- CLR中的类型转换
qzy0621
C#C++笔记c++c#
CLR中的类型转换字符串类型转换容器类型转换自定义类型相互转换项目设置CLR(CommonLanguageRuntime,公共语言运行时)是微软.NET框架的核心组件,是微软对CLI标准的具体实现,负责管理和执行托管代码,提供跨语言互操作性、内存管理、安全性等关键服务CLR的类型转换机制是.NET框架中实现类型安全与多语言互操作的核心功能之一若调试不能命中,可参考C#通过CLR调用C++代码无法命
- 贪心算法(9)(java)最优除法
奋进的小暄
java贪心算法算法
题目:给定一正整数数组nums,nums中的相邻整数将进行浮点除法。例如,[2,3.4]->2/3/4.例如,nums=[2,3,4],我们将求表达式的值“2/3/4"。但是,你可以在任意位置添加任意数目的括号,来改变算数的优先级。你需要找出怎么添加括号,以便计算后的表达式的值为最大值。以字符串格式返回具有最大值的对应表达式。注意:你的表达式不应该包含多余的括号。输入:【1000,100,10,2
- 基于Spring Boot的分布式任务调度实践
Blossom.118
分布式系统与高性能计算领域wpfspringbootjava后端分布式spring开发语言
在现代的分布式系统中,任务调度是一个常见的需求。无论是定时任务的执行,还是根据业务逻辑动态触发的任务,都需要一个高效、可靠的调度框架来管理。SpringBoot作为目前最流行的Java开发框架之一,提供了强大的依赖管理和快速开发的能力,结合分布式任务调度框架,可以极大地提升开发效率和系统的可维护性。本文将介绍如何基于SpringBoot实现一个分布式任务调度系统,主要涉及Elastic-Job框架
- 解释CALL_FORM,NEW_FORM和OPEN_FORM之间有什么区别?思维导图 代码示例(java 架构)
用心去追梦
java架构开发语言
CALL_FORM,NEW_FORM和OPEN_FORM之间的区别在OracleForms中,CALL_FORM、NEW_FORM和OPEN_FORM是用于管理和启动表单的不同命令。每个命令的行为和用途都有所不同,理解它们的区别对于正确构建和管理Forms应用程序非常重要。1.CALL_FORM定义:调用并运行另一个表单,但不会关闭当前表单。被调用的表单以模式对话框的形式显示,即用户必须完成或取消
- 我要写整个中文互联网界最牛逼的JVM系列教程 | 「JVM与Java体系架构」章节:JVM的生命周期
李阿昀
只要你有心人人都是JVM精通者jvmjava架构
这一讲,我们就来好好谈一谈JVM的生命周期。JVM的生命周期大家做了这么久的开发,应该知道很多的结构其实都有其生命周期吧!而关于JVM的生命周期,这里我们则主要讲述它的三个状态,即虚拟机的启动、虚拟机的执行以及虚拟机的退出,这也是一个结构的生命周期最起码应该具备的三个状态——开始、运行、结束。这就像哲学里面讨论的终极问题一样,我是谁?我从哪里来?我将到哪里去?其实,我觉得先提出我是谁这个问题不太合
