# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# /usr/bin/python
# 作者:kimicr
# 实验日期:201904026
# Python版本:3.6.3
# 《深度学习与神经网络》第一课第三周编程作业
# 建立一个简单神经网络,它有一个隐藏层,并用来进行二分类,其中搭建神经网络步骤如下:
# 1、定义神经网络结构;2、模型参数初始化;3、实现前向传播、损失函数、实现后向传播、更新参数
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from testCases import *
from planar_utils import plot_decision_boundary, sigmoid, load_planar_dataset, load_extra_datasets
np.random.seed(1) #设置一个固定的随机种子,以保证接下来的步骤中我们的结果是一致的
X,Y = load_planar_dataset() #得到花的图案的2类数据集
shape_X = X.shape
shape_Y = Y.shape
m = Y.shape[1] # 训练集里面的样本数量
print ("X的维度为: " + str(shape_X))
print ("Y的维度为: " + str(shape_Y))
print ("数据集里面的数据有:" + str(m) + " 个")
#简单的logistic回归的分类效果测试
'''
clf = sklearn.linear_model.LogisticRegressionCV()
clf.fit(X.T,Y.T)
plot_decision_boundary(lambda x: clf.predict(x), X, Y) #绘制决策边界
plt.title("Logistic Regression") #图标题
LR_predictions = clf.predict(X.T) #预测结果
print ("逻辑回归的准确性: %d " % float((np.dot(Y, LR_predictions) +
np.dot(1 - Y,1 - LR_predictions)) / float(Y.size) * 100) +
"% " + "(正确标记的数据点所占的百分比)")
'''
#-------------搭建神经网络模型----------------
#定义神经网络结构
def layer_sizes(X,Y):
'''
parameters:
n_x: 输入层节点的数量
n_h: 隐藏层节点的数量
n_y: 输出层节点的数量
返回:
n_x - 输入层的数量
n_h - 隐藏层的数量
n_y - 输出层的数量
'''
n_x = X.shape[0]
n_h = 4
n_y = Y.shape[0]
return (n_x,n_h,n_y)
#初始化模型参数W、b等
def initialize_parameters(n_x,n_h,n_y):
'''
paramerters:
n_x - 输入层的数量
n_h - 隐藏层的数量
n_y - 输出层的数量
返回:
W1 : 权重矩阵,dim(n_h,n_x)
b1 : 偏向量,dim(n_h,1)
W2 : 权重矩阵,dim(n_y,n_h)
b2 : 偏向量,dim(n_y,1)
'''
np.random.seed(2) #指定以随机种子
w1 = np.random.randn(n_h,n_x)*0.01
b1 = np.zeros(shape=(n_h,1))
w2 = np.random.randn(n_y,n_h)*0.01
b2 = np.zeros(shape=(n_y,1))
parameters = {'W1' : w1,
'b1' : b1,
'W2' : w2,
'b2' : b2,}
return parameters
#前向传播,M样本向量化
def forward_propagation(X,parameters):
'''
参数:
X - 输入的参数,dim(n_x,m)
parameters - 初始化函数(initialize_parameters)的输出
返回:
激活函数所需的Z1,Z2,A1,A2
'''
W1 = parameters['W1']
b1 = parameters['b1']
W2 = parameters['W2']
b2 = parameters['b2']
Z1 = np.dot(W1,X)+b1
A1 = np.tanh(Z1)
Z2 = np.dot(W2,A1)+b2
A2 = sigmoid(Z2)
cache = {'Z1' : Z1,
'A1' : A1,
'Z2' : Z2,
'A2' : A2,}
return (A2,cache)
#计算损失函数J,得到成本cost
def compute_cost(A2,Y):
"""
参数:
A2 - 使用sigmoid()函数计算的第二次激活后的数值
Y - "True"标签向量,维度为(1,数量)
parameters - 一个包含W1,B1,W2和B2的字典类型的变量
返回:
损失cost
"""
m = X.shape[1]
cost = -(np.dot(Y,np.log(A2).T)+np.dot((1-Y),np.log((1-A2)).T))/m
cost = np.squeeze(cost) # 压缩维度
return cost
#后向传播
def backward_propagation(parameters,cache,X,Y):
"""
使用上述说明搭建反向传播函数。
参数:
parameters - 包含我们的参数的一个字典类型的变量。
