DBSCAN算法研究(2)--matlab代码实现
DBSCAN聚类算法三部分
1、DBSCAN原理、流程、参数设置、优缺点以及算法;
http://blog.csdn.net/zhouxianen1987/article/details/68945844
2、matlab代码实现;
blog:http://blog.csdn.net/zhouxianen1987/article/details/68946169
code:http://download.csdn.net/detail/zhouxianen1987/9789230
3、C++代码实现及与matlab实例结果比较。
blog:http://blog.csdn.net/zhouxianen1987/article/details/68946278
code:http://download.csdn.net/detail/zhouxianen1987/9789231
matlab代码测试实验(代码从matlab官方网站[8]下载):
下载的代码主要包括一个测试数据集合mydata.mat,main.m,DBSCAN.m和PlotClusterinResult.m共4个文件,我们在测试实验实验中做了两个方面更改:1)更换了另外一个测试数据,测试数据来源于[13](取其中的一部分),2)添加了个K距离图部分代码(均在如下主程序代码中给出),代码按照个人对k-distance graph的理解编写,如有错误之处,望大家指正,3)改变参数Eps值大小,输出结果并显示。
所有测试代码在下文给出,包括DBSCAN.m和PlotClusterinResult.m子函数。
(所有测试代码下载:)
%main function:主函数
%all codes and test data downlown: http://yarpiz.com/255/ypml110-dbscan-clustering
% Copyright (c) 2015, Yarpiz (www.yarpiz.com)
% All rights reserved. Please read the "license.txt" for license terms.
%
% Project Code: YPML110
% Project Title: Implementation of DBSCAN Clustering in MATLAB
% Publisher: Yarpiz (www.yarpiz.com)
%
% Developer: S. Mostapha Kalami Heris (Member of Yarpiz Team)
%
% Contact Info: [email protected], [email protected]
clc;
clear;
close all;
%% test Data
%数据下载网站:http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/machine-learning-databases/iris/
%这里使用的iris数据的一部分,由于第3维和第4为数据数据区分度好,因此用3、4维数据测试
X1 =[5.1,3.5,1.4,0.2;%,Iris-setosa
4.9,3.0,1.4,0.2;
4.7,3.2,1.3,0.2;
4.6,3.1,1.5,0.2;
5.1,3.7,1.5,0.4;
4.6,3.6,1.0,0.2;
5.1,3.3,1.7,0.5;
5.0,3.6,1.4,0.2;
5.4,3.9,1.7,0.4;
4.6,3.4,1.4,0.3;
5.0,3.4,1.5,0.2;
4.4,2.9,1.4,0.2;
4.9,3.1,1.5,0.1;
5.4,3.7,1.5,0.2;
4.8,3.4,1.6,0.2;
4.8,3.0,1.4,0.1;
4.3,3.0,1.1,0.1;
5.8,4.0,1.2,0.2;
5.7,4.4,1.5,0.4;
5.4,3.9,1.3,0.4;
5.1,3.5,1.4,0.3;
5.7,3.8,1.7,0.3;
5.1,3.8,1.5,0.3;
5.4,3.4,1.7,0.2;
6.4,3.2,4.5,1.5;%Iris-versicolor
6.9,3.1,4.9,1.5;
5.5,2.3,4.0,1.3;
6.5,2.8,4.6,1.5;
5.7,2.8,4.5,1.3;
6.3,3.3,4.7,1.6;
4.9,2.4,3.3,1.0;
4.9,2.4,3.3,1.0;
6.6,2.9,4.6,1.3;
5.2,2.7,3.9,1.4;
5.0,2.0,3.5,1.0;
5.9,3.0,4.2,1.5;
6.0,2.2,4.0,1.0];
X=X1(:,3:4);
%%KNN k distance graph, to determine the epsilon
A=X;
numData=size(A,1);
Kdist=zeros(numData,1);
[IDX,Dist]=knnsearch(A(2:numData,:),A(1,:));
Kdist(1)=Dist;
for i=2:size(A,1)
[IDX,Dist] = knnsearch(A([1:i-1,i+1:numData],:),A(i,:));
Kdist(i)=Dist;
end
[sortKdist,sortKdistIdx]=sort(Kdist,'descend');
distX=[1:numData]';
plot(distX,sortKdist,'r+-','LineWidth',2);
set(gcf,'position',[1000 340 350 350]);
grid on;
%% Run DBSCAN Clustering Algorithm
epsilon= 0.15 ;
MinPts= 3 ;
IDX1=DBSCAN(X,epsilon,MinPts);
%% Plot Results
figure;
PlotClusterinResult(X, IDX1);
title(['DBSCAN Clustering (\epsilon = ' num2str(epsilon) ', MinPts = ' num2str(MinPts) ')']);
set(gcf,'position',[30 -10 500 500]);
epsilon= 0.25 ;
MinPts= 3 ;
IDX2=DBSCAN(X,epsilon,MinPts);
%% Plot Results
figure;
PlotClusterinResult(X, IDX2);
title(['DBSCAN Clustering (\epsilon = ' num2str(epsilon) ', MinPts = ' num2str(MinPts) ')']);
set(gcf,'position',[530 -10 500 500]);
epsilon= 0.5 ;
MinPts= 3 ;
IDX3=DBSCAN(X,epsilon,MinPts);
%% Plot Results
figure;
PlotClusterinResult(X, IDX3);
title(['DBSCAN Clustering (\epsilon = ' num2str(epsilon) ', MinPts = ' num2str(MinPts) ')']);
set(gcf,'position',[30 380 500 500]);
%DBSCAN算法子函数,需另外创建.m文件保存
% Copyright (c) 2015, Yarpiz (www.yarpiz.com)
% All rights reserved. Please read the "license.txt" for license terms.