- java笔试题以及答案详解
weixin-80213251
javaweb类javaclassjdk
一、单项选择题1.Java是从()语言改进重新设计。A.AdaB.C++C.PasacalD.BASIC答案:B2.下列语句哪一个正确()A.Java程序经编译后会产生machinecodeB.Java程序经编译后会产生bytecodeC.Java程序经编译后会产生DLLD.以上都不正确答案:B3.下列说法正确的选项有()A.class中的constructor不可省略B.constructor必
- 红宝书第十一讲:超易懂版「ES6类与继承」零基础教程:用现实例子+图解实现
kovlistudio
前端es6javascript开发语言前端学习
红宝书第十一讲:超易懂版「ES6类与继承」零基础教程:用现实例子+图解实现资料取自《JavaScript高级程序设计(第5版)》。查看总目录:红宝书学习大纲一、ES6类的核心语法:把事物抽象成“模板”想象你要设计一款「动物养成游戏」,需要创建多种动物对象。ES6的class就是一个代码模板://基础类(Animal是模板,有名称和吃东西方法)classAnimal{constructor(name
- 探索HTML5 Canvas的无限可能:一个丰富多彩的开源项目
黎情卉Desired
探索HTML5Canvas的无限可能:一个丰富多彩的开源项目去发现同类优质开源项目:https://gitcode.com/在这个充满活力的数字时代,JavaScript、HTML和CSS已经成为构建互动式网页体验的核心技术。今天,我们向您推荐一个独特而有趣的开源项目,它将这些技术结合在一起,创造出一系列生动活泼的可视化元素,包括时钟、计时器、地图、国际象棋、温度计等,让您在学习和实践中感受HTM
- 优化 Java 数据结构选择与使用,提升程序性能与可维护性
A-Kamen
java数据结构开发语言
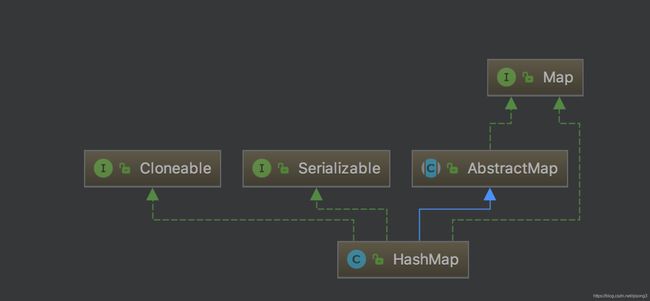
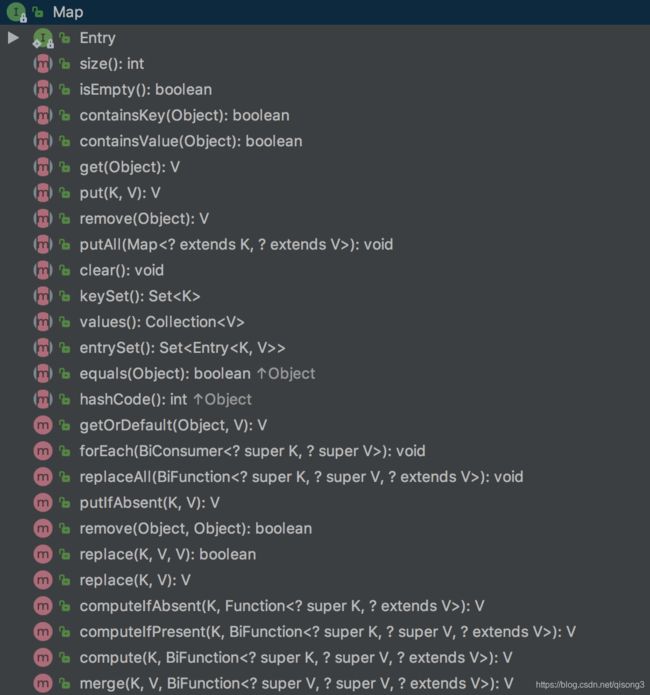
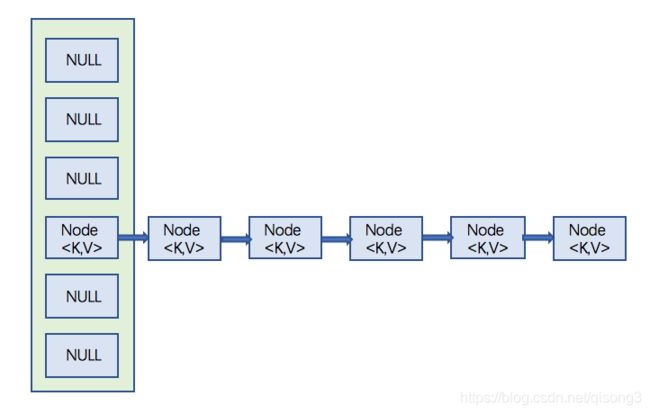
引言在软件开发中,数据结构的选择是影响程序性能、内存使用以及代码可维护性的关键因素之一。Java作为一门广泛使用的编程语言,提供了丰富的内置数据结构,如数组、链表、栈、队列、树、图以及集合框架中的各种接口实现(如List,Set,Map等)。然而,面对不同的应用场景,如何合理地选择和优化数据结构,成为了一个值得深入探讨的话题。本文将介绍几种常见的Java数据结构,并探讨如何根据实际需求进行优化选择
- TinyMCE插件是否支持Word图片的直接复制与web上传?
