从思想到架构之路(ArrayList源码解析)
1、概述
想想进入行业已经快3年半了,一开始学编程真的很痛苦,从打字到C语言入门,然后再html,C#,再到java,这一步走来是多么不容易!程序员真是夜以继日,日理万机,每天得想着如何解决工作中的问题又要吸收新的知识点来充实自己,在这样的环境下,我们通宵达旦,废寝忘食地挖掘底层知识。说了这么多,事实就是想装逼一下。当然装逼归装逼,我想表达的就是套路是永远不变的,学习一门语言,思想都是相通的。例如23种设计模式,6大抽象原则。所以我接下来想从思想锻炼自己,以后遇到问题就有思路去解决问题或自己创造问题了。所以数据结构是我们必修之课。
看完我这篇博客你将学会:
ArrayList集合源码思想采用方式
LinkedList集合源码思想采用方式
在解析源码之前我们需要了解几个东西
1.System.arraycopy意在复制集合
arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos, Object dst, int dstPos, int length);
<< : 左移运算符,num << 1,相当于num乘以2 假设num = 3,那么左移之后为3*2
>> : 右移运算符,num >> 1,相当于num除以2 假设num = 3,那么左移之后为3/2
如果有什么疑问可以看这篇文章:http://www.cnblogs.com/hongten/p/hongten_java_yiweiyunsuangfu.html
3.优化ArrayList集合添加效率
http://java-admin.iteye.com/blog/1061499
2、ArrayList集合源码思想采用方式
ArrayList集合有三个构造函数:
第一个:初始化一个大小为capacity的数组
// 将大小为size的集合初始化
// 假如a的类非Object数组的类就重新创建一个数组
if (a.getClass() != Object[].class) {
Object[] newArray = new Object[a.length];
System.arraycopy(a, 0, newArray, 0, a.length);
a = newArray;
}
array = a;
size = a.length;
}
接下来我们将增删改查:
第一个是增加对象:
1、add(E object)
源码解析:
解析方法组装思路:如何添加一个对象的呢?
Object[] a = array;
int s = size;
首先在方法内获取全局数组对象,数组长度,这是为了防止数据脏读。
if (s == a.length)
这个是当添加的长度等于开辟数组空间的大小时就重新加大开辟空间
a[s] = object;
size = s + 1;
modCount++;
我们可以假设size一开始为0,那么a[0] = object,size = 0 + 1,这样代表为数组赋值,赋值完成后长度 + 1。
刚开始的时候长度为0
if (s == a.length) {
Object[] newArray = new Object[s +
(s < (MIN_CAPACITY_INCREMENT / 2) ?
MIN_CAPACITY_INCREMENT : s >> 1)];
System.arraycopy(a, 0, newArray, 0, s);
array = a = newArray;
}
上面是开辟一个数组空间,s + (s < (MIN_CAPACITY_INCREMENT / 2) ? MIN_CAPACITY_INCREMENT : s >> 1),刚开始size为0,那么开辟的数组大小为MIN_CAPACITY_INCREMENT,则开辟空间为12,当下一次空间大于12之时,空间会扩大s >> 1,原本大小的一半。
System.arraycopy(a, 0, newArray, 0, s);
将开辟的空间把a对象从0~size复制到newArray中
array = a = newArray;
然后把newArray再赋值给array,表示重新开辟空间,到此整个add就结束了。
源码解析:
这个位置添加对象与上面的添加对象相似
if (s < a.length) {
System.arraycopy(a, index, a, index + 1, s - index);
} else {
// assert s == a.length;
Object[] newArray = new Object[newCapacity(s)];
System.arraycopy(a, 0, newArray, 0, index);
System.arraycopy(a, index, newArray, index + 1, s - index);
array = a = newArray;
}
当添加的长度还没有大过于开辟空间的大小之时
System.arraycopy(a, index, a, index + 1, s - index);
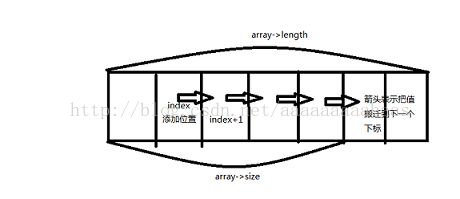
由上图可知,将index往后移一位。
a[index] = object;将object放到index位置
如果长度大于开辟的空间
private static int newCapacity(int currentCapacity) {
int increment = (currentCapacity < (MIN_CAPACITY_INCREMENT / 2) ?
