i2c对24c32进行读写
开发板环境:vivado 2017.1 ,开发板型号xc7z020clg400-1,这个工程主要是用i2c对24c32进行读写
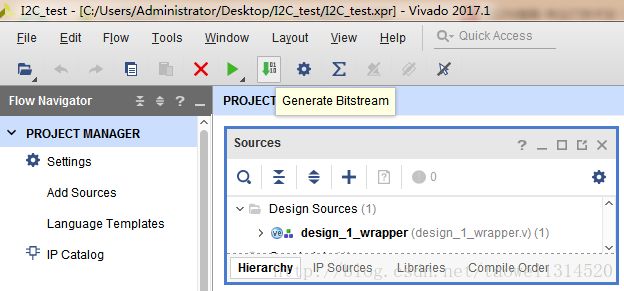
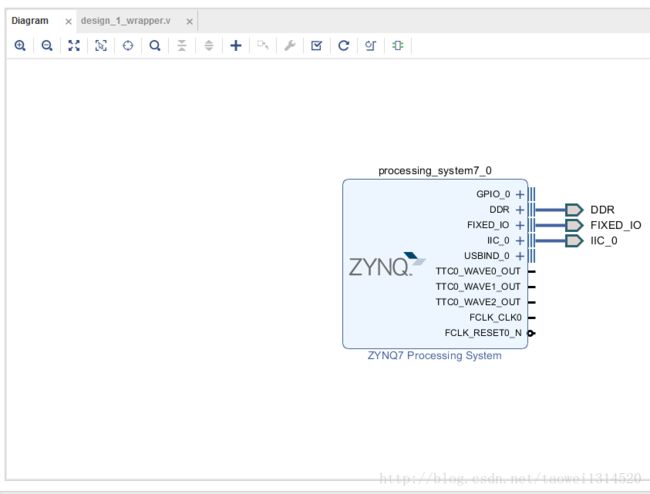
Step1 新建工程然后按照下面截图中进行配置(主要配置了DDR、i2c)
配置完成后进行综合、生成顶层文件,生成的顶层文件如下图所示
[csharp] view plain copy
[html] view plain copy
- //Copyright 1986-2017 Xilinx, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
- //--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- //Tool Version: Vivado v.2017.1 (win64) Build 1846317 Fri Apr 14 18:55:03 MDT 2017
- //Date : Sun Feb 18 22:06:05 2018
- //Host : MS-20180107KQQK running 64-bit Service Pack 1 (build 7601)
- //Command : generate_target design_1_wrapper.bd
- //Design : design_1_wrapper
- //Purpose : IP block netlist
- //--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- `timescale 1 ps / 1 ps
- module design_1_wrapper
- (DDR_addr,
- DDR_ba,
- DDR_cas_n,
- DDR_ck_n,
- DDR_ck_p,
- DDR_cke,
- DDR_cs_n,
- DDR_dm,
- DDR_dq,
- DDR_dqs_n,
- DDR_dqs_p,
- DDR_odt,
- DDR_ras_n,
- DDR_reset_n,
- DDR_we_n,
- FIXED_IO_ddr_vrn,
- FIXED_IO_ddr_vrp,
- FIXED_IO_mio,
- FIXED_IO_ps_clk,
- FIXED_IO_ps_porb,
- FIXED_IO_ps_srstb,
- iic_0_scl_io,
- iic_0_sda_io);
- inout [14:0]DDR_addr;
- inout [2:0]DDR_ba;
- inout DDR_cas_n;
- inout DDR_ck_n;
- inout DDR_ck_p;
- inout DDR_cke;
- inout DDR_cs_n;
- inout [3:0]DDR_dm;
- inout [31:0]DDR_dq;
- inout [3:0]DDR_dqs_n;
- inout [3:0]DDR_dqs_p;
- inout DDR_odt;
- inout DDR_ras_n;
- inout DDR_reset_n;
- inout DDR_we_n;
- inout FIXED_IO_ddr_vrn;
- inout FIXED_IO_ddr_vrp;
- inout [53:0]FIXED_IO_mio;
- inout FIXED_IO_ps_clk;
- inout FIXED_IO_ps_porb;
- inout FIXED_IO_ps_srstb;
- inout iic_0_scl_io;
- inout iic_0_sda_io;
- wire [14:0]DDR_addr;
- wire [2:0]DDR_ba;
- wire DDR_cas_n;
- wire DDR_ck_n;
- wire DDR_ck_p;
- wire DDR_cke;
- wire DDR_cs_n;
- wire [3:0]DDR_dm;
- wire [31:0]DDR_dq;
- wire [3:0]DDR_dqs_n;
- wire [3:0]DDR_dqs_p;
- wire DDR_odt;
- wire DDR_ras_n;
- wire DDR_reset_n;
- wire DDR_we_n;
- wire FIXED_IO_ddr_vrn;
- wire FIXED_IO_ddr_vrp;
- wire [53:0]FIXED_IO_mio;
- wire FIXED_IO_ps_clk;
- wire FIXED_IO_ps_porb;
- wire FIXED_IO_ps_srstb;
- wire iic_0_scl_i;
- wire iic_0_scl_io;
- wire iic_0_scl_o;
- wire iic_0_scl_t;
- wire iic_0_sda_i;
- wire iic_0_sda_io;
- wire iic_0_sda_o;
- wire iic_0_sda_t;
- design_1 design_1_i
- (.DDR_addr(DDR_addr),
- .DDR_ba(DDR_ba),
- .DDR_cas_n(DDR_cas_n),
- .DDR_ck_n(DDR_ck_n),
- .DDR_ck_p(DDR_ck_p),
- .DDR_cke(DDR_cke),
- .DDR_cs_n(DDR_cs_n),
- .DDR_dm(DDR_dm),
- .DDR_dq(DDR_dq),
- .DDR_dqs_n(DDR_dqs_n),
- .DDR_dqs_p(DDR_dqs_p),
- .DDR_odt(DDR_odt),
- .DDR_ras_n(DDR_ras_n),
- .DDR_reset_n(DDR_reset_n),
- .DDR_we_n(DDR_we_n),
- .FIXED_IO_ddr_vrn(FIXED_IO_ddr_vrn),
- .FIXED_IO_ddr_vrp(FIXED_IO_ddr_vrp),
- .FIXED_IO_mio(FIXED_IO_mio),
- .FIXED_IO_ps_clk(FIXED_IO_ps_clk),
- .FIXED_IO_ps_porb(FIXED_IO_ps_porb),
- .FIXED_IO_ps_srstb(FIXED_IO_ps_srstb),
- .IIC_0_scl_i(iic_0_scl_i),
- .IIC_0_scl_o(iic_0_scl_o),
- .IIC_0_scl_t(iic_0_scl_t),
- .IIC_0_sda_i(iic_0_sda_i),
