ld"),col1);
position11 += temp11;
//获取矩形框走上角写入位置:E8
CString locPst12(_T(""));
rowName(locPst12,row1);
CString temp12(_T(""));
CString position12(_T(""));
position12 = locPst12;
temp12.Format(_T("%ld"),col2);
position12 += temp12;
//获取右上角写入位置 :P3
CString locPst21(_T(""));
rowName(locPst21,row2);
CString temp21(_T(""));
CString position21(_T(""));
position21 = locPst21;
temp21.Format(_T("%ld"),col1);
position21 += temp21;
//获取右下角写入位置 :P8
CString locPst22(_T(""));
rowName(locPst22,row2);
CString temp22(_T(""));
CString position22(_T(""));
position22 = locPst22;
temp21.Format(_T("%ld"),col2);
position22 += temp21;
CString myMatName(str.c_str());
//首先将数据写入E3这一格中
m_range = m_sheet.get_Range(COleVariant(position11),COleVariant(position11));
m_range.put_Value2(_variant_t(myMatName));
//然后合并E3-P8,形成矩形框
m_range = m_sheet.get_Range(COleVariant(position11),COleVariant(position22));
//这里就是“m_coverOptional”用到的地方!
m_range.Merge(m_coverOptional);
return 1;
}
至此,excel的操作都已经实现完毕,有些注释给出了一个参数的定义,比如savsas函数,有兴趣的读者可以将里面的某些参数置换点,看看我在注释后面说的现象到底是什么。
第五步:测试程序:
双击dialog界面中的“实数”按钮,看看写入20列*1000行的效果。代码实现如下:
void CGenenalCreateExcelFileDlg::OnBnClickedRealdigital()
{
// TODO: 在此添加控件通知处理程序代码
//打开一个文件保存对话框
string filePathStr("D:\\ValExcel.xls");
string comment("");
CMyExcel Demon;
//在用户路径下生成文件
//将鼠标形状更改为漏洞状态
theApp.BeginWaitCursor();
if(!Demon.openfile(filePathStr,2))
{
MessageBox(_T("数据导出失败!"));
}
//我们往里面写入20列,每列1000行
int iCount = 1;
//添加一个时钟计数器,看代码导出消耗多少时间
DWORD start_time=::GetTickCount();
for(;iCount<=20;iCount++)
{
char valStr[10];
comment.clear();
sprintf_s(valStr,"%i",iCount);
comment += "第";
comment +=valStr;
comment +="列";
Demon.writeMatrix(comment,mateDataReal,1,1000);
}
DWORD end_time=::GetTickCount();
theApp.EndWaitCursor();
char timecost[1024];
sprintf_s(timecost,"%lu",end_time-start_time);
CString msg = _T("Excel生成完成,耗时:");
msg += Demon.String2CString(timecost);
msg += _T("毫秒");
MessageBox(msg);
}
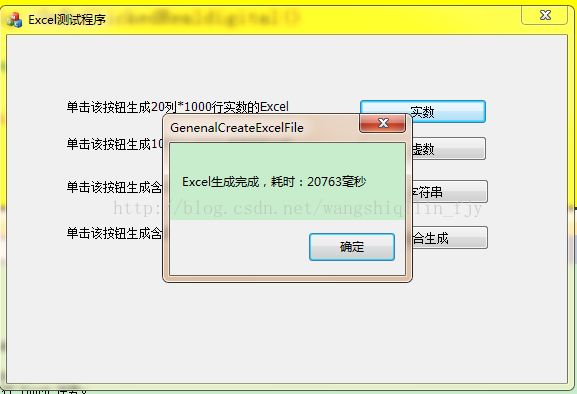
在该代码中,生成路径为D盘根目录,在生成过程中,将鼠标形状更改为等待状态的一个漏洞(XP系统可见),或者一个圈圈(win7系统可见),并且把生成时间打印了出来,效果图如图
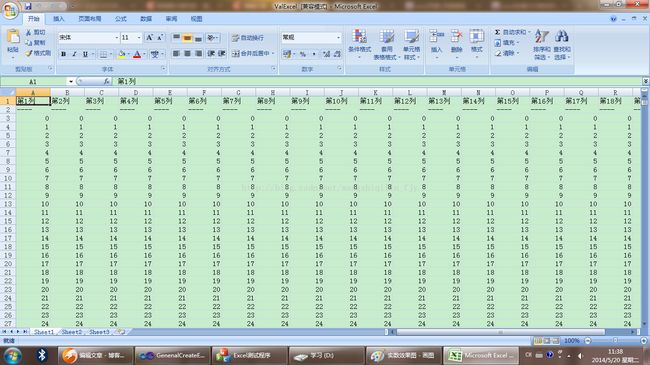
,生成的文件效果图如图所示