2501_90694782
umeditor粘贴wordueditor粘贴wordueditor复制wordueditor上传word图片ueditor导入wordueditor导入pdfueditor导入ppt
要求:开源,免费,技术支持编辑器:TinyMCE前端:vue,vue2-cli,vue3-cli后端:java,jsp,springboot,asp.net,php,asp,.netcore,.netmvc,.netform功能:导入Word,导入Excel,导入PPT(PowerPoint),导入PDF,复制粘贴word,导入微信公众号内容,web截屏平台:Windows,macOS,Linux
- java常用排序方法集合sort
吗喽对你问好
java开发语言数据结构
1.Arrays.sortArrays.sort是用于对数组进行排序的静态方法,位于java.util.Arrays类中。特点:只能用于数组(包括基本类型数组和对象数组)。对基本类型数组(如int[],double[]等)使用快速排序(Dual-PivotQuicksort)。对对象数组(如Integer[],String[]等)使用归并排序(TimSort)。排序是原地进行的(即直接修改原数组)
- 探索HTML5 Canvas:创造动态与交互性网页内容的强大工具
A-Kamen
html5前端html
探索HTML5Canvas:创造动态与交互性网页内容的强大工具引言在HTML5的众多新特性中,Canvas无疑是最引人注目的元素之一。它为网页设计师和开发者提供了一个通过JavaScript和HTML直接在网页上绘制图形、图像以及进行动画处理的画布。Canvas的灵活性和强大功能,使得它成为创造动态、交互性网页内容的首选工具。本文将深入探讨HTML5Canvas的基本用法、应用场景以及如何利用它来
- 【JavaWeb学习Day25】
quo-te
JavaWebvue黑马
Web前端实战ElementPlus什么是ElementPlusElementPlus:是饿了么团队研发的,基于Vue3,面向设计师和开发者的组件库。组件:组成网页的部件,例如超链接、按钮、图片、表格、表单、分页条等等。官网:一个Vue3UI框架|ElementPlus快速入门准备工作:1.创建vue项目2.参照官方文档,安装ElementPlus组件库(在当前工程的目录下):npminstall
- 分布式中间件:Redisson 入门和分布式锁
顾北辰20
分布式中间件分布式中间件redisson
分布式中间件:Redisson入门和分布式锁在分布式系统的开发中,处理并发问题是一个常见且具有挑战性的任务。为了确保数据的一致性和完整性,我们常常需要使用分布式锁。Redisson作为一个强大的分布式Java驻内存数据网格(In-MemoryDataGrid)中间件,为我们提供了简单且高效的分布式锁解决方案。本文将带你入门Redisson,并介绍如何使用它实现分布式锁。1.引入Redisson依赖
- Java高并发容器的内核解析:从无锁算法到分段锁的架构演进
猿享天开
开发语言java
《Java高并发容器的内核解析:从无锁算法到分段锁的架构演进》本文将以JUC包核心容器为切入点,深入剖析ConcurrentHashMap在Java8中的64位Hash分段技术,解密LinkedBlockingQueue双锁队列设计的吞吐量秘密,并给出各容器在亿级流量场景下的性能压测对比与选型决策矩阵。一、BlockingQueue体系:生产者-消费者模式的工业级实现1.阻塞队列的四大行为矩阵行为
- 开源文档管理系统教程
戚逸玫Silas
开源文档管理系统教程document-management-systemOpenKMisaOpenSourceDocumentManagementSystem项目地址:https://gitcode.com/gh_mirrors/do/document-management-system1.项目的目录结构及介绍openkm/├──src/│├──main/││├──java/││└──resour
- Java常用集合与映射的线程安全问题深度解析
QQ828929QQ
java安全开发语言
Java常用集合与映射的线程安全问题深度解析一、线程安全基础认知在并发编程环境下,当多个线程同时操作同一集合对象时,若未采取同步措施,可能导致以下典型问题:数据竞争:多个线程同时修改数据导致结果不可预测状态不一致:部分线程看到集合的中间状态内存可见性:线程本地缓存与主内存数据不同步死循环风险:特定操作引发无限循环(如JDK7的HashMap扩容)二、典型非线程安全集合问题分析1.ArrayList