- .IIC_0_sda_o(iic_0_sda_o),
- .IIC_0_sda_t(iic_0_sda_t));
- IOBUF iic_0_scl_iobuf
- (.I(iic_0_scl_o),
- .IO(iic_0_scl_io),
- .O(iic_0_scl_i),
- .T(iic_0_scl_t));
- IOBUF iic_0_sda_iobuf
- (.I(iic_0_sda_o),
- .IO(iic_0_sda_io),
- .O(iic_0_sda_i),
- .T(iic_0_sda_t));
- endmodule
这个i2c工程的管脚是用emio引出的,所以要加这两个IOBUF,如果是mio引出的可以不加这两个IOBUF
[html] view plain copy
- IOBUF iic_0_scl_iobuf
[html] view plain copy
- IOBUF iic_0_sda_iobuf
Step2 新建一个xdc文件
[html] view plain copy
- set_property PACKAGE_PIN B19 [get_ports iic_0_sda_io]
- set_property PACKAGE_PIN A20 [get_ports iic_0_scl_io]
- set_property IOSTANDARD LVCMOS33 [get_ports iic_0_scl_io]
- set_property IOSTANDARD LVCMOS33 [get_ports iic_0_sda_io]
- set_property PULLUP true [get_ports iic_0_scl_io]
- set_property PULLUP true [get_ports iic_0_sda_io]
新建的工程因为是emio引出的所以要分配管脚,如果mio就不用分配引脚。
这个xdc文件主要注意下面这两行,这两行主要是加内部上拉电阻
[html] view plain copy
- set_property PULLUP true [get_ports iic_0_scl_io]
- set_property PULLUP true [get_ports iic_0_sda_io]
Step3 生成bit文件
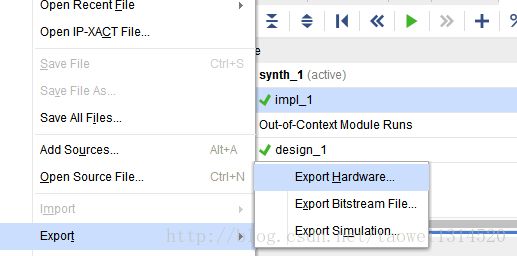
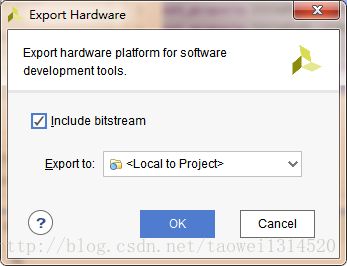
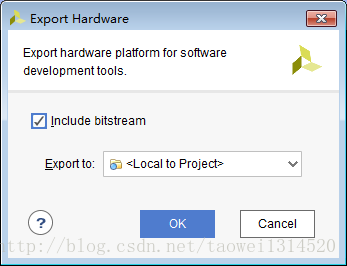
Step4点击菜单栏上的 File->Export->Export Hardware 导出硬件配置文件
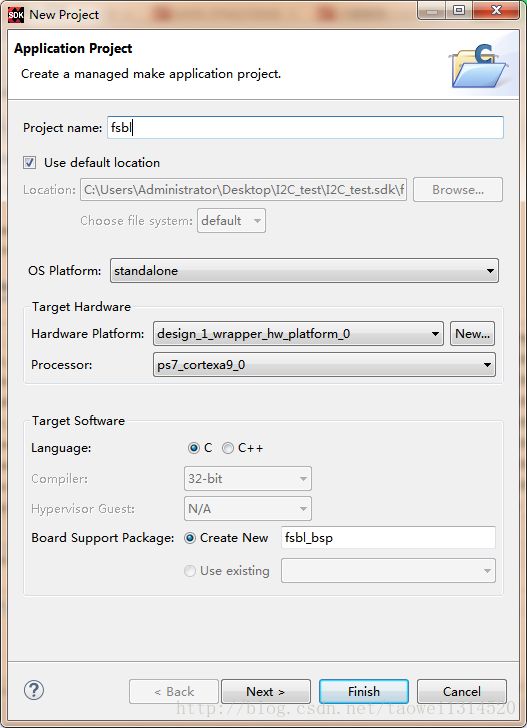
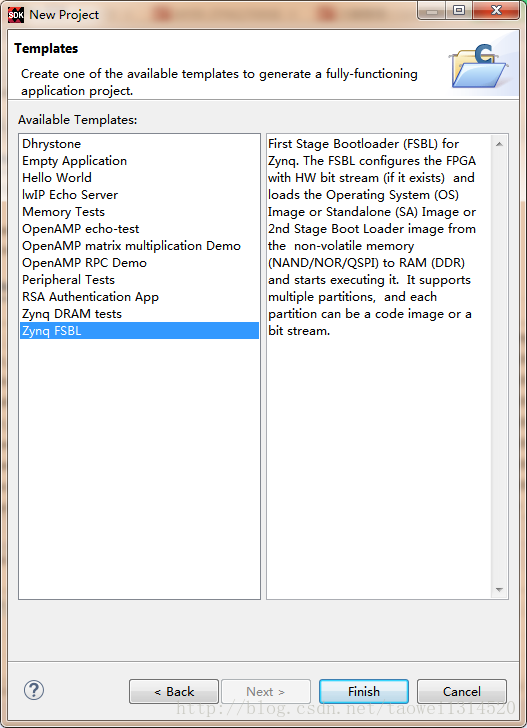
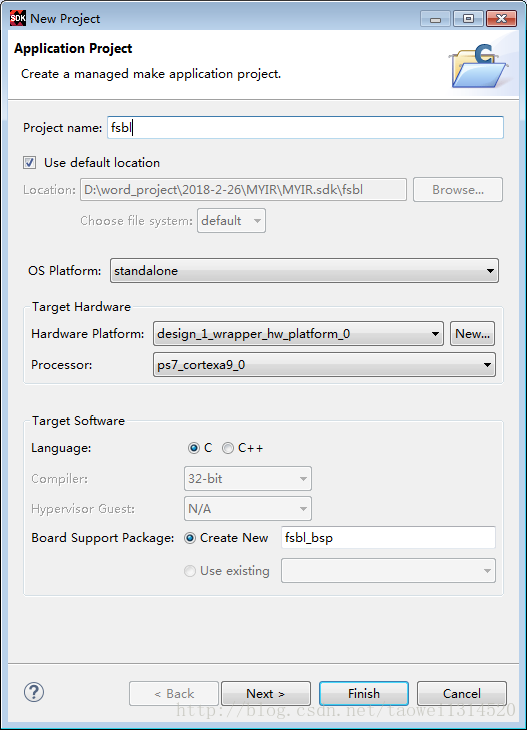
Step5 打开SDK,然后新建一个fsbl
点击Next
点击Finish
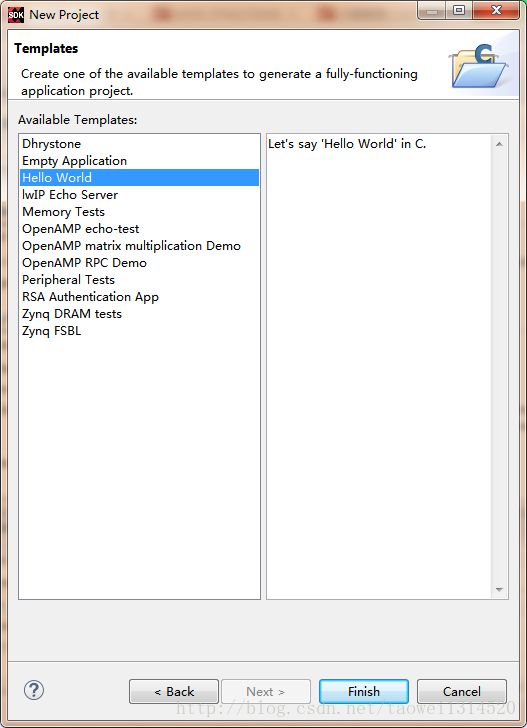
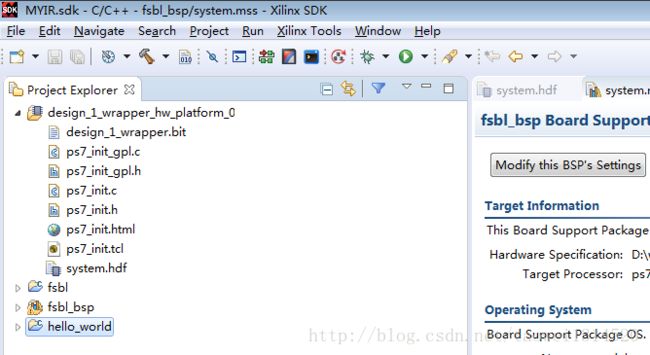
Step 6 新建一个hello_world模板工程
新建完成后如下图所示
下面是hello_world的主程序这里是写入16位起始地址0x00进行连续写和读
[html] view plain copy
- /******************************************************************************
- *
- * Copyright (C) 2009 - 2014 Xilinx, Inc. All rights reserved.
- *
- * Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
- * of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
- * in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
- * to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
- * copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
- * furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
- *
- * The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in
- * all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
- *
- * Use of the Software is limited solely to applications:
- * (a) running on a Xilinx device, or
- * (b) that interact with a Xilinx device through a bus or interconnect.
- *
- * THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
- * IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
- * FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL
- * XILINX BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY,
- * WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF
- * OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
- * SOFTWARE.
- *
- * Except as contained in this notice, the name of the Xilinx shall not be used
- * in advertising or otherwise to promote the sale, use or other dealings in
- * this Software without prior written authorization from Xilinx.