MIN_CAPACITY_INCREMENT : currentCapacity >> 1);
return currentCapacity + increment;
}
Object[] newArray = new Object[newCapacity(s)];
System.arraycopy(a, 0, newArray, 0, index);
System.arraycopy(a, index, newArray, index + 1, s - index);
array = a = newArray;
与之前的添加方法一样,先开辟一个空间然后在index位置往后移一位。
源码解说:
假如数组的长度为0时候则不执行添加
Object[] newPart = collection.toArray();
int newPartSize = newPart.length;
if (newPartSize == 0) {
return false;
}
以下是添加数组,首先是扩充的总长度大小
int newSize = s + newPartSize;
如果总长度比开辟空间的长度还大的时候
if (newSize > a.length)
以总长度的容量重新开辟一个空间
int newCapacity = newCapacity(newSize - 1);
Object[] newArray = new Object[newCapacity];
// 把a的内容复制到newArray数组中
System.arraycopy(a, 0, newArray, 0, s);
// 然后把新开辟出来的数组重新赋值给数组
array = a = newArray;
// 把要添加的数组添加至原先数组从size位置至newPartSize+size
System.arraycopy(newPart, 0, a, s, newPartSize);
源码解说:
这个方法跟前面的add(int index, E object)相似,我就大致说一下步骤
计算添加后总长度
判断添加后总长度是否大于数组长度,如果总长度小于数组长度则向后移动newPartSize个位置
如果添加总长度比数组的长度大,那么需要重新开辟一个大小为(总长度+总长度/2)的空间数组,然后再向后移动newPartSize个位置
最后把要添加的数组添加至之前的数组中
源码解说:
通过Arrays.fill(array, 0, size, null)这个把array数组从0~size填null值表示清空数组
源码解说:
由于ArrayList是实现了Cloneable,所以可以将本地的对象进行克隆获取数组
源码解说:
这个方法很有意思,我们来看看网上怎么说的?
我们在使用Arraylist时,经常要对它进行初始化工作,在使用add()方法增加新的元素时,如果要增加的数据量很大,应该使用ensureCapacity()方法,该方法的作用是预先设置Arraylist的大小,这样可以大大提高初始化速度。
意思代表着要执行add()方法添加对象之前可以使用ensureCapacity这个进行设置数组的初始化对象数组进行优化,它的好处就是让你在添加对象可以加快速度添加
源码解说:
这个简单,就是获取array下的下标对象
源码解说:
这个方法是查询操作,查询数组中是否包含object
源码解说:
这个方法是查询对象object的位置,如果查询不到就返回-1表示没有该对象
源码解说:
这个方法是从尾往前查询对象,如果查询不到就返回-1表示没有该对象
源码解说:
假如一个数组要删除某个位置你会怎么做呢?我画个图给你们看
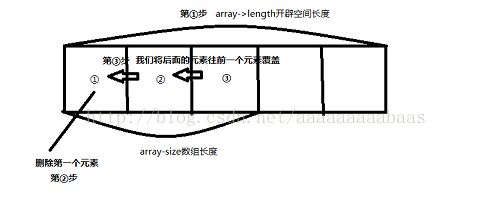
只要将index后面的数据往前移动一位就可以删除
a[s] = null;然后再把最后元素置空
下面是一个例子:
String[] ids = { "1", "2", "3", "4", "5", "6", "7", "0", "0" };
int index = 0;
int s = 7;
System.arraycopy(ids, index + 1, ids, index, --s - index);
ids[s] = "0";
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ids) + "-" + s);
[2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 0, 0, 0]
假如要移除一个对象,那么需要查询是否包含该对象,如果包含该对象,那么用上面的方法进行覆盖,移除该对象,我们看到该方法有个惊奇的判断if (a[i] == null),假如我们要删除一个数组里面所有对象为null的值时,只要remove(null)就可以了。
源码解说:
该方法用于删除一个连续的数据
主要部分:
System.arraycopy(a, toIndex, a, fromIndex, s - toIndex);
int rangeSize = toIndex - fromIndex;
Arrays.fill(a, s - rangeSize, s, null);
size = s - rangeSize;
先删除从fromIndex覆盖到toIndex位置
接着获取删除的数量
然后将后面的数据置空
最后长度减rangeSize
源码解说:
a[index] = object;通过这个修改数据
int N = 10;
ArrayList list = new ArrayList();
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
list.add(i + "---");
}
Iterator iterator = list.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
那么这个迭代器它是怎么做的呢?我们一探究竟
public Iterator iterator() {
return new ArrayListIterator();
}
这个方法初始化迭代器
将数组的长度获取到,遍历到的索引位置
private int remaining = size;