双击dialog界面中的“复数”按钮,看看写入10列*1000行复数的效果。因为复数有一个实部和一个虚部,因此一次需要写两列,代码实现如下:
void CGenenalCreateExcelFileDlg::OnBnClickedImagedigital()
{
// TODO: 在此添加控件通知处理程序代码
//打开一个文件保存对话框
string filePathStr("D:\\MatExcer.xls");
string comment("");
CMyExcel Demon;
//在用户路径下生成文件
//将鼠标形状更改为漏洞状态
theApp.BeginWaitCursor();
if(!Demon.openfile(filePathStr,2))
{
MessageBox(_T("数据导出失败!"));
}
//我们往里面写入10列,每列1000行
int iCount = 1;
//添加一个时钟计数器,看代码导出消耗多少时间
DWORD start_time=::GetTickCount();
for(;iCount<=10;iCount++)
{
char valStr[10];
comment.clear();
sprintf_s(valStr,"%i",iCount);
comment += "第";
comment +=valStr;
comment +="列复数";
Demon.writeMatrix(comment,mateDataReal,mateDataImge,1,1000);
}
DWORD end_time=::GetTickCount();
theApp.EndWaitCursor();
char timecost[1024];
sprintf_s(timecost,"%lu",end_time-start_time);
CString msg = _T("Excel生成完成,耗时:");
msg += Demon.String2CString(timecost);
msg += _T("毫秒");
MessageBox(msg);
}
void CGenenalCreateExcelFileDlg::OnBnClickedStr()
{
// TODO: 在此添加控件通知处理程序代码
string filePathStr("D:\\StrExcel.xls");
string comment("这是一个简单的测试程序!");
CMyExcel Demon;
//在用户路径下生成文件
if(!Demon.openfile(filePathStr,2))
{
MessageBox(_T("数据导出失败!"));
}
//尝试在Excel的左上角(3,E)、右下角(8,P)的矩形框范围内写入数据!
int col1 = 3;
int row1 = 5;
int col2 = 8;
int row2 = 16;
Demon.writeString(comment,col1,row1,col2,row2);
CString msg = _T("含有字符串的Excel生成完成!");
MessageBox(msg);
}双击dialog界面中的“综合生成”按钮,看看写入一列实数和一列复数的效果。代码实现如下:
void CGenenalCreateExcelFileDlg::OnBnClickedTotal()
{
// TODO: 在此添加控件通知处理程序代码
string filePathStr("D:\\TotalExcel.xls");
string comment1("一列实数!");
string comment2("一列复数!");
CMyExcel Demon;
//在用户路径下生成文件
if(!Demon.openfile(filePathStr,2))
{
MessageBox(_T("数据导出失败!"));
}
//仅仅写入一列实数以及一列复数,作为测试!
Demon.writeMatrix(comment1,mateDataReal,1,1000);
Demon.writeMatrix(comment2,mateDataReal,mateDataImge,1,1000);
CString msg = _T("Excel生成完成!");
MessageBox(msg);
}
其他问题分析:我特意在复数以及实数写入的代码段中添加了时间测试语句,从图片中可以看到,但10*1000复数或者20*1000实数的时候,时间都不是很理想,假如数据换成其他的,如100列*60000行的时候,时间的花费就更大了,因此上述程序在数据量小的时候是有效的,但数据量大了的时候是不太理想的。改进的方法是想生成CSV文件,然后将它另存为Excel关于这方面的论述,将在下一篇博客中提及。
由于时间有限,有些注释可能不是非常理想,欢迎提出不同见解。
该文章使用到的源码:点击打开链接