- *
- ******************************************************************************/
- /*
- * helloworld.c: simple test application
- *
- * This application configures UART 16550 to baud rate 9600.
- * PS7 UART (Zynq) is not initialized by this application, since
- * bootrom/bsp configures it to baud rate 115200
- *
- * ------------------------------------------------
- * | UART TYPE BAUD RATE |
- * ------------------------------------------------
- * uartns550 9600
- * uartlite Configurable only in HW design
- * ps7_uart 115200 (configured by bootrom/bsp)
- */
- #include
- #include "platform.h"
- #include "xil_printf.h"
- #include "sleep.h"
- #include "xiicps.h"
- XIicPs IicInstance; /* The instance of the IIC device. */
- #define IIC_DEVICE_ID XPAR_XIICPS_0_DEVICE_ID
- u8 WriteBuffer[2 + 1];
- u8 ReadBuffer[1]; /* Read buffer for reading a page. */
- struct sensor_register {
- u8 value;
- };
- static const struct sensor_register i2c_data[] = {
- { 0x00},
- { 0x00},
- { 0x04},
- { 0x01},
- { 0x11},
- { 0x02},
- { 0x3a},
- { 0x70},
- { 0x17},
- { 0x98},
- { 0x08},
- { 0x65},
- { 0x04},
- { 0x70},
- { 0x01},
- { 0xff},/* over */
- };
- int iic_master_init(void)
- {
- int Status;
- XIicPs_Config *ConfigPtr; /* Pointer to configuration data */
- ConfigPtr = XIicPs_LookupConfig(IIC_DEVICE_ID);
- if (ConfigPtr == NULL) {
- return XST_FAILURE;
- }
- Status = XIicPs_CfgInitialize(&IicInstance, ConfigPtr,
- ConfigPtr->BaseAddress);
- if (Status != XST_SUCCESS) {
- return XST_FAILURE;
- }
- XIicPs_SetSClk(&IicInstance, 400000);
- return XST_SUCCESS;
- }
- int iic_write_read_8(u8 Device_Address,u8 First_Word_Address,u8 Second_Word_address,u8 data)
- {
- int Status;
- WriteBuffer[0] = First_Word_Address;
- WriteBuffer[1] = Second_Word_address;
- WriteBuffer[2] = data;
- Status = XIicPs_MasterSendPolled(&IicInstance, WriteBuffer,
- 3, Device_Address>>1);
- if (Status != XST_SUCCESS) {
- return XST_FAILURE;
- }
- while (XIicPs_BusIsBusy(&IicInstance));
- usleep(2500);
- if (Status != XST_SUCCESS) {
- return XST_FAILURE;
- }
- WriteBuffer[0] = First_Word_Address;
- WriteBuffer[1] = Second_Word_address;
- Status = XIicPs_MasterSendPolled(&IicInstance, WriteBuffer,
- 2, Device_Address>>1);
- if (Status != XST_SUCCESS) {
- return XST_FAILURE;
- }
- while (XIicPs_BusIsBusy(&IicInstance));
- usleep(2500);
- Status = XIicPs_MasterRecvPolled(&IicInstance, ReadBuffer,
- 1, Device_Address>>1);
- if (Status != XST_SUCCESS) {
- return XST_FAILURE;
- }
- while (XIicPs_BusIsBusy(&IicInstance));
- xil_printf("0x%02x\r\n",ReadBuffer[0]);
- return 0;
- }
- int main(void)
- {
- int i;
- u8 Device_Address;
- u8 First_Word_Address;
- u8 Second_Word_address;
- Device_Address = 0xAE;
- First_Word_Address = 0x00;
- Second_Word_address = 0x00;
- i = 0;
- iic_master_init();
- while(1)
- {
- if(i2c_data[i].value==0xff)
- break;
- iic_write_read_8(Device_Address,First_Word_Address,Second_Word_address,i2c_data[i].value);
- i++;
- }
- return 0;