private int removalIndex = -1;
通过hasNext来判断该迭代器剩下的个数是否已经到结束
public boolean hasNext() {
return remaining != 0;
}
那么遍历中通过什么来获取呢?next方法
remaining = rem - 1,获取一次数据将剩余量-1
ourList.array[removalIndex = ourList.size - rem],从头到尾遍历,这样达到循环一次获取一次数据的目的。
最后剩下一个remove方法,这个方法是做什么的呢?跟ArrayList的remove(index)一样,从头到尾删除
想想进入行业已经快3年半了,一开始学编程真的很痛苦,从打字到C语言入门,然后再html,C#,再到java,这一步走来是多么不容易!程序员真是夜以继日,日理万机,每天得想着如何解决工作中的问题又要吸收新的知识点来充实自己,在这样的环境下,我们通宵达旦,废寝忘食地挖掘底层知识。说了这么多,事实就是想装逼一下。当然装逼归装逼,我想表达的就是套路是永远不变的,学习一门语言,思想都是相通的。例如23种设计模式,6大抽象原则。所以我接下来想从思想锻炼自己,以后遇到问题就有思路去解决问题或自己创造问题了。所以数据结构是我们必修之课。
看完我这篇博客你将学会:
ArrayList集合源码思想采用方式
LinkedList集合源码思想采用方式
在解析源码之前我们需要了解几个东西
1.System.arraycopy意在复制集合
int[] ids = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 };
int index = 0;
int s = 5;
System.arraycopy(ids, index, ids, index + 1, s - index);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ids)); // [1, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5]arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos, Object dst, int dstPos, int length);
- 第一个参数:
- src:将复制的对象
- 第二个参数:
- srcPos:复制起点
- 第三个参数:
- dst:粘贴对象
- 第四个参数:
- dstPos:粘贴起点
- 第五个参数:
- length:复制的长度
<< : 左移运算符,num << 1,相当于num乘以2 假设num = 3,那么左移之后为3*2
>> : 右移运算符,num >> 1,相当于num除以2 假设num = 3,那么左移之后为3/2
如果有什么疑问可以看这篇文章:http://www.cnblogs.com/hongten/p/hongten_java_yiweiyunsuangfu.html
3.优化ArrayList集合添加效率
http://java-admin.iteye.com/blog/1061499
2、ArrayList集合源码思想采用方式
private static final int MIN_CAPACITY_INCREMENT = 12;
int size;
transient Object[] array;ArrayList集合有三个构造函数:
第一个:初始化一个大小为capacity的数组
public ArrayList(int capacity) {
if (capacity < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("capacity < 0: " + capacity);
}
array = (capacity == 0 ? EmptyArray.OBJECT : new Object[capacity]);
}public ArrayList() {
array = EmptyArray.OBJECT;
}// 将大小为size的集合初始化
@Override
public Object[] toArray() {
int s = size;
Object[] result = new Object[s];
System.arraycopy(array, 0, result, 0, s);
return result;
}public ArrayList(Collection collection) {
if (collection == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("collection == null");
}
}// 假如a的类非Object数组的类就重新创建一个数组
if (a.getClass() != Object[].class) {
Object[] newArray = new Object[a.length];
System.arraycopy(a, 0, newArray, 0, a.length);
a = newArray;
}
array = a;
size = a.length;
}
接下来我们将增删改查:
第一个是增加对象:
1、add(E object)
源码解析:
解析方法组装思路:如何添加一个对象的呢?
Object[] a = array;
int s = size;
首先在方法内获取全局数组对象,数组长度,这是为了防止数据脏读。
if (s == a.length)
这个是当添加的长度等于开辟数组空间的大小时就重新加大开辟空间
a[s] = object;
size = s + 1;
modCount++;
我们可以假设size一开始为0,那么a[0] = object,size = 0 + 1,这样代表为数组赋值,赋值完成后长度 + 1。
刚开始的时候长度为0
if (s == a.length) {
Object[] newArray = new Object[s +
(s < (MIN_CAPACITY_INCREMENT / 2) ?
