2018数模国赛B题(3.1)完整实现代码
4.3第三种具体情况的求解
4.3.1故障判断和维修时间的确定模型
针对第三种具体情况,我们首先确定故障判断和维修时间的实现。
对于故障判断,我们选择为每一个CNC工作的时刻生成一个从0到100的随机数a,如果生成的随机数a<1,即该时刻会发生故障。
而对于维修时间,我们同样采用了随机数的方法,生成了一个从600到1200的随机数b,b代表该次维修所花的秒数。
4.3.2基于智能RGV动态过程的改进模型
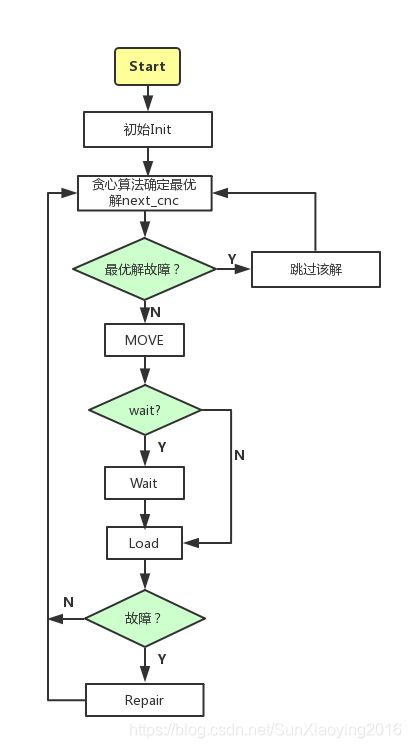
在这个模型中,我们对RGV与CNC赋予了更多的智能,使得它们能够识别故障行为。具体过程为:当利用贪心算法确定最优解时,我们会进行最优解是否故障的判断,如果判断为真,则跳过该解,重新进行利用贪心算法确定优解的步骤。如果判断为假,则按照4.1,4.2的模型继续进行调度。当调度过程进行至上下料完成时刻,我们会对CNC进行一次故障判断,如果判断为真,则进入维修操作,如果判断为假,则重新进行利用贪心算法确定优解的步骤。算法流程图如下图所示:
图7
对于这种模型,我们进行了C++的代码实现,得到了RGV的调度策略和系统的作业效率。针对结果,我们发现故障的发生基本服从泊松过程,且故障发生之后调度策略会发生极大的变化,而产量也会下降,与我们的预期相同。
/*------------------------CNC.h-----------------------*/
#pragma once
class CNC
{
private:
int number; //CNC编号
int position; //CNC位置
int count; //CNC剩余工作时间
int n; //加工物序列号
int flag; //CNC当前状态,1故障,0正常
public:
CNC(int num, int pos);
void countdown(int tem);
friend class RGV;
};
/*------------------------CNC.cpp-----------------------*/
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "CNC.h"
using namespace std;
CNC::CNC( int num, int pos)
{
number = (num > 0) ? num : ERROR;
position = (pos >= 0) ? pos : ERROR;
count = 0;
n = 0;
flag = 0;
}
void CNC::countdown(int temp)
{
if (count > temp) {
count -= temp;
}
else {
count = 0;
if (flag) {
flag = 0; //恢复正常
cout << "CNC#" << number << "恢复正常" << endl;
}
}
}
/*------------------------RGV.h-----------------------*/
#pragma once
#include "CNC.h"
class RGV
{
private:
int position; //rgv当前位置
int now_cnc; //当前目标
int rgv_flag; //rgv_flag,1有熟料,0无
public:
int t_time; //总用时
int scr_times; //报废次数
int sum; //加工熟料总数
RGV();
void Init(CNC *p); //第一轮初始化
int posCalculate(int pos1, int pos2); //计算RGV移动时间
void move(CNC *p); //RGV移动
void load(CNC *p); //RGV上下料
void clean(CNC *p);//RGV清洗
void wait(CNC *p);//RGV等待
void repair(CNC *p);//RGV故障修复
};
/*------------------------RGV.cpp-----------------------*/
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "RGV.h"
#define STEP1 23
#define STEP2 41
#define STEP3 59
#define CNC_WORKTIME 580
#define CNC1 30
#define CNC0 35
#define CLEAN 30
#define CNCNUMBER 8
using namespace std;
int n = 0; //加工物序列号
RGV::RGV()
{
position = 0;
now_cnc = 1;
rgv_flag = 0;
t_time = 0;
scr_times = 0;
sum = 0;
}
void RGV::Init(CNC *p)
{
CNC* ptr = p;
for (int i = 0; i < CNCNUMBER; i++, now_cnc++) //所有CNC剩余时间 - rgv移动时间
{
int temp = posCalculate(position, (p + now_cnc - 1)->position);
if (temp) {
t_time += temp;
CNC*ptr1 = p;
for (int i = 0; i < CNCNUMBER; i++, ptr1++) //所有CNC剩余时间 - rgv移动时间
{
ptr1->countdown(temp);
}
}
load(p);
position = (p + now_cnc - 1)->position;
}
}
int RGV::posCalculate(int pos1, int pos2)//RGV移动时间计算
{
switch (abs(pos1 - pos2))
{
case 3: return STEP3;
case 2: return STEP2;
case 1: return STEP1;
case 0: return 0;
default: return ERROR;
}
}