- }
[html] view plain copy
这两个i2c的读写程序都比较简单,这里只是简单的介绍下要注意的地方
这个主要是对master控制器进行初始化
[html] view plain copy
- iic_master_init();
初始化中主要主要注意:
[html] view plain copy
- ConfigPtr = XIicPs_LookupConfig(IIC_DEVICE_ID);
其中这个i2c的设备ID主要是看你用zynq哪个设备,一般都是用的i2c0、i2c1
XPAR_XIICPS_0_DEVICE_ID //对应i2c0
XPAR_XIICPS_1_DEVICE_ID //对应i2c1
下面的这段代码主要设置i2c的工作频率,我这里用的是400k
[html] view plain copy
- XIicPs_SetSClk(&IicInstance, 400000);
初始化完成后主要就是进行读写了,在读写之前要将进行的读写的数据进行缓冲,所以会用到Buffer
这个24c32的地址是16位,数据是8位,所以一共要用到3个Buffer进行缓冲
[html] view plain copy
- WriteBuffer[0] = First_Word_Address;
- WriteBuffer[1] = Second_Word_address;
- WriteBuffer[2] = data;
上面的是写的3个缓冲Buffer,这个是读的缓冲Buffer只有一个
[html] view plain copy
- ReadBuffer[0]
缓冲Buffer做完后就开始进行写,这里进行写的函数只要设置缓冲Buffer的个数以及所接的24C32的设备地址就可以了
[html] view plain copy
- Status = XIicPs_MasterSendPolled(&IicInstance, WriteBuffer,
- 3, Device_Address>>1);
当数据写完成后开始进行读,读分为两步:第一步写入你所要读的地址、第二步读这个地址里的数据
[html] view plain copy
- 1. Status = XIicPs_MasterSendPolled(&IicInstance, WriteBuffer,
- 2, Device_Address>>1);
[html] view plain copy
- 2. Status = XIicPs_MasterRecvPolled(&IicInstance, ReadBuffer,
- 1, Device_Address>>1);
这里是连续读写,所以开始写入16位的0x00的起始地址,然后对这个起始地址不断累加进行连续读
对特定地址进行读写和连续读写差不多,这里不再进行介绍
最后的这个是打印i2c读Buffer里的数据
[html] view plain copy
- xil_printf("0x%02x\r\n",ReadBuffer[0]);
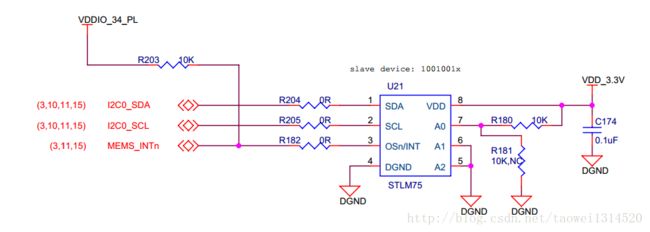
开发板环境:vivado 2017.1 ,开发板型号xc7z020clg400-1,这个工程主要用I2C接口读取STLM75的温度,
同时也会对其它的相关寄存器进行读写以验证程序的正确性。
下面的这个截图是STLM75的一些管脚介绍:
下面的截图是z-turn开发板上STLM75的硬件连接情况,可以看出这个STLM75的设备地址是 1001001×(最后一位是读写控制位)
Step1 新建vivado 工程后,调用zynq核并配置,这里主要配置了DDR、I2C
Step2 新建一个xdc文件
[html] view plain copy
- set_property PACKAGE_PIN P15 [get_ports iic_0_sda_io]
- set_property PACKAGE_PIN P16 [get_ports iic_0_scl_io]
- set_property IOSTANDARD LVCMOS33 [get_ports iic_0_scl_io]
- set_property IOSTANDARD LVCMOS33 [get_ports iic_0_sda_io]
- set_property PULLUP true [get_ports iic_0_scl_io]
- set_property PULLUP true [get_ports iic_0_sda_io]
这个STLM75是接在PL端所以用的emio来进行I2C的读写
Step3 进行综合、生成顶层文件,顶层文件如下所示(注意I2C一定要加下面的IOBUF)
[html] view plain copy
- //Copyright 1986-2017 Xilinx, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
- //--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- //Tool Version: Vivado v.2017.1 (win64) Build 1846317 Fri Apr 14 18:55:03 MDT 2017
- //Date : Mon Feb 26 18:28:07 2018
- //Host : taowei running 64-bit Service Pack 1 (build 7601)
- //Command : generate_target design_1_wrapper.bd
- //Design : design_1_wrapper
- //Purpose : IP block netlist
- //--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- `timescale 1 ps / 1 ps
- module design_1_wrapper
- (DDR_addr,
- DDR_ba,
- DDR_cas_n,
- DDR_ck_n,
- DDR_ck_p,
- DDR_cke,
- DDR_cs_n,
- DDR_dm,
- DDR_dq,
- DDR_dqs_n,
- DDR_dqs_p,
- DDR_odt,
- DDR_ras_n,
- DDR_reset_n,
- DDR_we_n,
- FIXED_IO_ddr_vrn,
- FIXED_IO_ddr_vrp,
- FIXED_IO_mio,
- FIXED_IO_ps_clk,
- FIXED_IO_ps_porb,
- FIXED_IO_ps_srstb,
- iic_0_scl_io,
- iic_0_sda_io);
- inout [14:0]DDR_addr;
