java程序高cpu占用,内存过高问题
本文转自:hankchen,http://www.blogjava.net/hankchen
cpu占用两个原因,一是高密度计算,一个是死循环,一般后者占用比例较大,下面以一个示例为准
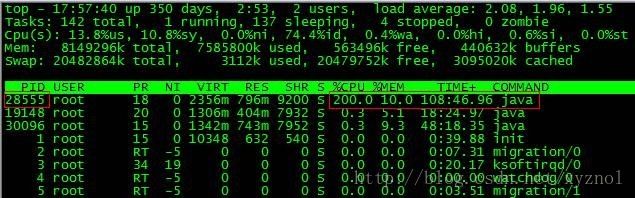
根据top命令,发现PID为28555的Java进程占用CPU高达200%,出现故障。
这时候通过ps aux | grep PID 知道哪个工程出现了问题。然后可以通过命令查看进程中的线程列表
ps -mp pid -o THREAD,tid,time
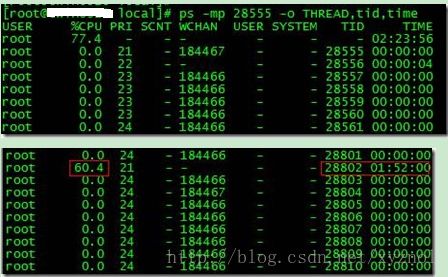
找到了耗时最高的线程28802,占用CPU时间快两个小时了
因为jstack打印信息出来是16进制,所以这里先进行转换显示
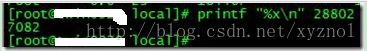
printf “%x\n” tid
jstack pid | grep tid -A 30
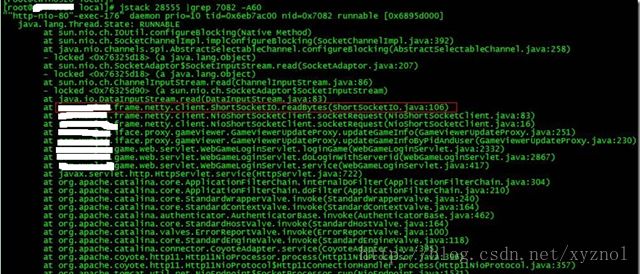
从里面看到具体执行方法出了问题,现在具体分析
ShortSocketIO是应用封装的一个用短连接Socket通信的工具类。readBytes函数的代码如下:
public byte[] readBytes(int length) throws IOException {
if ((this.socket == null) || (!this.socket.isConnected())) {
throw new IOException("++++ attempting to read from closed socket");
}
byte[] result = null;
ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
if (this.recIndex >= length) {
bos.write(this.recBuf, 0, length);
byte[] newBuf = new byte[this.recBufSize];
if (this.recIndex > length) {
System.arraycopy(this.recBuf, length, newBuf, 0, this.recIndex - length);
}
this.recBuf = newBuf;
this.recIndex -= length;
} else {
int totalread = length;
if (this.recIndex > 0) {
totalread -= this.recIndex;
bos.write(this.recBuf, 0, this.recIndex);
this.recBuf = new byte[this.recBufSize];
this.recIndex = 0;
}
int readCount = 0;
while (totalread > 0) {
if ((readCount = this.in.read(this.recBuf)) > 0) {
if (totalread > readCount) {
bos.write(this.recBuf, 0, readCount);
this.recBuf = new byte[this.recBufSize];
this.recIndex = 0;
} else {
bos.write(this.recBuf, 0, totalread);
byte[] newBuf = new byte[this.recBufSize];
System.arraycopy(this.recBuf, totalread, newBuf, 0, readCount - totalread);
this.recBuf = newBuf;
this.recIndex = (readCount - totalread);
}
totalread -= readCount;
}
}
}问题就出在if ((readCount = this.in.read(this.recBuf)) > 0)部分。如果this.in.read()返回的数据小于等于0时,循环就一直进行下去了。而这种情况在网络拥塞的时候是可能发生的。
至于具体怎么修改就看业务逻辑应该怎么对待这种特殊情况了。
最后,总结下排查CPU故障的方法和技巧有哪些:
1、top命令:Linux命令。可以查看实时的CPU使用情况。也可以查看最近一段时间的CPU使用情况。
2、PS命令:Linux命令。强大的进程状态监控命令。可以查看进程以及进程中线程的当前CPU使用情况。属于当前状态的采样数据。