void RGV::move(CNC *p)//RGV移动
{
CNC* ptr = p;
int time1 = 10000;//最少时间
int time2 = 0; //当前时间
int next_cnc = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < CNCNUMBER; i++, ptr++)
{
if (!(ptr->flag)) {
int postime = posCalculate(position, ptr->position);
time2 = ptr->count + postime;//CNC工作剩余时间 + RGV移动到当前位置时间
if (time1 > time2) {
time1 = time2;
next_cnc = ptr->number;
}
}
else continue;
}
if (now_cnc != next_cnc) {//当前对象不是最优对象,移动
int temp = posCalculate(position, (p + next_cnc - 1)->position);
if (temp) {
t_time += temp;
CNC*ptr1 = p;
for (int i = 0; i < CNCNUMBER; i++, ptr1++) //所有CNC剩余时间 - rgv移动时间
{
ptr1->countdown(temp);
}
}
position = (p + next_cnc - 1)->position;
now_cnc = next_cnc;
}
//cout << "position" << position << '\t' << "now_cnc" << now_cnc << endl; //test
wait(p);
}
void RGV::load(CNC *p)//RGV上下料
{
CNC* ptr = p + now_cnc - 1; //此处数组下标和CNC编号要注意!
int temp = 0;
cout << t_time << '\t' << '\t' << ptr->n << '\t' << '\t' << ++n << '\t' << now_cnc << endl;
if ((ptr->number % 2) == 1) {
temp = CNC1;
}
else {
temp = CNC0;
}
t_time += temp;
CNC*ptr1 = p;
for (int i = 0; i < CNCNUMBER; i++, ptr1++) //所有CNC剩余时间 - rgv移动时间
{
ptr1->countdown(temp);
}
ptr->n = n;
ptr->count = CNC_WORKTIME;
rgv_flag = 1;
}
void RGV::clean(CNC* p)//RGV清洗
{
sum++;
int temp = CLEAN;
t_time += temp;
CNC*ptr1 = p;
for (int i = 0; i < CNCNUMBER; i++, ptr1++) //所有CNC剩余时间 - rgv移动时间
{
ptr1->countdown(temp);
}
}
void RGV::wait(CNC* p)
{
CNC* ptr = p + now_cnc - 1;
if (ptr->count) {
int temp = ptr->count;
t_time += temp;
CNC*ptr1 = p;
for (int i = 0; i < CNCNUMBER; i++, ptr1++) //所有CNC剩余时间 - rgv移动时间
{
ptr1->countdown(temp);
}
ptr->count = 0;
}
else return;
}
void RGV::repair(CNC *p)
{
CNC*ptr = p + now_cnc - 1;
double rand_num = rand() % 100; //生成随机数
if (rand_num < 1.0) { //故障概率0.01
scr_times++;
cout << t_time << '\t' << n << "号物料报废" << '\t' << "CNC#" << ptr->number << "发生故障" << endl;
ptr->flag = 1; //故障
int repair_time = rand() % 600 + 600;
ptr->count = repair_time;
}
else return;
}
/*------------------------main.cpp--------------------------*/
// main.cpp: 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "RGV.h"
#include "CNC.h"
#define CNCNUMBER 8
#define TIME 28800
using namespace std;
int main()
{
RGV rgv;
CNC cnc[CNCNUMBER] = {
CNC(1,0), CNC(2,0), CNC(3,1), CNC(4,1),
CNC(5,2), CNC(6,2), CNC(7,3), CNC(8,3) };
CNC *pCNC = cnc;
cout <<"时间" << '\t' << "下料开始" << '\t' << "上料开始" << '\t' << "CNC#" << endl;
/*第一轮
仅需考虑RGV“移动”和“上下料”动作*/
rgv.Init(pCNC);
/*第(n+1)轮
RGV循环“移动”,“上下料”和“清洗”动作*/
while (rgv.t_time <= TIME)
{
rgv.move(pCNC);
rgv.load(pCNC);
rgv.repair(pCNC);
rgv.clean(pCNC);
}
cout << "生成熟料总数:" << rgv.sum-rgv.scr_times << endl;
cout << "发生故障次数" << rgv.scr_times << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}