- inout [2:0]DDR_ba;
- inout DDR_cas_n;
- inout DDR_ck_n;
- inout DDR_ck_p;
- inout DDR_cke;
- inout DDR_cs_n;
- inout [3:0]DDR_dm;
- inout [31:0]DDR_dq;
- inout [3:0]DDR_dqs_n;
- inout [3:0]DDR_dqs_p;
- inout DDR_odt;
- inout DDR_ras_n;
- inout DDR_reset_n;
- inout DDR_we_n;
- inout FIXED_IO_ddr_vrn;
- inout FIXED_IO_ddr_vrp;
- inout [53:0]FIXED_IO_mio;
- inout FIXED_IO_ps_clk;
- inout FIXED_IO_ps_porb;
- inout FIXED_IO_ps_srstb;
- inout iic_0_scl_io;
- inout iic_0_sda_io;
- wire [14:0]DDR_addr;
- wire [2:0]DDR_ba;
- wire DDR_cas_n;
- wire DDR_ck_n;
- wire DDR_ck_p;
- wire DDR_cke;
- wire DDR_cs_n;
- wire [3:0]DDR_dm;
- wire [31:0]DDR_dq;
- wire [3:0]DDR_dqs_n;
- wire [3:0]DDR_dqs_p;
- wire DDR_odt;
- wire DDR_ras_n;
- wire DDR_reset_n;
- wire DDR_we_n;
- wire FIXED_IO_ddr_vrn;
- wire FIXED_IO_ddr_vrp;
- wire [53:0]FIXED_IO_mio;
- wire FIXED_IO_ps_clk;
- wire FIXED_IO_ps_porb;
- wire FIXED_IO_ps_srstb;
- wire iic_0_scl_i;
- wire iic_0_scl_io;
- wire iic_0_scl_o;
- wire iic_0_scl_t;
- wire iic_0_sda_i;
- wire iic_0_sda_io;
- wire iic_0_sda_o;
- wire iic_0_sda_t;
- design_1 design_1_i
- (.DDR_addr(DDR_addr),
- .DDR_ba(DDR_ba),
- .DDR_cas_n(DDR_cas_n),
- .DDR_ck_n(DDR_ck_n),
- .DDR_ck_p(DDR_ck_p),
- .DDR_cke(DDR_cke),
- .DDR_cs_n(DDR_cs_n),
- .DDR_dm(DDR_dm),
- .DDR_dq(DDR_dq),
- .DDR_dqs_n(DDR_dqs_n),
- .DDR_dqs_p(DDR_dqs_p),
- .DDR_odt(DDR_odt),
- .DDR_ras_n(DDR_ras_n),
- .DDR_reset_n(DDR_reset_n),
- .DDR_we_n(DDR_we_n),
- .FIXED_IO_ddr_vrn(FIXED_IO_ddr_vrn),
- .FIXED_IO_ddr_vrp(FIXED_IO_ddr_vrp),
- .FIXED_IO_mio(FIXED_IO_mio),
- .FIXED_IO_ps_clk(FIXED_IO_ps_clk),
- .FIXED_IO_ps_porb(FIXED_IO_ps_porb),
- .FIXED_IO_ps_srstb(FIXED_IO_ps_srstb),
- .IIC_0_scl_i(iic_0_scl_i),
- .IIC_0_scl_o(iic_0_scl_o),
- .IIC_0_scl_t(iic_0_scl_t),
- .IIC_0_sda_i(iic_0_sda_i),
- .IIC_0_sda_o(iic_0_sda_o),
- .IIC_0_sda_t(iic_0_sda_t));
- IOBUF iic_0_scl_iobuf
- (.I(iic_0_scl_o),
- .IO(iic_0_scl_io),
- .O(iic_0_scl_i),
- .T(iic_0_scl_t));
- IOBUF iic_0_sda_iobuf
- (.I(iic_0_sda_o),
- .IO(iic_0_sda_io),
- .O(iic_0_sda_i),
- .T(iic_0_sda_t));
- endmodule
Step4 生成bit文件
Step5 点击菜单栏上的 File->Export->Export Hardware 导出硬件配置文件
Step 5 打开SDK,然后新建一个fsbl
Step 6 新建一个hello_world模板工程
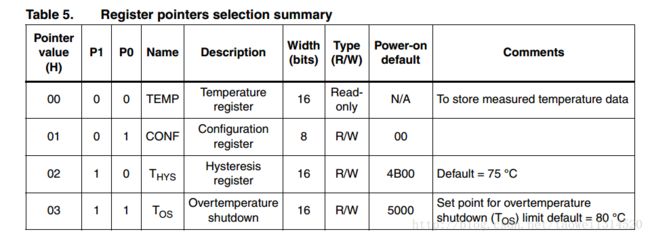
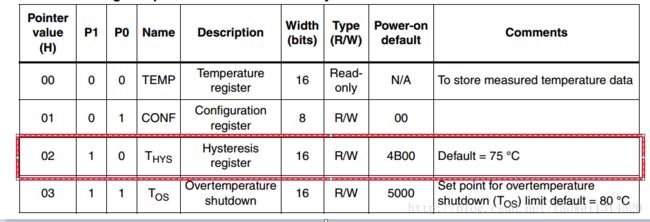
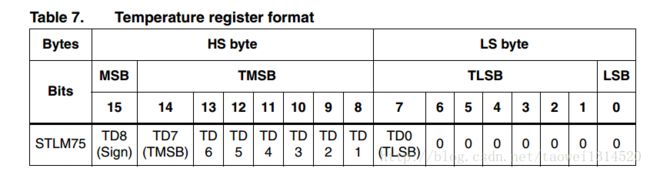
工程新建完成后,我们看手册可以看到这个STLM75一个有4个寄存器
当指针寄存器值不同时可以对不同的寄存器进行操作,当然这个指针寄存器上电后的初始状态是处在温度寄存器,指针寄存器数值:
00 可以对温度寄存器进行读(Temperature register)
01 可以对配置寄存器进行读写(Configuration register)
10 可以对滞后寄存器进行读写(Hysteresis register)
11 可以对超温阈值寄存器进行读写(Overtemperature shutdown)
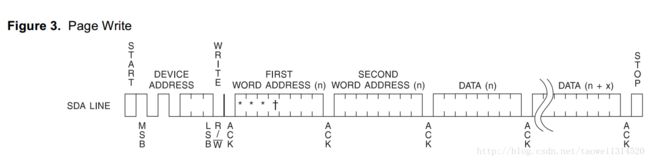
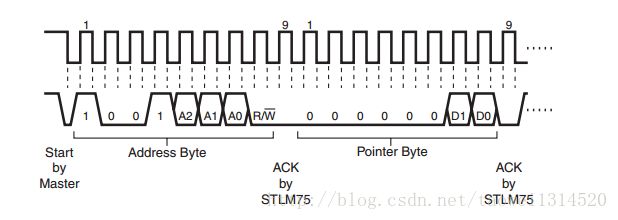
对这个指针寄存器进行写的波形图如下所示
这个D0和D1分别对应手册上的P0和P1,只要对指针寄存器写入不同的值就可以对上面四个寄存器进行访问
这个对指针寄存器进行写的过程中要注意这个D2~D7要都为0,D0和D1可以是00、01、10、11中的一个就行
我这里先对配置寄存器进行读,下面是hello_world工程的主程序
[html] view plain copy
- /******************************************************************************
- *
- * Copyright (C) 2009 - 2014 Xilinx, Inc. All rights reserved.
