springcloud实现负载均衡的方式 与 手写ribbon负载均衡器
1 负载均衡简述
1.什么是负载均衡
Load balancing,即负载均衡,是一种计算机技术,用来在多个计算机(计算机集群)、网络连接、CPU、磁盘驱动器或其他资源中分配负载,以达到最优化资源使用、最大化吞吐率、最小化响应时间、同时避免过载的目的。
2.为什么需要负载均衡
五个窗口排队买电影票,人们肯定是看着哪个队人少就去哪个队,然后最后的结果就是每个队伍长度都差不多,这就形成了一种均衡的状态,在计算机技术上来讲,这个就可以形象的比喻成负载均衡
1.1 集中式LB 和 进程内LB
负载均衡分为两种
集中式LB
在服务的消费方和提供方之间使用独立的LB设施(可以是硬件,也可以是软件,比如nginx),由该设施负责把访问请求通过某种策略转发至服务的提供方
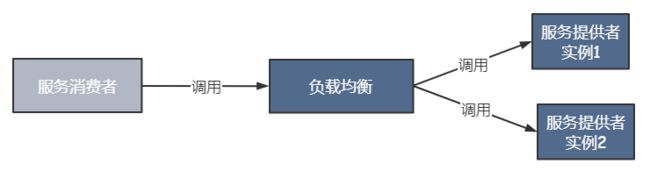
进程内LB
将LB逻辑集成到消费方,消费方从注册中心直到哪些地址可用,然后再从这些地址中选择一个合适的进行使用
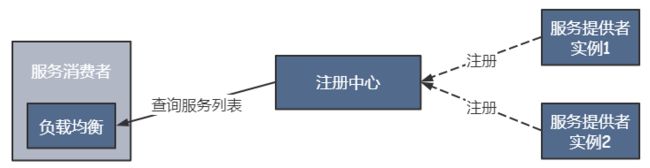
Ribbon属于进程内LB,是一个类库,继承于消费方进程,消费方通过它来获取到服务提供方的地址
2 ribbon 简述
springcloud中提供了一系列的组件,我们使用ribbon实现负载均衡,eureka中也内置了ribbon,所以,引入了eureka其实就可以直接使用ribbon了
ribbon中的负载均衡用在客户端,或者说成消费端也可以,在消费者访问提供者时,就会进行负载均衡算法,然后找到一个最优的提供者提供服务
2.1 ribbon 的核心组件(接口)
ServerList :用于获取地址列表。它既可以是静态的(提供一组固定的地址),也可以是动态的(从注册中心中定期查询地址列表)。
ServerListFilter :仅当使用动态ServerList时使用,用于在原始的服务列表中使用一定策略过虑掉一部分地址。
IRule :选择一个最终的服务地址作为LB结果。选择策略有轮询、根据响应时间加权、断路器(当Hystrix可用时)等。
Ribbon 在工作时首选会通过 ServerList 来获取所有可用的服务列表,然后通过 ServerListFilter 过虑掉一部分地址,最后在剩下的地址中通过 IRule 选择出一台服务器作为最终结果。
2.2 ribbon 自带的负载均衡算法
这些算法全都在 com.netflix.loadbalancer 包下
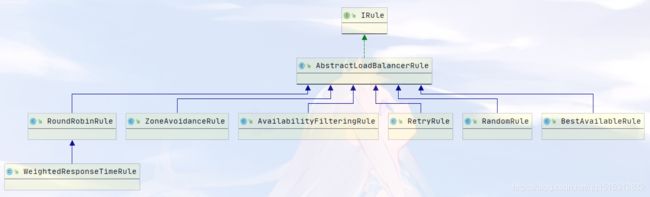
| 策略名 | 策略声明 | 策略描述 | 实现说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| BestAvailableRule | public class BestAvailableRule extends ClientConfigEnabledRoundRobinRule | 选择一个最小的并发请求的server | 逐个考察Server,如果Server被tripped了,则忽略,在选择其中ActiveRequestsCount最小的server |
| AvailabilityFilteringRule | public class AvailabilityFilteringRule extends PredicateBasedRule | 过滤掉那些因为一直连接失败的被标记为circuit tripped的后端server,并过滤掉那些高并发的的后端server(active connections 超过配置的阈值) | 使用一个AvailabilityPredicate来包含过滤server的逻辑,其实就就是检查status里记录的各个server的运行状态 |
| WeightedResponseTimeRule | public class WeightedResponseTimeRule extends RoundRobinRule | 根据相应时间分配一个weight,相应时间越长,weight越小,被选中的可能性越低。 | 一个后台线程定期的从status里面读取评价响应时间,为每个server计算一个weight。Weight的计算也比较简单responsetime 减去每个server自己平均的responsetime是server的权重。当刚开始运行,没有形成statas时,使用roubine策略选择server。 |
| RetryRule | public class RetryRule extends AbstractLoadBalancerRule | 对选定的负载均衡策略机上重试机制。 | 在一个配置时间段内当选择server不成功,则一直尝试使用subRule的方式选择一个可用的server |
| RoundRobinRule | public class RoundRobinRule extends AbstractLoadBalancerRule | 简单轮询服务列表来选择服务器。它是Ribbon默认的负载均衡规则。 | 轮询index,选择index对应位置的server |
| RandomRule | public class RandomRule extends AbstractLoadBalancerRule | 随机选择一个server | 在index上随机,选择index对应位置的server |
| ZoneAvoidanceRule | public class ZoneAvoidanceRule extends PredicateBasedRule | 复合判断server所在区域的性能和server的可用性选择server | 使用ZoneAvoidancePredicate和AvailabilityPredicate来判断是否选择某个server,前一个判断判定一个zone的运行性能是否可用,剔除不可用的zone(的所有server),AvailabilityPred |
3 ribbon 随机负载均衡的实现
3.1 添加消费者模块 cloud-consumer-order-8010
3.1.1 pom.xml
版本号来自父项目,这里主要做介绍
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.bananagroupId>
<artifactId>cloud-api-commonsartifactId>
<version>${project.version}version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuatorartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombokgroupId>
<artifactId>lombokartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloudgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-clientartifactId>
dependency>
dependencies>
3.1.2 启动类
package com.banana.cloud;