- javaweb学习Day10
乐一粒学编程
学习java开发语言
来源:尚硅谷2022版javaweb今日内容:1.日期和字符串之间的格式化//String->java.util.DateStringdateStr1="2021-12-3012:59:59";SimpleDateFormatsdf=newSimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-ddHH:mm:ss");try{Datedate1=sdf.parse(dateStr1);}catch(
- Java 中 final 与 effectively final
yaoxin521123
【原来如此】java开发语言
Java中final与effectivelyfinal一、为什么我们需要final和effectivelyfinal?为什么这些关键字重要?在Java中,一些变量需要在初始化后不再变化,以确保程序的安全性和可读性。为什么你需要关心final和effectivelyfinal?防止变量进一步修改导致的不可控度问题。提高代码可读性和维护性。对于区别final和effectivelyfinal来说,懂得
- Java面试黄金宝典5
ylfhpy
Java面试黄金宝典java面试开发语言职场和发展算法
1.ConcurrentHashMap和HashTable有哪些区别原理HashTable:它继承自Dictionary类,是Java早期提供的线程安全哈希表。其线程安全的实现方式是对每个方法都使用synchronized关键字进行同步。例如,在调用put、get等方法时,整个HashTable会被锁定,其他线程必须等待当前线程释放锁后才能访问该方法。javaimportjava.util.Has
- Java基础面试题学习
PowerCloud
java学习开发语言
转换成自已的语言来回答,来源小林coding、沉默王二以及其它资源和自已改编。1、概念1、说一下Java的特点我认为Java有很多特点首先是平台无关性:Java可以实现一次编译到处运行,因为Java的编译器将源代码编译成字节码,使得该字节码可以在任意装有JVM的操作系统上运行。其次是面向对象的性质:Java是面向对象编程语言,这种OOP的特性使得代码易于维护和重用。主要源于封装继承多态这三大特性。
- Java复习路线
Code good g
面试准备javamysql数据库
Java复习1、Java基础2、Java多线程3、Javaweb的复习4、MySql复习数据库常用的代码:思维导图:5、计算机组成原理6、网络编程7、Java注解和反射8、计算机网络9、html/css/js10、ssm11、spring12、springmvc13、springboot14、vue15、springcloud16、jvm17、Juc18、mybatis-plus学习19、git2
- 基于LangChain-Chatchat实现智能问答系统
2301_79125431
java
题解|#统计输入正数个数#5.6importjava.util.*;publicclassMain{publics广汽丰田发动机薪酬福利待遇1、工作时间:基本上为5天8小时工作制;2、薪资结构:基本工资+加班工资+各类补贴津贴+各类慰问金+小红书24届春招和25届实习,内部推荐小红书24届春招和25届实习,推荐码为:0T019BWYNARK,内推码仅适用于校招内推及微信小程序题解|#试卷发布当天作
- 23种设计模式-抽象工厂(Abstract Factory)设计模式
程序员汉升
#设计模式设计模式java抽象工厂模式
抽象工厂设计模式什么是抽象工厂设计模式?抽象工厂模式的特点抽象工厂模式的结构抽象工厂模式的优缺点抽象工厂方法的Java实现代码总结总结什么是抽象工厂设计模式?抽象工厂模式(AbstractFactoryDesignPattern)是一种创建型设计模式,它提供了一种方式来创建一系列相关或相互依赖的对象,而无需指定它们的具体类。与工厂方法模式的区别在于,抽象工厂模式通常用于处理产品族的创建,确保创建的
- Caffeine vs Guava Cache:性能巅峰对决,谁才是 Java 本地缓存之王?