- *
- * Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
- * of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
- * in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
- * to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
- * copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
- * furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
- *
- * The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in
- * all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
- *
- * Use of the Software is limited solely to applications:
- * (a) running on a Xilinx device, or
- * (b) that interact with a Xilinx device through a bus or interconnect.
- *
- * THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
- * IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
- * FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL
- * XILINX BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY,
- * WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF
- * OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
- * SOFTWARE.
- *
- * Except as contained in this notice, the name of the Xilinx shall not be used
- * in advertising or otherwise to promote the sale, use or other dealings in
- * this Software without prior written authorization from Xilinx.
- *
- ******************************************************************************/
- /*
- * helloworld.c: simple test application
- *
- * This application configures UART 16550 to baud rate 9600.
- * PS7 UART (Zynq) is not initialized by this application, since
- * bootrom/bsp configures it to baud rate 115200
- *
- * ------------------------------------------------
- * | UART TYPE BAUD RATE |
- * ------------------------------------------------
- * uartns550 9600
- * uartlite Configurable only in HW design
- * ps7_uart 115200 (configured by bootrom/bsp)
- */
- #include
- #include "platform.h"
- #include "xil_printf.h"
- #include "sleep.h"
- #include "xiicps.h"
- XIicPs IicInstance; /* The instance of the IIC device. */
- #define IIC_DEVICE_ID XPAR_XIICPS_0_DEVICE_ID
- u8 WriteBuffer[1];
- u16 ReadBuffer[1]; /* Read buffer for reading a page. */
- int iic_master_init(void)
- {
- int Status;
- XIicPs_Config *ConfigPtr; /* Pointer to configuration data */
- ConfigPtr = XIicPs_LookupConfig(IIC_DEVICE_ID);
- if (ConfigPtr == NULL) {
- return XST_FAILURE;
- }
- Status = XIicPs_CfgInitialize(&IicInstance, ConfigPtr,
- ConfigPtr->BaseAddress);
- if (Status != XST_SUCCESS) {
- return XST_FAILURE;
- }
- XIicPs_SetSClk(&IicInstance, 400000);
- return XST_SUCCESS;
- }
- int iic_write_read_8(u8 Device_Address,u8 Pointer_Address)
- {
- int Status;
- WriteBuffer[0] = Pointer_Address; //0x01
- Status = XIicPs_MasterSendPolled(&IicInstance, WriteBuffer,
- 1, Device_Address>>1);
- if (Status != XST_SUCCESS) {
- return XST_FAILURE;
- }
- while (XIicPs_BusIsBusy(&IicInstance));
- usleep(2500);
- if (Status != XST_SUCCESS) {
- return XST_FAILURE;
- }
- Status = XIicPs_MasterRecvPolled(&IicInstance, ReadBuffer,
- 1, Device_Address>>1);
- if (Status != XST_SUCCESS) {
- return XST_FAILURE;
- }
- while (XIicPs_BusIsBusy(&IicInstance));
- xil_printf("0x%04x\r\n",ReadBuffer[0]);
- return 0;
- }
- int main(void)
- {
- u8 Device_Address;
- Device_Address = 0x93; //10010011
- iic_master_init();
- while(1)
- {
- iic_write_read_8(Device_Address,0x01);
- sleep(1);
- }
- return 0;
- }
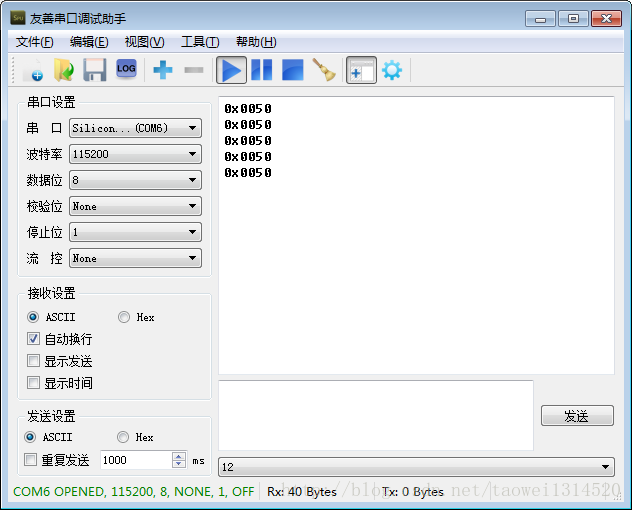
下面是打印的寄存器的值
可以看到和手册里的一致
接下来是对滞后寄存器进行读,下面是hello_world工程的主程序
[html] view plain copy
- /******************************************************************************
- *
- * Copyright (C) 2009 - 2014 Xilinx, Inc. All rights reserved.
- *
- * Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
- * of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
- * in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
- * to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
- * copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
- * furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
- *
- * The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in
- * all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
- *
- * Use of the Software is limited solely to applications:
- * (a) running on a Xilinx device, or
- * (b) that interact with a Xilinx device through a bus or interconnect.
- *
- * THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
- * IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
- * FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL
- * XILINX BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY,
- * WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF
- * OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
- * SOFTWARE.
- *
- * Except as contained in this notice, the name of the Xilinx shall not be used
- * in advertising or otherwise to promote the sale, use or other dealings in
- * this Software without prior written authorization from Xilinx.
- *
- ******************************************************************************/
- /*
- * helloworld.c: simple test application
- *
- * This application configures UART 16550 to baud rate 9600.