cache - 包含“Z1”,“A1”,“Z2”和“A2”的字典类型的变量。
X - 输入数据,维度为(2,数量)
Y - “True”标签,维度为(1,数量)
返回:
grads - 包含W和b的导数一个字典类型的变量。
"""
m = X.shape[1]
W1 = parameters['W1']
W2 = parameters['W2']
A1 = cache['A1']
A2 = cache['A2']
dZ2 = A2 - Y
dW2 = np.dot(dZ2, A1.T)/m
db2 = np.sum(dZ2, axis=1, keepdims=True)/m
dZ1 = np.multiply(np.dot(W2.T, dZ2), 1 - np.power(A1, 2))
dW1 = np.dot(dZ1, X.T)/m
db1 = np.sum(dZ1, axis=1, keepdims=True)/m
grads = {"dW1": dW1,
"db1": db1,
"dW2": dW2,
"db2": db2}
return grads
#更新参数
def update_parameters(parameters,grads,learning_rate = 1.2):
W1 = parameters['W1']
b1 = parameters['b1']
W2 = parameters['W2']
b2 = parameters['b2']
dW1 = grads['dW1']
db1 = grads['db1']
dW2 = grads['dW2']
db2 = grads['db2']
W1 = W1 - learning_rate*dW1
b1 = b1 - learning_rate*db1
W2 = W2 - learning_rate*dW2
b2 = b2 - learning_rate*db2
parameters = {'W1' : W1,
'b1' : b1,
'W2' : W2,
'b2' : b2,}
return parameters
#建立神经网络模型
def model(X,Y,n_h,num_iterations,print_cost=False):
"""
参数:
X - 数据集,维度为(2,示例数)
Y - 标签,维度为(1,示例数)
n_h - 隐藏层的数量
num_iterations - 梯度下降循环中的迭代次数
print_cost - 如果为True,则每1000次迭代打印一次成本数值
返回:
parameters - 模型学习的参数,它们可以用来进行预测。
"""
np.random.seed(3) #指定随机种子
n_x = layer_sizes(X, Y)[0]
n_y = layer_sizes(X, Y)[2]
parameters = initialize_parameters(n_x,n_h,n_y)
for i in range(num_iterations):
A2 , cache = forward_propagation(X,parameters)
cost = compute_cost(A2,Y)
grads = backward_propagation(parameters,cache,X,Y)
parameters = update_parameters(parameters,grads,learning_rate = 0.5)
if print_cost:
if i%1000 == 0:
print("第 ",i," 次循环,成本为:"+str(cost))
return parameters
#预测模型
def predict(parameters,X):
"""
使用学习的参数,为X中的每个示例预测一个类
参数:
parameters - 包含参数的字典类型的变量。
X - 输入数据(n_x,m)
返回
predictions - 我们模型预测的向量(红色:0 /蓝色:1)
"""
A2 , cache = forward_propagation(X,parameters)
predictions = np.round(A2)
return predictions
#正式运行
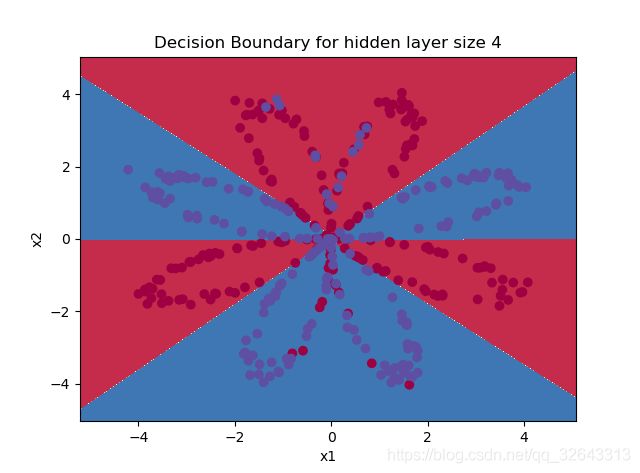
parameters = model(X, Y, n_h = 4, num_iterations=10000, print_cost=True)
#绘制边界
plot_decision_boundary(lambda x: predict(parameters, x.T), X, Y)
plt.title("Decision Boundary for hidden layer size " + str(4))
predictions = predict(parameters, X)
print ('准确率: %d' % float((np.dot(Y, predictions.T) + np.dot(1 - Y, 1 - predictions.T)) / float(Y.size) * 100) + '%')
'''
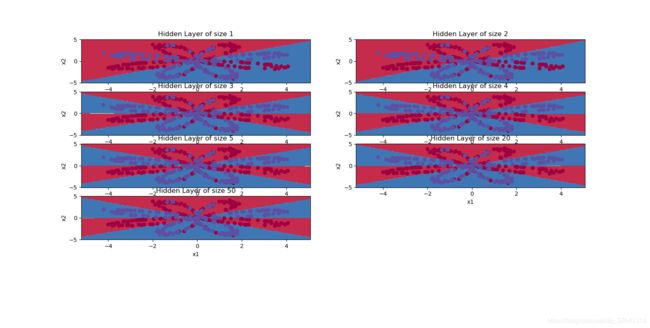
plt.figure(figsize=(16, 32))
hidden_layer_sizes = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 20, 50] #隐藏层数量
for i, n_h in enumerate(hidden_layer_sizes):
plt.subplot(5, 2, i + 1)
plt.title('Hidden Layer of size %d' % n_h)