Julian.zhou
Java开发基础技能缓存java算法
CaffeinevsGuavaCache:性能巅峰对决,谁才是Java本地缓存之王?导语:在Java本地缓存的战场上,Caffeine和GuavaCache是开发者最常用的两大神器。但究竟谁的性能更胜一筹?为何Caffeine被称为“GuavaCache的终结者”?本文通过算法原理、并发性能、内存管理、实战测试四大维度,彻底揭秘两者的性能差异,文末附迁移指南和选型建议!一、核心差异:算法与淘汰策略
- nginx助力打包部署
潜意识Java
Java知识javanginx开发语言
目录一、打包部署基础入门(一)为什n么要打包部署(二)打包部署的基本流程二、Java项目打包(一)使用Maven进行打包(二)使用Gradle进行打包三、服务器环境准备(一)选择合适的服务器(二)安装Java运行环境四、Nginx初相识(一)Nginx是什么(二)Nginx的安装五、Nginx配置Java项目反向代理(一)反向代理的概念(二)Nginx反向代理配置示例六、Nginx实现负载均衡(一
- java面试题,既然你说到了创建线程池,那么你知道创建线程池的方式有哪几种吗?
java程序员CC
java开发语言
在Java中,创建线程池的方式有多种,其中比较常用的方式包括:FixedThreadPool(固定大小线程池):通过Executors.newFixedThreadPool(intn)方法创建,线程池中的线程数量固定为n,适合处理任务量稳定的场景。CachedThreadPool(缓存线程池):通过Executors.newCachedThreadPool()方法创建,线程池的线程数量不固定,根据
- java集合List,Set,Map怎么理解存储数据有序,无序以及可重复,不可重复
java程序员CC
JAVA基础java面试list
学习java已经有一段时间了,在练习开发项目的过程中经常用到List和Map却不知道其到底有何区别,今天整理了一下知识点对这几个进行浅显易懂的区分。PS:本文中的“有序”指的是存储数据时输入顺序与数据输出顺序相等,“唯一”:指的是不重复首先我们知道java集合有两个接口;一个是Collection,一个是Map;其中Colection衍生出了两个子接口也就是平时我们常见的--List【有序,不唯一
- 定时任务调度框架xxl-job与quartz的区别
java程序员CC
java
XXL-Job和Quartz都是Java项目中常用的定时任务框架,它们有以下几点区别:xxl-job和Quartz都是用于任务调度的开源框架,它们之间有一些区别,主要体现在以下几个方面:语言支持:Quartz主要是基于Java的任务调度框架,支持Java语言。xxl-job是一个分布式任务调度平台,它提供了Java版本的调度中心,同时还提供了Python、PHP等语言的任务执行器,因此支持多种语言
- 鸿蒙开发:ArkTs语言变量和常量
前言本文代码案例基于Api13。正因为有了变量和常量,才有了程序之间的数据存储和管理,无论是变量还是常量,在命名的时候,一定要知名其意,能够很好的表达出所声明的意图,这一点非常的重要,千万不要以拼音或者简单的字母进行定义,不为别的,我害怕别人嘲笑你。变量(Variable)变量是一种用于存储数据的容器,并且其存储的数据值可以在程序执行过程中被改变,变量通常有一个名字(标识符),用于在程序中引用它。
- apache 安装linux windows
墙头上一根草
apacheinuxwindows
linux安装Apache 有两种方式一种是手动安装通过二进制的文件进行安装,另外一种就是通过yum 安装,此中安装方式,需要物理机联网。以下分别介绍两种的安装方式
通过二进制文件安装Apache需要的软件有apr,apr-util,pcre
1,安装 apr 下载地址:htt
- fill_parent、wrap_content和match_parent的区别
Cb123456
match_parentfill_parent
fill_parent、wrap_content和match_parent的区别:
1)fill_parent
设置一个构件的布局为fill_parent将强制性地使构件扩展,以填充布局单元内尽可能多的空间。这跟Windows控件的dockstyle属性大体一致。设置一个顶部布局或控件为fill_parent将强制性让它布满整个屏幕。
2) wrap_conte
- 网页自适应设计
天子之骄
htmlcss响应式设计页面自适应
网页自适应设计