- * PS7 UART (Zynq) is not initialized by this application, since
- * bootrom/bsp configures it to baud rate 115200
- *
- * ------------------------------------------------
- * | UART TYPE BAUD RATE |
- * ------------------------------------------------
- * uartns550 9600
- * uartlite Configurable only in HW design
- * ps7_uart 115200 (configured by bootrom/bsp)
- */
- #include
- #include "platform.h"
- #include "xil_printf.h"
- #include "sleep.h"
- #include "xiicps.h"
- XIicPs IicInstance; /* The instance of the IIC device. */
- #define IIC_DEVICE_ID XPAR_XIICPS_0_DEVICE_ID
- u8 WriteBuffer[1];
- u16 ReadBuffer[1]; /* Read buffer for reading a page. */
- int iic_master_init(void)
- {
- int Status;
- XIicPs_Config *ConfigPtr; /* Pointer to configuration data */
- ConfigPtr = XIicPs_LookupConfig(IIC_DEVICE_ID);
- if (ConfigPtr == NULL) {
- return XST_FAILURE;
- }
- Status = XIicPs_CfgInitialize(&IicInstance, ConfigPtr,
- ConfigPtr->BaseAddress);
- if (Status != XST_SUCCESS) {
- return XST_FAILURE;
- }
- XIicPs_SetSClk(&IicInstance, 400000);
- return XST_SUCCESS;
- }
- int iic_write_read_8(u8 Device_Address,u8 Pointer_Address)
- {
- int Status;
- WriteBuffer[0] = Pointer_Address; //0x02
- Status = XIicPs_MasterSendPolled(&IicInstance, WriteBuffer,
- 1, Device_Address>>1);
- if (Status != XST_SUCCESS) {
- return XST_FAILURE;
- }
- while (XIicPs_BusIsBusy(&IicInstance));
- usleep(2500);
- if (Status != XST_SUCCESS) {
- return XST_FAILURE;
- }
- Status = XIicPs_MasterRecvPolled(&IicInstance, ReadBuffer,
- 1, Device_Address>>1);
- if (Status != XST_SUCCESS) {
- return XST_FAILURE;
- }
- while (XIicPs_BusIsBusy(&IicInstance));
- xil_printf("0x%04x\r\n",ReadBuffer[0]);
- return 0;
- }
- int main(void)
- {
- u8 Device_Address;
- Device_Address = 0x93; //10010011
- iic_master_init();
- while(1)
- {
- iic_write_read_8(Device_Address,0x02);
- sleep(1);
- }
- return 0;
- }
下面是打印的寄存器的值
可以看到和手册里的一致
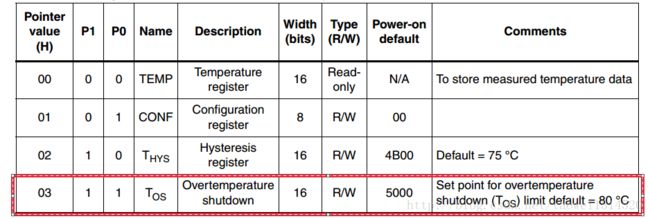
再对超温阈值寄存器进行读,下面是hello_world工程的主程序
[html] view plain copy
- /******************************************************************************
- *
- * Copyright (C) 2009 - 2014 Xilinx, Inc. All rights reserved.
- *
- * Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
- * of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
- * in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
- * to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
- * copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
- * furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
- *
- * The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in
- * all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
- *
- * Use of the Software is limited solely to applications:
- * (a) running on a Xilinx device, or
- * (b) that interact with a Xilinx device through a bus or interconnect.
- *
- * THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
- * IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
- * FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL
- * XILINX BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY,
- * WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF
- * OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
- * SOFTWARE.
- *
- * Except as contained in this notice, the name of the Xilinx shall not be used
- * in advertising or otherwise to promote the sale, use or other dealings in
- * this Software without prior written authorization from Xilinx.
- *
- ******************************************************************************/
- /*
- * helloworld.c: simple test application
- *
- * This application configures UART 16550 to baud rate 9600.
- * PS7 UART (Zynq) is not initialized by this application, since
- * bootrom/bsp configures it to baud rate 115200
- *
- * ------------------------------------------------
- * | UART TYPE BAUD RATE |
- * ------------------------------------------------
- * uartns550 9600
- * uartlite Configurable only in HW design
- * ps7_uart 115200 (configured by bootrom/bsp)
- */
- #include
- #include "platform.h"
- #include "xil_printf.h"
- #include "sleep.h"
- #include "xiicps.h"
- XIicPs IicInstance; /* The instance of the IIC device. */
- #define IIC_DEVICE_ID XPAR_XIICPS_0_DEVICE_ID
- u8 WriteBuffer[1];
- u16 ReadBuffer[1]; /* Read buffer for reading a page. */
- int iic_master_init(void)
- {
- int Status;
- XIicPs_Config *ConfigPtr; /* Pointer to configuration data */
- ConfigPtr = XIicPs_LookupConfig(IIC_DEVICE_ID);
- if (ConfigPtr == NULL) {
- return XST_FAILURE;
- }
- Status = XIicPs_CfgInitialize(&IicInstance, ConfigPtr,
- ConfigPtr->BaseAddress);
- if (Status != XST_SUCCESS) {
- return XST_FAILURE;
- }
- XIicPs_SetSClk(&IicInstance, 400000);
- return XST_SUCCESS;
- }
- int iic_write_read_8(u8 Device_Address,u8 Pointer_Address)
- {
- int Status;
- WriteBuffer[0] = Pointer_Address; //0x03
- Status = XIicPs_MasterSendPolled(&IicInstance, WriteBuffer,
- 1, Device_Address>>1);
- if (Status != XST_SUCCESS) {
- return XST_FAILURE;
- }
- while (XIicPs_BusIsBusy(&IicInstance));
- usleep(2500);
- if (Status != XST_SUCCESS) {
- return XST_FAILURE;
- }
- Status = XIicPs_MasterRecvPolled(&IicInstance, ReadBuffer,
- 1, Device_Address>>1);
- if (Status != XST_SUCCESS) {
- return XST_FAILURE;
- }
- while (XIicPs_BusIsBusy(&IicInstance));
- xil_printf("0x%04x\r\n",ReadBuffer[0]);
- return 0;
- }
- int main(void)
- {
- u8 Device_Address;
- Device_Address = 0x93; //10010011
- iic_master_init();
- while(1)
- {
- iic_write_read_8(Device_Address,0x03);
- sleep(1);
- }
- return 0;
- }
下面是打印的寄存器的值
可以看到和手册里的一致
从上面可以看出对前面的几个寄存器进行读出的数据和手册一样说明,这个I2C读写是正确的,
最后对温度寄存器进行读,下面是hello_world工程的主程序
[html] view plain copy
- /******************************************************************************
- *
- * Copyright (C) 2009 - 2014 Xilinx, Inc. All rights reserved.
- *
- * Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
- * of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
- * in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
- * to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
- * copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
- * furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
- *
- * The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in
- * all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
- *
- * Use of the Software is limited solely to applications:
- * (a) running on a Xilinx device, or
- * (b) that interact with a Xilinx device through a bus or interconnect.
- *
- * THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
- * IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
- * FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL
- * XILINX BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY,
- * WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF
- * OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
- * SOFTWARE.