MIN_CAPACITY_INCREMENT : s >> 1)];
System.arraycopy(a, 0, newArray, 0, s);
array = a = newArray;
}
上面是开辟一个数组空间,s + (s < (MIN_CAPACITY_INCREMENT / 2) ? MIN_CAPACITY_INCREMENT : s >> 1),刚开始size为0,那么开辟的数组大小为MIN_CAPACITY_INCREMENT,则开辟空间为12,当下一次空间大于12之时,空间会扩大s >> 1,原本大小的一半。
System.arraycopy(a, 0, newArray, 0, s);
将开辟的空间把a对象从0~size复制到newArray中
array = a = newArray;
然后把newArray再赋值给array,表示重新开辟空间,到此整个add就结束了。
@Override
public boolean add(E object) {
Object[] a = array;
int s = size;
if (s == a.length) {
Object[] newArray = new Object[s +
(s < (MIN_CAPACITY_INCREMENT / 2) ?
MIN_CAPACITY_INCREMENT : s >> 1)];
System.arraycopy(a, 0, newArray, 0, s);
array = a = newArray;
}
a[s] = object;
size = s + 1;
modCount++;
return true;
}源码解析:
这个位置添加对象与上面的添加对象相似
if (s < a.length) {
System.arraycopy(a, index, a, index + 1, s - index);
} else {
// assert s == a.length;
Object[] newArray = new Object[newCapacity(s)];
System.arraycopy(a, 0, newArray, 0, index);
System.arraycopy(a, index, newArray, index + 1, s - index);
array = a = newArray;
}
当添加的长度还没有大过于开辟空间的大小之时
System.arraycopy(a, index, a, index + 1, s - index);

由上图可知,将index往后移一位。
a[index] = object;将object放到index位置
如果长度大于开辟的空间
private static int newCapacity(int currentCapacity) {
int increment = (currentCapacity < (MIN_CAPACITY_INCREMENT / 2) ?
MIN_CAPACITY_INCREMENT : currentCapacity >> 1);
return currentCapacity + increment;
}
Object[] newArray = new Object[newCapacity(s)];
System.arraycopy(a, 0, newArray, 0, index);
System.arraycopy(a, index, newArray, index + 1, s - index);
array = a = newArray;
与之前的添加方法一样,先开辟一个空间然后在index位置往后移一位。
@Override
public void add(int index, E object) {
Object[] a = array;
int s = size;
if (index > s || index < 0) {
throwIndexOutOfBoundsException(index, s);
}
if (s < a.length) {
System.arraycopy(a, index, a, index + 1, s - index);
} else {
// assert s == a.length;
Object[] newArray = new Object[newCapacity(s)];
System.arraycopy(a, 0, newArray, 0, index);
System.arraycopy(a, index, newArray, index + 1, s - index);
array = a = newArray;
}
a[index] = object;
size = s + 1;
modCount++;
}源码解说:
假如数组的长度为0时候则不执行添加
Object[] newPart = collection.toArray();
int newPartSize = newPart.length;
if (newPartSize == 0) {
return false;
}
以下是添加数组,首先是扩充的总长度大小
int newSize = s + newPartSize;
如果总长度比开辟空间的长度还大的时候
if (newSize > a.length)
以总长度的容量重新开辟一个空间
int newCapacity = newCapacity(newSize - 1);
Object[] newArray = new Object[newCapacity];
// 把a的内容复制到newArray数组中
System.arraycopy(a, 0, newArray, 0, s);
// 然后把新开辟出来的数组重新赋值给数组
array = a = newArray;
// 把要添加的数组添加至原先数组从size位置至newPartSize+size
System.arraycopy(newPart, 0, a, s, newPartSize);
@Override
public boolean addAll(Collection collection) {
Object[] newPart = collection.toArray();
int newPartSize = newPart.length;
if (newPartSize == 0) {
return false;
}
Object[] a = array;
int s = size;
int newSize = s + newPartSize; // If add overflows, arraycopy will fail
if (newSize > a.length) {
int newCapacity = newCapacity(newSize - 1); // ~33% growth room
Object[] newArray = new Object[newCapacity];
System.arraycopy(a, 0, newArray, 0, s);
array = a = newArray;
}
System.arraycopy(newPart, 0, a, s, newPartSize);
size = newSize;
modCount++;
return true;
}源码解说:
这个方法跟前面的add(int index, E object)相似,我就大致说一下步骤
计算添加后总长度
判断添加后总长度是否大于数组长度,如果总长度小于数组长度则向后移动newPartSize个位置
如果添加总长度比数组的长度大,那么需要重新开辟一个大小为(总长度+总长度/2)的空间数组,然后再向后移动newPartSize个位置
最后把要添加的数组添加至之前的数组中
@Override
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection collection) {
int s = size;