网页对浏览器窗口的自适应支持变得越来越重要了。自适应响应设计更是异常火爆。再加上移动端的崛起,更是如日中天。以前为了适应不同屏幕分布率和浏览器窗口的扩大和缩小,需要设计几套css样式,用js脚本判断窗口大小,选择加载。结构臃肿,加载负担较大。现笔者经过一定时间的学习,有所心得,故分享于此,加强交流,共同进步。同时希望对大家有所
- [sql server] 分组取最大最小常用sql
一炮送你回车库
SQL Server
--分组取最大最小常用sql--测试环境if OBJECT_ID('tb') is not null drop table tb;gocreate table tb( col1 int, col2 int, Fcount int)insert into tbselect 11,20,1 union allselect 11,22,1 union allselect 1
- ImageIO写图片输出到硬盘
3213213333332132
javaimage
package awt;
import java.awt.Color;
import java.awt.Font;
import java.awt.Graphics;
import java.awt.image.BufferedImage;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.imagei
- 自己的String动态数组
宝剑锋梅花香
java动态数组数组
数组还是好说,学过一两门编程语言的就知道,需要注意的是数组声明时需要把大小给它定下来,比如声明一个字符串类型的数组:String str[]=new String[10]; 但是问题就来了,每次都是大小确定的数组,我需要数组大小不固定随时变化怎么办呢? 动态数组就这样应运而生,龙哥给我们讲的是自己用代码写动态数组,并非用的ArrayList 看看字符
- pinyin4j工具类
darkranger
.net
pinyin4j工具类Java工具类 2010-04-24 00:47:00 阅读69 评论0 字号:大中小
引入pinyin4j-2.5.0.jar包:
pinyin4j是一个功能强悍的汉语拼音工具包,主要是从汉语获取各种格式和需求的拼音,功能强悍,下面看看如何使用pinyin4j。
本人以前用AscII编码提取工具,效果不理想,现在用pinyin4j简单实现了一个。功能还不是很完美,
- StarUML学习笔记----基本概念
aijuans
UML建模
介绍StarUML的基本概念,这些都是有效运用StarUML?所需要的。包括对模型、视图、图、项目、单元、方法、框架、模型块及其差异以及UML轮廓。
模型、视与图(Model, View and Diagram)
&
- Activiti最终总结
avords
Activiti id 工作流
1、流程定义ID:ProcessDefinitionId,当定义一个流程就会产生。
2、流程实例ID:ProcessInstanceId,当开始一个具体的流程时就会产生,也就是不同的流程实例ID可能有相同的流程定义ID。
3、TaskId,每一个userTask都会有一个Id这个是存在于流程实例上的。
4、TaskDefinitionKey和(ActivityImpl activityId
- 从省市区多重级联想到的,react和jquery的差别
bee1314
jqueryUIreact
在我们的前端项目里经常会用到级联的select,比如省市区这样。通常这种级联大多是动态的。比如先加载了省,点击省加载市,点击市加载区。然后数据通常ajax返回。如果没有数据则说明到了叶子节点。 针对这种场景,如果我们使用jquery来实现,要考虑很多的问题,数据部分,以及大量的dom操作。比如这个页面上显示了某个区,这时候我切换省,要把市重新初始化数据,然后区域的部分要从页面
- Eclipse快捷键大全
bijian1013
javaeclipse快捷键
Ctrl+1 快速修复(最经典的快捷键,就不用多说了)Ctrl+D: 删除当前行 Ctrl+Alt+↓ 复制当前行到下一行(复制增加)Ctrl+Alt+↑ 复制当前行到上一行(复制增加)Alt+↓ 当前行和下面一行交互位置(特别实用,可以省去先剪切,再粘贴了)Alt+↑ 当前行和上面一行交互位置(同上)Alt+← 前一个编辑的页面Alt+→ 下一个编辑的页面(当然是针对上面那条来说了)Alt+En
- js 笔记 函数
征客丶
JavaScript
一、函数的使用
1.1、定义函数变量
var vName = funcation(params){
}
1.2、函数的调用
函数变量的调用: vName(params);
函数定义时自发调用:(function(params){})(params);
