c++输出文件流ofstream用法详解
目录
-
- 一. 输入流 ofstream 用法
- Public member functions (1-6)
- 1, (constructor)
- 2, ofstream::open
- 3, ofstream::is_open
- 4, ofstream::close
- 5, ofstream::rdbuf
- 6,ofstream::operator=
- Public member functions inherited from ostream (7-11)
- 7,std::ostream::operator<<
- 8,ostream::put
- 9,ostream::write
- 10,ostream::tellp
- 11,ostream::seekp
- Public member functions inherited from ios(12-14)
- 12,ios::good
- 13,ios::operator!
- 14,ios::operator bool
- Public member functions (1-6)
- 一. 输入流 ofstream 用法
头文件
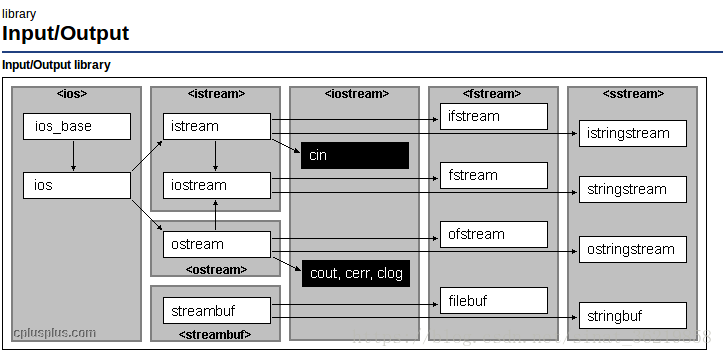
ifstreamInput file stream class (class )链接ofstreamOutput file stream (class )链接fstreamInput/output file stream class (class )链接filebufFile stream buffer (class )链接
一. 输入流 ofstream 用法
输入流的继承关系:
ios_base <- ios <- ostream <- ofstream
Public member functions (1-6)
1, (constructor)
default (1) ofstream(); // 只定义不关联
initialization (2) //关联文件filename,默认模式 ios_base::out
explicit ofstream (const char* filename, ios_base::openmode mode = ios_base::out);
explicit ofstream (const string& filename, ios_base::openmode mode = ios_base::out);
copy (3) //禁止拷贝赋值
ofstream (const ofstream&) = delete;
move (4) //可以右值引用临时变量赋值
ofstream (ofstream&& x);2, ofstream::open
//和第二种构造函数一样,绑定文件
void open (const char* filename, ios_base::openmode mode = ios_base::out);
void open (const string& filename, ios_base::openmode mode = ios_base::out);3, ofstream::is_open
bool is_open() const;
// 文件打开返回 true ,否则 false4, ofstream::close
void close();
// Closes the file currently associated with the object, disassociating it from the stream.5, ofstream::rdbuf
filebuf* rdbuf() const;
// 返回一个指针,指向 filebuf 对象,filebuf 要么通过open()和文件绑定,要么通过rdbuf()与fstream对象绑定,绑定后才能使用。
int main () {
std::ifstream ifs ("test.txt");
std::ofstream ofs ("copy.txt");
std::filebuf* inbuf = ifs.rdbuf();
std::filebuf* outbuf = ofs.rdbuf();
char c = inbuf->sbumpc();
while (c != EOF)
{
outbuf->sputc (c);
c = inbuf->sbumpc();
}
ofs.close();
ifs.close();
return 0;
}6,ofstream::operator=
copy (1) //禁止copy赋值
ofstream& operator= (const ofstream&) = delete;
move (2) // 可以右值引用创建对象。
ofstream& operator= (ofstream&& rhs);Public member functions inherited from ostream (7-11)
7,std::ostream::operator<<
用法和 cout<< 一样,是写数据到文件最方便的函数,重载了常用的数据类型。
arithmetic types (1)
ostream& operator<< (bool val);
ostream& operator<< (short val);
ostream& operator<< (unsigned short val);
ostream& operator<< (int val);
ostream& operator<< (unsigned int val);
ostream& operator<< (long val);
ostream& operator<< (unsigned long val);
ostream& operator<< (long long val);
ostream& operator<< (unsigned long long val);
ostream& operator<< (float val);
ostream& operator<< (double val);
ostream& operator<< (long double val);
ostream& operator<< (void* val);
stream buffers (2)
ostream& operator<< (streambuf* sb );
manipulators (3)
ostream& operator<< (ostream& (*pf)(ostream&));
ostream& operator<< (ios& (*pf)(ios&));
ostream& operator<< (ios_base& (*pf)(ios_base&));用string数据类型,作为参数写入到ofstream,在头文件
std::operator<< (string)
ostream& operator<< (ostream& os, const string& str);8,ostream::put
ostream& put (char c);
//插入字符 c 到流中9,ostream::write
ostream& write (const char* s, streamsize n);
//从数组s中取n 个字符插入到流中10,ostream::tellp
streampos tellp();
返回文件指针的位置, streampos 可以转为int11,ostream::seekp
(1)
ostream& seekp (streampos pos);
(2)
ostream& seekp (streamoff off, ios_base::seekdir way);
//Sets the position where the next character is to be inserted into the output stream.参数 pos 是流中的绝对位置可以转化为 int
参数 off 是偏移量,与way相关,类型是 int
参数 way 可以选下表中的任意一个常量。
| value | offset is relative to… |
|---|---|
| ios_base::beg | beginning of the stream |
| ios_base::cur | current position in the stream |
| ios_base::end | end of the stream |
Public member functions inherited from ios(12-14)
12,ios::good
bool good() const;
bool eof() const;
bool fail() const;
bool bad() const;检测流的状态是否正常。当错误的状态flags (eofbit, failbit and badbit) 都没被设置的时候返回true
特定的错误状态可以用下面的函数(eof, fail, and bad)来检测。
| iostate value (member constant) | indicates | good() | eof() | fail() | bad() | rdstate() |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| goodbit | No errors (zero value iostate) | true | false | false | false | goodbit |
| eofbit | End-of-File reached on input operation | false | true | false | false | eofbit |
| failbit | Logical error on i/o operation | false | false | true | false | failbit |
| badbit | Read/writing error on i/o operation | false | false | true | true | badbit |
13,ios::operator!
bool operator!() const;
//Returns true if either failbit or badbit is set, and false otherwise.
// 有错误状态返回 true
// evaluating a stream (not)
#include // std::cout
#include // std::ifstream
int main () {
std::ifstream is;
is.open ("test.txt");
if (!is)
std::cerr << "Error opening 'test.txt'\n";
return 0;
}14,ios::operator bool
explicit operator bool() const;
C++11: Return true if none of failbit or badbit is set. false otherwise.
// 在条件语句中,无错误返回真,有错返回假。
int main () {
std::ifstream is;
is.open ("test.txt");
if (is) {
// read file
}
else {
std::cerr << "Error opening 'test.txt'\n";
}
return 0;
}