if (index > s || index < 0) {
throwIndexOutOfBoundsException(index, s);
}
Object[] newPart = collection.toArray();
int newPartSize = newPart.length;
if (newPartSize == 0) {
return false;
}
Object[] a = array;
int newSize = s + newPartSize; // If add overflows, arraycopy will fail
if (newSize <= a.length) {
System.arraycopy(a, index, a, index + newPartSize, s - index);
} else {
int newCapacity = newCapacity(newSize - 1); // ~33% growth room
Object[] newArray = new Object[newCapacity];
System.arraycopy(a, 0, newArray, 0, index);
System.arraycopy(a, index, newArray, index + newPartSize, s-index);
array = a = newArray;
}
System.arraycopy(newPart, 0, a, index, newPartSize);
size = newSize;
modCount++;
return true;
}源码解说:
通过Arrays.fill(array, 0, size, null)这个把array数组从0~size填null值表示清空数组
@Override
public void clear() {
if (size != 0) {
Arrays.fill(array, 0, size, null);
size = 0;
modCount++;
}
}源码解说:
由于ArrayList是实现了Cloneable,所以可以将本地的对象进行克隆获取数组
@Override
public Object clone() {
try {
ArrayList result = (ArrayList) super.clone();
result.array = array.clone();
return result;
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
throw new AssertionError();
}
}源码解说:
这个方法很有意思,我们来看看网上怎么说的?
我们在使用Arraylist时,经常要对它进行初始化工作,在使用add()方法增加新的元素时,如果要增加的数据量很大,应该使用ensureCapacity()方法,该方法的作用是预先设置Arraylist的大小,这样可以大大提高初始化速度。
意思代表着要执行add()方法添加对象之前可以使用ensureCapacity这个进行设置数组的初始化对象数组进行优化,它的好处就是让你在添加对象可以加快速度添加
public void ensureCapacity(int minimumCapacity) {
Object[] a = array;
if (a.length < minimumCapacity) {
Object[] newArray = new Object[minimumCapacity];
System.arraycopy(a, 0, newArray, 0, size);
array = newArray;
modCount++;
}
}源码解说:
这个简单,就是获取array下的下标对象
@Override
public E get(int index) {
if (index >= size) {
throwIndexOutOfBoundsException(index, size);
}
return (E) array[index];
}源码解说:
这个方法是查询操作,查询数组中是否包含object
@Override
public boolean contains(Object object) {
Object[] a = array;
int s = size;
if (object != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < s; i++) {
if (object.equals(a[i])) {
return true;
}
}
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < s; i++) {
if (a[i] == null) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}源码解说:
这个方法是查询对象object的位置,如果查询不到就返回-1表示没有该对象
@Override
public int indexOf(Object object) {
Object[] a = array;
int s = size;
if (object != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < s; i++) {
if (object.equals(a[i])) {
return i;
}
}
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < s; i++) {
if (a[i] == null) {
return i;
}
}
}
return -1;
}源码解说:
这个方法是从尾往前查询对象,如果查询不到就返回-1表示没有该对象
@Override
public int lastIndexOf(Object object) {
Object[] a = array;
if (object != null) {
for (int i = size - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (object.equals(a[i])) {
return i;
}
}
} else {
for (int i = size - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (a[i] == null) {
return i;
}
}
}
return -1;
}源码解说:
假如一个数组要删除某个位置你会怎么做呢?我画个图给你们看

只要将index后面的数据往前移动一位就可以删除
a[s] = null;然后再把最后元素置空
下面是一个例子:
String[] ids = { "1", "2", "3", "4", "5", "6", "7", "0", "0" };
int index = 0;
int s = 7;
System.arraycopy(ids, index + 1, ids, index, --s - index);
ids[s] = "0";
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ids) + "-" + s);
[2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 0, 0, 0]
@Override
public E remove(int index) {
Object[] a = array;
int s = size;
if (index >= s) {
throwIndexOutOfBoundsException(index, s);
}
E result = (E) a[index];
System.arraycopy(a, index + 1, a, index, --s - index);