import com.banana.cloud.myrule.MySelfRule;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.loadbalancer.LoadBalanced;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.EnableEurekaClient;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.ribbon.RibbonClient;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaClient
@RibbonClient(name = "CLOUD-PROVIDER-PAYMENT-SERVICE", configuration = MySelfRule.class)
public class ProviderPaymentApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ProviderPaymentApplication.class, args);
}
}
3.1.3 注入 RestTemplate
package com.banana.cloud.config;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.loadbalancer.LoadBalanced;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
@Configuration
public class ApplicationContextConfig {
@Bean
@LoadBalanced
public RestTemplate restTemplate() {
return new RestTemplate();
}
}
3.1.4 添加自定义规则类 MySelfRule
package com.banana.cloud.myrule;
import com.netflix.loadbalancer.IRule;
import com.netflix.loadbalancer.RandomRule;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class MySelfRule {
@Bean
public IRule myRule() {
return new RandomRule();
}
}
3.1.5 PaymentController
@Slf4j
@RestController
public class PaymentController {
public static final String PAYMENT_URL = "http://CLOUD-PROVIDER-PAYMENT-SERVICE";
@Resource
private RestTemplate restTemplate;
@Value("${server.port}")
private String serverPort;
@GetMapping(value = "/consumer/payment/get/{id}")
public ResultMsg<Payment> getPaymentById(@PathVariable("id") Long id) {
return restTemplate.getForObject(PAYMENT_URL + "/payment/get/" + id, ResultMsg.class);
}
}
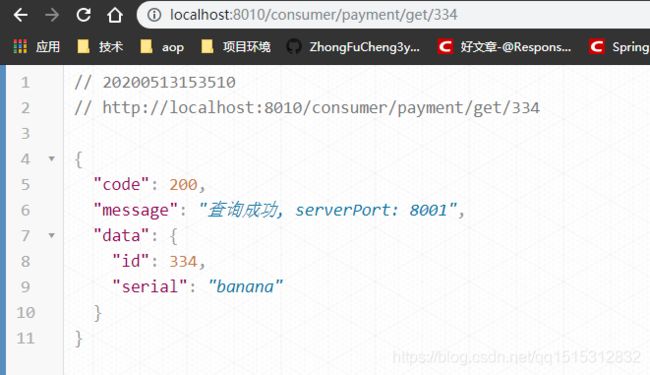
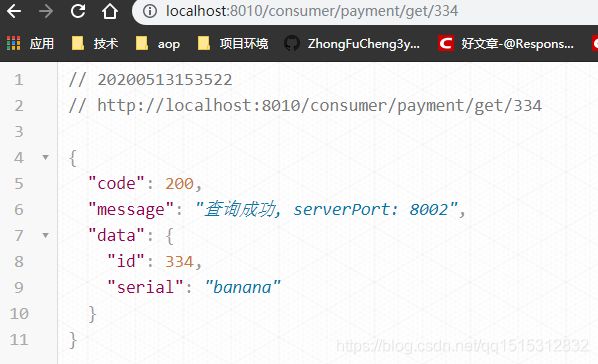
3.2 测试
访问controller中的接口,8001和8002随机出现,达到了我们所需要的效果
4 手写ribbon负载均衡器
4.1 添加 LoadBalancer 接口
package com.banana.cloud.lb;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.ServiceInstance;
import java.util.List;
public interface LoadBalancer {
ServiceInstance instances(List<ServiceInstance> serviceInstances);
}
4.2 均衡器类
维护一个原子整形 AtomicInteger,用来记录访问的次数
获取到总的服务数量,用访问的次数,对服务数量取模,就可以得到定向到的服务,以此达到负载均衡
也就是:接口请求次数 % 服务集群数量 = 调用服务下标
package com.banana.cloud.lb;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.ServiceInstance;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
@Component
public class MyLB implements LoadBalancer {
private AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger(0);
public final int getAndIncrement() {
int cur;
int next;
do {
cur = this.atomicInteger.get();
next = cur >= Integer.MAX_VALUE ? 0 : cur + 1;
} while (!this.atomicInteger.compareAndSet(cur, next));
System.out.println("***第几次访问,次数next: " + next);
return next;
}
@Override
public ServiceInstance instances(List<ServiceInstance> serviceInstances) {
int index = getAndIncrement() % serviceInstances.size();
return serviceInstances.get(index);
}
}
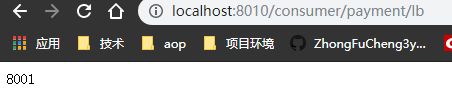
4.3 在 controller 中添加负载均衡测试的接口
@Slf4j
@RestController
public class PaymentController {
@Resource
private RestTemplate restTemplate;
@Resource
private LoadBalancer loadBalancer;
@GetMapping(value = "/consumer/payment/lb")
public String getPaymentLB() {
List<ServiceInstance> instances = discoveryClient.getInstances("CLOUD-PROVIDER-PAYMENT-SERVICE");
if (instances == null || instances.size() <= 0) return null;
ServiceInstance serviceInstance = loadBalancer.instances(instances);
URI uri = serviceInstance.getUri();
return restTemplate.getForObject(uri + "/payment/lb", String.class);
}
}