React --- 深入浅出redux
1.为什么需要redux?
2.redux核心理念
3.redux三大原则
4.初学redux
- 简单演示redux的使用过程
//commonJS
//导入redux
const redux = require('redux');
const initialState = {
counter:0
}
//reducer
function reducer(state = initialState, action){
switch(action.type) {
case "INCREMENT":
return {
...state , counter : state.counter + 1}
case "DECREMENT":
return {
...state , counter : state.counter - 1}
case "ADD_NUMBER":
return {
...state , counter : state.counter + action.num}
case "SUB_NUMBER":
return {
...state , counter : state.counter - action.num}
default:
return state;
}
}
//store(创建的时候需要一个reducer)
const store = redux.createStore(reducer)
//action
const action1 = {
type:"INCREMENT"};
const action2 = {
type:"DECREMENT"};
const action3 = {
type:"ADD_NUMBER",num:5};
const action4 = {
type:"SUB_NUMBER",num:12};
//订阅store的修改
store.subscribe( () => {
console.log('state发生了改变' + store.getState().counter)
} )
//派发action
store.dispatch(action1)
store.dispatch(action2)
store.dispatch(action2)
store.dispatch(action3)
store.dispatch(action4)
5.实战redux代码组织如下
redux目录结构的划分。
我们日常的开发中,需要将redux代码安排在一个文件夹中。
首先我们创建一个store文件夹。
紧接着,需要创建 index.js,constants.js,reducer.js,actionCreators.js
- reducer.js
这里负责写好reducer纯函数,
import {
ADD_NUMBER,
SUB_NUMBER
} from './constants.js'
const initialState = {
counter:0
}
function reducer(state = initialState, action){
switch(action.type) {
case ADD_NUMBER:
return {
...state, counter : state.counter + action.num}
case SUB_NUMBER:
return {
...state, counter : state.counter - action.num}
default:
return state;
}
}
export default reducer;
- actionCreators.js
这里我们将需要派发的action封装为更加灵活的函数。
//将action封装为更加灵活的函数
import {
ADD_NUMBER,
SUB_NUMBER
} from './constants.js'
export const addAction = num => {
return {
type:ADD_NUMBER,
num
}
}
export const subAction = num => {
return {
type:SUB_NUMBER,
num
}
}
- constants.js
这里为了放置我们的变量由于使用不统一造成的问题,我们将我们要使用的变量定义为常量。
export const ADD_NUMBER = "ADD_NUMBER";
export const SUB_NUMBER = "SUB_NUMBER";
- index.js
这里写好store,同时导出页面,供其他组件使用.
import redux from 'redux'
import reducer from './reducer.js'
const store = redux.createStore(reducer);
export default store;
- 在某个组件内部使用redux
import store from './store/index.js'
import {
addAction,
subAction
} from './store/actionCreators.js'
store.subscribe( () => {
console.log(store.getState());
})
store.dispatch(addAction(10))
store.dispatch(subAction(19))
store.dispatch(addAction(5))
6.将react代码和redux结合在一起使用
import React, {
PureComponent } from 'react'
import store from '../store'
import {
addAction
} from '../store/actionCreators'
export default class home extends PureComponent {
constructor(props){
super(props)
this.state = {
counter: store.getState().counter
}
}
//增加订阅,重新调用render函数,实现页面更新
componentDidMount(){
this.unSubscribe = store.subscribe( () => {
this.setState({
counter:store.getState().counter
})
})
}
//取消订阅,在页面销毁之后取消订阅
componentWillUnmount(){
this.unSubscribe();
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<h2>home</h2>
<h3>当前计数:{
this.state.counter}</h3>
<button onClick={
e => this.increment()}>+1</button>
<button onClick={
e => this.addNumber()}>+5</button>
<hr/>
</div>
)
}
increment(){
store.dispatch(addAction(1))
}
addNumber(){
store.dispatch(addAction(5))4333e3
}
}
7.react-redux代码优化(手动封装一个react-redux)
前面因为我们的代码里面有了home.js 和 about.js中,因为两个代码里面在使用redux的问题上基本出现了代码类似的情况,所以我们需要将共同代码封装为一个函数之后使用就很很方便.