- *
- * Except as contained in this notice, the name of the Xilinx shall not be used
- * in advertising or otherwise to promote the sale, use or other dealings in
- * this Software without prior written authorization from Xilinx.
- *
- ******************************************************************************/
- /*
- * helloworld.c: simple test application
- *
- * This application configures UART 16550 to baud rate 9600.
- * PS7 UART (Zynq) is not initialized by this application, since
- * bootrom/bsp configures it to baud rate 115200
- *
- * ------------------------------------------------
- * | UART TYPE BAUD RATE |
- * ------------------------------------------------
- * uartns550 9600
- * uartlite Configurable only in HW design
- * ps7_uart 115200 (configured by bootrom/bsp)
- */
- #include
- #include "platform.h"
- #include "xil_printf.h"
- #include "sleep.h"
- #include "xiicps.h"
- XIicPs IicInstance; /* The instance of the IIC device. */
- #define IIC_DEVICE_ID XPAR_XIICPS_0_DEVICE_ID
- u8 WriteBuffer[1];
- u16 ReadBuffer[1]; /* Read buffer for reading a page. */
- int iic_master_init(void)
- {
- int Status;
- XIicPs_Config *ConfigPtr; /* Pointer to configuration data */
- ConfigPtr = XIicPs_LookupConfig(IIC_DEVICE_ID);
- if (ConfigPtr == NULL) {
- return XST_FAILURE;
- }
- Status = XIicPs_CfgInitialize(&IicInstance, ConfigPtr,
- ConfigPtr->BaseAddress);
- if (Status != XST_SUCCESS) {
- return XST_FAILURE;
- }
- XIicPs_SetSClk(&IicInstance, 400000);
- return XST_SUCCESS;
- }
- int iic_write_read_8(u8 Device_Address,u8 Pointer_Address)
- {
- int Status;
- WriteBuffer[0] = Pointer_Address; //0x00
- Status = XIicPs_MasterSendPolled(&IicInstance, WriteBuffer,
- 1, Device_Address>>1);
- if (Status != XST_SUCCESS) {
- return XST_FAILURE;
- }
- while (XIicPs_BusIsBusy(&IicInstance));
- usleep(2500);
- if (Status != XST_SUCCESS) {
- return XST_FAILURE;
- }
- Status = XIicPs_MasterRecvPolled(&IicInstance, ReadBuffer,
- 1, Device_Address>>1);
- if (Status != XST_SUCCESS) {
- return XST_FAILURE;
- }
- while (XIicPs_BusIsBusy(&IicInstance));
- xil_printf("0x%04x\r\n",ReadBuffer[0]);
- return 0;
- }
- int main(void)
- {
- u8 Device_Address;
- Device_Address = 0x93; //10010011
- iic_master_init();
- while(1)
- {
- iic_write_read_8(Device_Address,0x00);
- sleep(1);
- }
- return 0;
- }
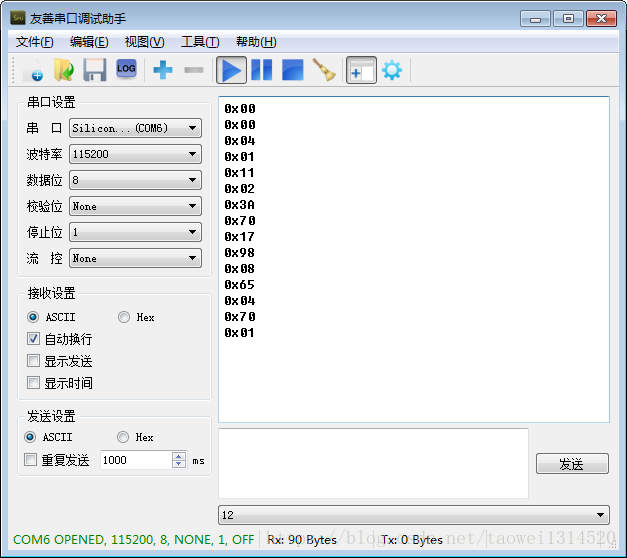
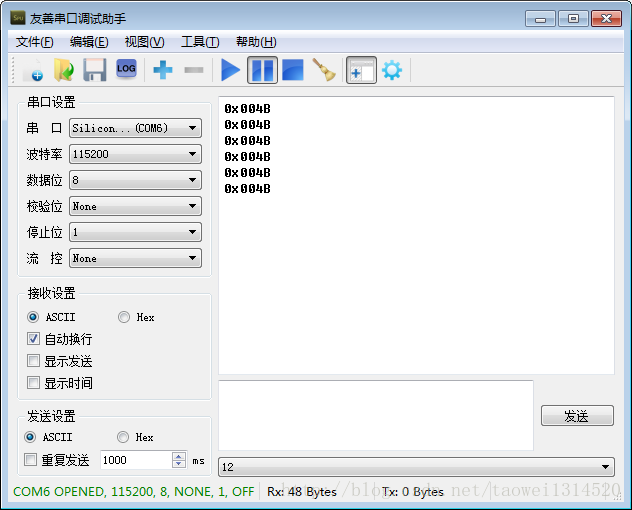
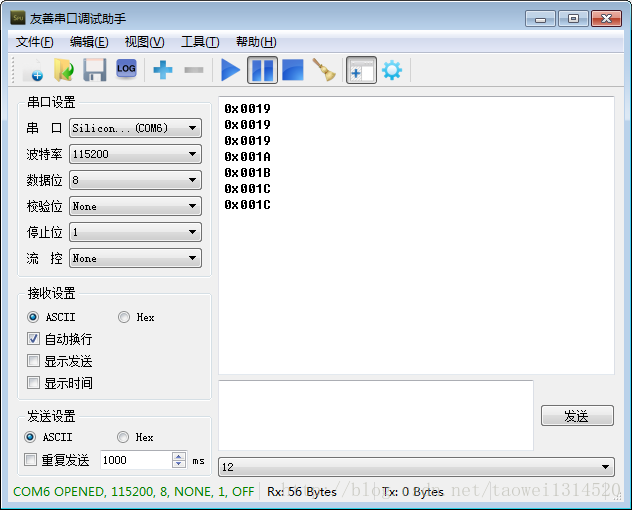
下面是打印的寄存器的值
今天天气预报差不多是11度左右,将0x0019十六进制数化为10进制是25再除2差不多是12.5度这是在屋内所以差不多
之后我将手放到STLM75上可以看到温度从0x0019上升到0x001A说明温度是在上升的。
我们再看这个温度寄存器0x0019的最高位是0所以温度是一个正的温度