1.3、函数中变量赋值
var a = 'a';
var ff
- 【Scala四】分析Spark源代码总结的Scala语法二
bit1129
scala
1. Some操作
在下面的代码中,使用了Some操作:if (self.partitioner == Some(partitioner)),那么Some(partitioner)表示什么含义?首先partitioner是方法combineByKey传入的变量,
Some的文档说明:
/** Class `Some[A]` represents existin
- java 匿名内部类
BlueSkator
java匿名内部类
组合优先于继承
Java的匿名类,就是提供了一个快捷方便的手段,令继承关系可以方便地变成组合关系
继承只有一个时候才能用,当你要求子类的实例可以替代父类实例的位置时才可以用继承。
在Java中内部类主要分为成员内部类、局部内部类、匿名内部类、静态内部类。
内部类不是很好理解,但说白了其实也就是一个类中还包含着另外一个类如同一个人是由大脑、肢体、器官等身体结果组成,而内部类相
- 盗版win装在MAC有害发热,苹果的东西不值得买,win应该不用
ljy325
游戏applewindowsXPOS
Mac mini 型号: MC270CH-A RMB:5,688
Apple 对windows的产品支持不好,有以下问题:
1.装完了xp,发现机身很热虽然没有运行任何程序!貌似显卡跑游戏发热一样,按照那样的发热量,那部机子损耗很大,使用寿命受到严重的影响!
2.反观安装了Mac os的展示机,发热量很小,运行了1天温度也没有那么高
&nbs
- 读《研磨设计模式》-代码笔记-生成器模式-Builder
bylijinnan
java设计模式
声明: 本文只为方便我个人查阅和理解,详细的分析以及源代码请移步 原作者的博客http://chjavach.iteye.com/
/**
* 生成器模式的意图在于将一个复杂的构建与其表示相分离,使得同样的构建过程可以创建不同的表示(GoF)
* 个人理解:
* 构建一个复杂的对象,对于创建者(Builder)来说,一是要有数据来源(rawData),二是要返回构
- JIRA与SVN插件安装
chenyu19891124
SVNjira
JIRA安装好后提交代码并要显示在JIRA上,这得需要用SVN的插件才能看见开发人员提交的代码。
1.下载svn与jira插件安装包,解压后在安装包(atlassian-jira-subversion-plugin-0.10.1)
2.解压出来的包里下的lib文件夹下的jar拷贝到(C:\Program Files\Atlassian\JIRA 4.3.4\atlassian-jira\WEB
- 常用数学思想方法
comsci
工作
对于搞工程和技术的朋友来讲,在工作中常常遇到一些实际问题,而采用常规的思维方式无法很好的解决这些问题,那么这个时候我们就需要用数学语言和数学工具,而使用数学工具的前提却是用数学思想的方法来描述问题。。下面转帖几种常用的数学思想方法,仅供学习和参考
函数思想
把某一数学问题用函数表示出来,并且利用函数探究这个问题的一般规律。这是最基本、最常用的数学方法
- pl/sql集合类型
daizj
oracle集合typepl/sql
--集合类型
/*
单行单列的数据,使用标量变量
单行多列数据,使用记录
单列多行数据,使用集合(。。。)
*集合:类似于数组也就是。pl/sql集合类型包括索引表(pl/sql table)、嵌套表(Nested Table)、变长数组(VARRAY)等
*/
/*
--集合方法
&n
- [Ofbiz]ofbiz初用
dinguangx
电商ofbiz
从github下载最新的ofbiz(截止2015-7-13),从源码进行ofbiz的试用
1. 加载测试库
ofbiz内置derby,通过下面的命令初始化测试库
./ant load-demo (与load-seed有一些区别)
2. 启动内置tomcat
./ant start
或
./startofbiz.sh
或
java -jar ofbiz.jar
&
- 结构体中最后一个元素是长度为0的数组
dcj3sjt126com
cgcc
在Linux源代码中,有很多的结构体最后都定义了一个元素个数为0个的数组,如/usr/include/linux/if_pppox.h中有这样一个结构体: struct pppoe_tag { __u16 tag_type; __u16 tag_len; &n
- Linux cp 实现强行覆盖
dcj3sjt126com
linux