parameters = model(X, Y, n_h, num_iterations=5000)
plot_decision_boundary(lambda x: predict(parameters, x.T), X, Y)
predictions = predict(parameters, X)
accuracy = float((np.dot(Y, predictions.T) + np.dot(1 - Y, 1 - predictions.T)) / float(Y.size) * 100)
print ("隐藏层的节点数量: {} ,准确率: {} %".format(n_h, accuracy))
plt.show()
'''
结果:
附程序:testCases.py
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import sklearn
import sklearn.datasets
import sklearn.linear_model
def plot_decision_boundary(model, X, y):
# Set min and max values and give it some padding
x_min, x_max = X[0, :].min() - 1, X[0, :].max() + 1
y_min, y_max = X[1, :].min() - 1, X[1, :].max() + 1
h = 0.01
# Generate a grid of points with distance h between them
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, h), np.arange(y_min, y_max, h))
# Predict the function value for the whole grid
Z = model(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
# Plot the contour and training examples
plt.contourf(xx, yy, Z, cmap=plt.cm.Spectral)
plt.ylabel('x2')
plt.xlabel('x1')
#plt.scatter(X[0, :], X[1, :], c=y, cmap=plt.cm.Spectral)
plt.scatter(X[0, :], X[1, :], c=np.squeeze(y), cmap=plt.cm.Spectral)
def sigmoid(x):
"""
Compute the sigmoid of x
Arguments:
x -- A scalar or numpy array of any size.
Return:
s -- sigmoid(x)
"""
s = 1/(1+np.exp(-x))
return s
def load_planar_dataset():
np.random.seed(1)
m = 400 # number of examples
N = int(m/2) # number of points per class (分类数量)
D = 2 # dimensionality
X = np.zeros((m,D)) # data matrix where each row is a single example
Y = np.zeros((m,1), dtype='uint8') # labels vector (0 for red, 1 for blue)
a = 4 # maximum ray of the flower (最大花束--花瓣长度<=abs(4))
for j in range(2):
ix = range(N*j,N*(j+1))
t = np.linspace(j*3.12,(j+1)*3.12,N) + np.random.randn(N)*0.2 # theta(角度θ)
r = a*np.sin(4*t) + np.random.randn(N)*0.2 # radius
X[ix] = np.c_[r*np.sin(t), r*np.cos(t)]
Y[ix] = j
X = X.T
Y = Y.T
return X, Y
def load_extra_datasets():
N = 200
noisy_circles = sklearn.datasets.make_circles(n_samples=N, factor=.5, noise=.3)
noisy_moons = sklearn.datasets.make_moons(n_samples=N, noise=.2)
blobs = sklearn.datasets.make_blobs(n_samples=N, random_state=5, n_features=2, centers=6)
gaussian_quantiles = sklearn.datasets.make_gaussian_quantiles(mean=None, cov=0.5, n_samples=N, n_features=2, n_classes=2, shuffle=True, random_state=None)
no_structure = np.random.rand(N, 2), np.random.rand(N, 2)
return noisy_circles, noisy_moons, blobs, gaussian_quantiles, no_structure