a[s] = null; // Prevent memory leak
size = s;
modCount++;
return result;
}假如要移除一个对象,那么需要查询是否包含该对象,如果包含该对象,那么用上面的方法进行覆盖,移除该对象,我们看到该方法有个惊奇的判断if (a[i] == null),假如我们要删除一个数组里面所有对象为null的值时,只要remove(null)就可以了。
@Override
public boolean remove(Object object) {
Object[] a = array;
int s = size;
if (object != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < s; i++) {
if (object.equals(a[i])) {
System.arraycopy(a, i + 1, a, i, --s - i);
a[s] = null; // Prevent memory leak
size = s;
modCount++;
return true;
}
}
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < s; i++) {
if (a[i] == null) {
System.arraycopy(a, i + 1, a, i, --s - i);
a[s] = null; // Prevent memory leak
size = s;
modCount++;
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}源码解说:
该方法用于删除一个连续的数据
主要部分:
System.arraycopy(a, toIndex, a, fromIndex, s - toIndex);
int rangeSize = toIndex - fromIndex;
Arrays.fill(a, s - rangeSize, s, null);
size = s - rangeSize;
先删除从fromIndex覆盖到toIndex位置
接着获取删除的数量
然后将后面的数据置空
最后长度减rangeSize
@Override
protected void removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
if (fromIndex == toIndex) {
return;
}
Object[] a = array;
int s = size;
if (fromIndex >= s) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("fromIndex " + fromIndex
+ " >= size " + size);
}
if (toIndex > s) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("toIndex " + toIndex
+ " > size " + size);
}
if (fromIndex > toIndex) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("fromIndex " + fromIndex
+ " > toIndex " + toIndex);
}
System.arraycopy(a, toIndex, a, fromIndex, s - toIndex);
int rangeSize = toIndex - fromIndex;
Arrays.fill(a, s - rangeSize, s, null);
size = s - rangeSize;
modCount++;
}源码解说:
a[index] = object;通过这个修改数据
@Override
public E set(int index, E object) {
Object[] a = array;
if (index >= size) {
throwIndexOutOfBoundsException(index, size);
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E result = (E) a[index];
a[index] = object;
return result;
}int N = 10;
ArrayList
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
list.add(i + "---");
}
Iterator
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
那么这个迭代器它是怎么做的呢?我们一探究竟
private class ArrayListIterator implements Iterator {
private int remaining = size;
private int removalIndex = -1;
private int expectedModCount = modCount;
public boolean hasNext() {
return remaining != 0;
}
public E next() {
ArrayList ourList = ArrayList.this;
int rem = remaining;
if (ourList.modCount != expectedModCount) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
if (rem == 0) {
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
remaining = rem - 1;
return (E) ourList.array[removalIndex = ourList.size - rem];
}
public void remove() {
Object[] a = array;
int removalIdx = removalIndex;
if (modCount != expectedModCount) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
if (removalIdx < 0) {
throw new IllegalStateException();
}
System.arraycopy(a, removalIdx + 1, a, removalIdx, remaining);
a[--size] = null; // Prevent memory leak
removalIndex = -1;
expectedModCount = ++modCount;
}
} public Iterator
return new ArrayListIterator();
}
这个方法初始化迭代器
将数组的长度获取到,遍历到的索引位置
private int remaining = size;
private int removalIndex = -1;
通过hasNext来判断该迭代器剩下的个数是否已经到结束
public boolean hasNext() {
return remaining != 0;
}
那么遍历中通过什么来获取呢?next方法
remaining = rem - 1,获取一次数据将剩余量-1
ourList.array[removalIndex = ourList.size - rem],从头到尾遍历,这样达到循环一次获取一次数据的目的。
最后剩下一个remove方法,这个方法是做什么的呢?跟ArrayList的remove(index)一样,从头到尾删除