发现在Fedora 10 /ubutun 里面用cp -fr src dest,即使加了-f也是不能强行覆盖的,这时怎么回事的呢?一两个文件还好说,就输几个yes吧,但是要是n多文件怎么办,那还不输死人呢?下面提供三种解决办法。 方法一
我们输入alias命令,看看系统给cp起了一个什么别名。
[root@localhost ~]# aliasalias cp=’cp -i’a
- Memcached(一)、HelloWorld
frank1234
memcached
一、简介
高性能的架构离不开缓存,分布式缓存中的佼佼者当属memcached,它通过客户端将不同的key hash到不同的memcached服务器中,而获取的时候也到相同的服务器中获取,由于不需要做集群同步,也就省去了集群间同步的开销和延迟,所以它相对于ehcache等缓存来说能更好的支持分布式应用,具有更强的横向伸缩能力。
二、客户端
选择一个memcached客户端,我这里用的是memc
- Search in Rotated Sorted Array II
hcx2013
search
Follow up for "Search in Rotated Sorted Array":What if duplicates are allowed?
Would this affect the run-time complexity? How and why?
Write a function to determine if a given ta
- Spring4新特性——更好的Java泛型操作API
jinnianshilongnian
spring4generic type
Spring4新特性——泛型限定式依赖注入
Spring4新特性——核心容器的其他改进
Spring4新特性——Web开发的增强
Spring4新特性——集成Bean Validation 1.1(JSR-349)到SpringMVC
Spring4新特性——Groovy Bean定义DSL
Spring4新特性——更好的Java泛型操作API
Spring4新
- CentOS安装JDK
liuxingguome
centos
1、行卸载原来的:
[root@localhost opt]# rpm -qa | grep java
tzdata-java-2014g-1.el6.noarch
java-1.7.0-openjdk-1.7.0.65-2.5.1.2.el6_5.x86_64
java-1.6.0-openjdk-1.6.0.0-11.1.13.4.el6.x86_64
[root@localhost
- 二分搜索专题2-在有序二维数组中搜索一个元素
OpenMind
二维数组算法二分搜索
1,设二维数组p的每行每列都按照下标递增的顺序递增。
用数学语言描述如下:p满足
(1),对任意的x1,x2,y,如果x1<x2,则p(x1,y)<p(x2,y);
(2),对任意的x,y1,y2, 如果y1<y2,则p(x,y1)<p(x,y2);
2,问题:
给定满足1的数组p和一个整数k,求是否存在x0,y0使得p(x0,y0)=k?
3,算法分析:
(
- java 随机数 Math与Random
SaraWon
javaMathRandom
今天需要在程序中产生随机数,知道有两种方法可以使用,但是使用Math和Random的区别还不是特别清楚,看到一篇文章是关于的,觉得写的还挺不错的,原文地址是
http://www.oschina.net/question/157182_45274?sort=default&p=1#answers
产生1到10之间的随机数的两种实现方式:
//Math
Math.roun
- oracle创建表空间
tugn
oracle
create temporary tablespace TXSJ_TEMP
tempfile 'E:\Oracle\oradata\TXSJ_TEMP.dbf'
size 32m
autoextend on
next 32m maxsize 2048m
extent m
- 使用Java8实现自己的个性化搜索引擎
yangshangchuan
javasuperword搜索引擎java8全文检索
需要对249本软件著作实现句子级别全文检索,这些著作均为PDF文件,不使用现有的框架如lucene,自己实现的方法如下:
1、从PDF文件中提取文本,这里的重点是如何最大可能地还原文本。提取之后的文本,一个句子一行保存为文本文件。
2、将所有文本文件合并为一个单一的文本文件,这样,每一个句子就有一个唯一行号。
3、对每一行文本进行分词,建立倒排表,倒排表的格式为:词=包含该词的总行数N=行号