3、jstack:Java提供的命令。可以查看某个进程的当前线程栈运行情况。根据这个命令的输出可以定位某个进程的所有线程的当前运行状态、运行代码,以及是否死锁等等。
4、pstack:Linux命令。可以查看某个进程的当前线程栈运行情况。
排查了CPU故障,有时候还有堆内存的问题:
在查看内存问题之前,先执行内存回收命令查看内存回收情况:
jstat -gcutil [pid] 250 6
内存会随着程序执行上升,执行FCG后,若内存未回收,则有内存泄露风险
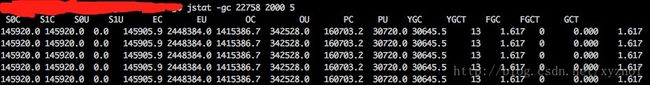
堆内存 = 年轻代 + 年老代 + 永久代
年轻代 = Eden区 + 两个Survivor区(From和To)各个名词含义:
S0C、S1C、S0U、S1U:Survivor 0/1区容量(Capacity)和使用量(Used)
EC、EU:Eden区容量和使用量
OC、OU:年老代容量和使用量
PC、PU:永久代容量和使用量
YGC、YGT:年轻代GC次数和GC耗时
FGC、FGCT:Full GC次数和Full GC耗时
GCT:GC总耗时jmap命令查看堆内存溢出的问题,一般有下面几种使用方式:
- jmap [pid]
- jmap -histo:live [pid] > a.log
- jmap -dump:live,format=b,file=xxx [pid]
后面两个使用比较多,jmap -histo:live [pid]可以用来查看当前java进程中创建的活跃对象的数目和占用内存的大小
下一个命令jmap -dump:live,format=b,file=xxx [pid]这个命令可以导出当前java进程的内存占用情况,可以使用第三方工具,例如MAT来分析
root@ubuntu:/# jmap -histo:live 21711 | more
num #instances #bytes class name
----------------------------------------------
1: 38445 5597736
2: 38445 5237288
3: 3500 3749504
4: 60858 3242600
5: 3500 2715264
6: 2796 2131424
7: 5543 1317400 [I
8: 13714 1010768 [C
9: 4752 1003344 [B
10: 1225 639656
11: 14194 454208 java.lang.String
12: 3809 396136 java.lang.Class
13: 4979 311952 [S
14: 5598 287064 [[I
15: 3028 266464 java.lang.reflect.Method
16: 280 163520
17: 4355 139360 java.util.HashMap$Entry
18: 1869 138568 [Ljava.util.HashMap$Entry;
19: 2443 97720 java.util.LinkedHashMap$Entry
20: 2072 82880 java.lang.ref.SoftReference
21: 1807 71528 [Ljava.lang.Object;
22: 2206 70592 java.lang.ref.WeakReference
23: 934 52304 java.util.LinkedHashMap
24: 871 48776 java.beans.MethodDescriptor
25: 1442 46144 java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap$HashEntry
26: 804 38592 java.util.HashMap
27: 948 37920 java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap$Segment
28: 1621 35696 [Ljava.lang.Class;
29: 1313 34880 [Ljava.lang.String;
30: 1396 33504 java.util.LinkedList$Entry
31: 462 33264 java.lang.reflect.Field
32: 1024 32768 java.util.Hashtable$Entry
33: 948 31440 [Ljava.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap$HashEntry; 这里class name表示对象类型,解释如下:
B byte
C char
D double
F float
I int
J long
Z boolean
[ 数组,如[I表示int[]
[L+类名 其他对象