%
% Project Code: YPML110
% Project Title: Implementation of DBSCAN Clustering in MATLAB
% Publisher: Yarpiz (www.yarpiz.com)
%
% Developer: S. Mostapha Kalami Heris (Member of Yarpiz Team)
%
% Contact Info: [email protected], [email protected]
function [IDX, isnoise]=DBSCAN(X,epsilon,MinPts)
C=0;
n=size(X,1);
IDX=zeros(n,1);
D=pdist2(X,X);
visited=false(n,1);
isnoise=false(n,1);
for i=1:n
if ~visited(i)
visited(i)=true;
Neighbors=RegionQuery(i);
if numel(Neighbors)=MinPts
Neighbors=[Neighbors Neighbors2]; %#ok
end
end
if IDX(j)==0
IDX(j)=C;
end
k = k + 1;
if k > numel(Neighbors)
break;
end
end
end
function Neighbors=RegionQuery(i)
Neighbors=find(D(i,:)<=epsilon);
end
end
%结果显示子函数,需另外创建.m文件保存
% Copyright (c) 2015, Yarpiz (www.yarpiz.com)
% All rights reserved. Please read the "license.txt" for license terms.
%
% Project Code: YPML110
% Project Title: Implementation of DBSCAN Clustering in MATLAB
% Publisher: Yarpiz (www.yarpiz.com)
%
% Developer: S. Mostapha Kalami Heris (Member of Yarpiz Team)
%
% Contact Info: [email protected], [email protected]
function PlotClusterinResult(X, IDX)
k=max(IDX);
Colors=hsv(k);
Legends = {};
for i=0:k
Xi=X(IDX==i,:);
if i~=0
Style = 'x';
MarkerSize = 8;
Color = Colors(i,:);
Legends{end+1} = ['Cluster #' num2str(i)];
else
Style = 'o';
MarkerSize = 6;
Color = [0 0 0];
if ~isempty(Xi)
Legends{end+1} = 'Noise';
end
end
if ~isempty(Xi)
plot(Xi(:,1),Xi(:,2),Style,'MarkerSize',MarkerSize,'Color',Color);
end
hold on;
end
hold off;
axis equal;
grid on;
legend(Legends);
legend('Location', 'NorthEastOutside');
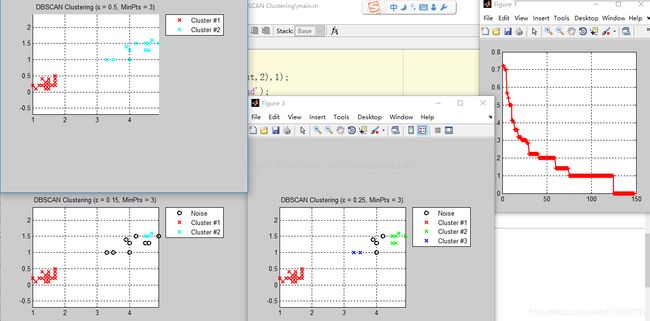
end 运行结果:
观察当Eps由小到大变化时候,当Eps=0.15时,数据分成2类,噪音点有9个,当Eps=0.25时,数据分成3来,噪音点4个,Eps=0.15时,被分成2类,无噪音点,而根据k距离图大致确定0.15为较适合的Eps参数值,但是这不能很好的将这两类数据分开(数据来源:http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/machine-learning-databases/iris/,数据详细说明可到上述网站查看),这可能是数据密度分布不均匀,导致参数Eps不太容易确定,在这种时候按照参数设置的指导原则不能选取较好的参数,而是需要根据具体应用先验进行参数适当调整。
有关matlab版本的DBSCAN算法代码,除了matlab官网可以下载DBSCAN算法代码知网,[9]也给出一个最原始的DBSCAN的matlab实现,只能处理小规模的数据。
参考资料:
[1] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/DBSCAN
[2] Ester,Martin; Kriegel, Hans-Peter; Sander,Jörg; Xu, Xiaowei (1996). Simoudis, Evangelos; Han, Jiawei; Fayyad, Usama M.,eds. Adensity-based algorithm for discovering clusters in large spatial databaseswith noise. Proceedings of the Second International Conference on KnowledgeDiscovery and Data Mining (KDD-96). AAAI Press.pp. 226–231.CiteSeerX 10.1.1.121.9220. ISBN 1-57735-004-9.
[3] 各种聚类算法的比较
http://blog.163.com/qianshch@126/blog/static/48972522201092254141315/
[4] http://www.cnblogs.com/chaosimple/p/3164775.html
[5] https://wenku.baidu.com/view/ce3e324aa8956bec0975e3d5.html
[6]http://blog.csdn.net/itplus/article/details/10088625
[7] http://www.tuicool.com/articles/euAZneu
[8] http://cn.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/52905-dbscan-clustering-algorithm
[9] http://blog.csdn.net/snnxb/article/details/29880387
[10] 聚类算法-DBSCAN-C++实现,http://blog.csdn.net/k76853/article/details/50440182
[11] DBSCAN聚类算法C++实现,http://blog.csdn.net/u011367448/article/details/18549823
[12] DBSCAN 算法介绍以及C++实现,http://blog.csdn.net/u011557212/article/details/53203323
[13] https://github.com/siddharth-agrawal/DBSCAN
[14] http://download.csdn.net/download/piaominnan/8480767