- 封装好的connect.js
import React, {
PureComponent } from 'react'
import store from '../store'
export function connect(mapStateToProps,mapDispatchToProp) {
return function enhanceHOC(WrappedComponent) {
return class extends PureComponent {
constructor(props){
super(props)
this.state = {
storeState: mapStateToProps(store.getState())
}
}
//订阅监听
componentDidMount(){
this.unsubscribe = store.subscribe( () => {
this.setState({
storeState : mapStateToProps(store.getState())
})
})
}
componentWillUnmount(){
this.unsubscribe();
}
render(){
return <WrappedComponent
{
...this.props}
{
...mapStateToProps(store.getState())}
{
...mapDispatchToProp(store.dispatch)}/>
//将传递过来的参数传递过去
}
}
}
}
在about.js中使用。
import React, {
PureComponent } from 'react'
import {
subAction
} from '../store/actionCreators'
import {
connect } from '../utils/connect'
function About(props) {
return (
<div>
<h2>about</h2>
<h3>当前计数:{
props.counter}</h3>
<button onClick={
e => props.decrement()}>-2</button>
<button onClick={
e => props.subNumber()}>-4</button>
<hr />
</div>
)
}
const mapStateToProps = state => {
return {
counter: state.counter
}
}
const mapDispatchToProp = dispatch => {
return {
decrement: function () {
dispatch(subAction(2))
},
subNumber: function () {
dispatch(subAction(4))
}
}
}
export default connect(mapStateToProps, mapDispatchToProp)(About)
8.react-redux库的使用
安装react-redux库:yarn add react-redux
react-redux库,主要封装了两个库,就是我们前面封装好的connect和context库。
9.组件之中异步操作
普通开发中将我们请求服务器上的数据放在redux中管理。
、
因为网络请求到的数据我们i想要都放在redux中处理,根据redux而言,我们想要将网络请求也放在redux中去处理。这个时候我们就需要用到中间件(redux-thunk)

代码演示:
import {
createStore, applyMiddleware } from 'redux'
import thunkMiddleware from 'redux-thunk'
import reducer from './reducer.js'
//应用一些中间件
// applyMiddleware('中间件1','中间件2','中间件3')
const storeenhancer = applyMiddleware(thunkMiddleware)
const store = createStore(reducer, storeenhancer);
export default store;
//redux-thunk中定义的action函数
export const getHomeDataAction = dispatch => {
// console.log('action函数中中')
axios({
url:"http://123.207.32.32:8000/home/multidata"
}).then((res) => {
const data = res.data.data;
dispatch(changeBannersAction(data.banner.list))
})
}
在actionCreators中定义axios请求数据。
10.reducer拆分
拆解reducer中的各种操作:
- 原本的reducer是这样的,如果我们的逻辑太多就会出现过多的switch,不利于我们代码的重构。
function reducer(state = initialState, action){
switch(action.type) {
case ADD_NUMBER:
return {
...state, counter : state.counter + action.num}
case SUB_NUMBER:
return {
...state, counter : state.counter - action.num}
case CHANGE_BANNERS:
return {
...state, banners : action.banners}
case CHANGE_RECOMMANDS:
return {
...state, recommends : action.recommends}
default:
return state;
}
}
- 因此我们需要拆分reducer来实现,共同功能的reducer我们拆分成一个函数。
const initialCounterState = {
counter:0
}
//拆分counter的reducer
function counterReducer(state = initialCounterState, action) {
switch(action.type) {
case ADD_NUMBER:
return {
...state, counter : state.counter + action.num}
case SUB_NUMBER:
return {
...state, counter : state.counter - action.num}
default:
return state;
}
}
const initialHomeState = {
banners:[],
recommends:[]
}
//拆分home的reducer
function homeReducer(state = initialHomeState, action) {
switch(action.type) {
case CHANGE_BANNERS:
return {
...state, banners : action.banners}
case CHANGE_RECOMMANDS:
return {
...state, recommends : action.recommends}
default:
return state;
}
}
const defaultState = {
counterInfo:null,
homeInfo:null
}
function reducer(state = {
}, action){
return {
counterInfo: counterReducer(state.counterInfo, action),
homeInfo: homeReducer(state.homeInfo, action)
}
}
将原本的数据格式定义为初始化数据。
最后在使用的时候,需要使用为state.counterInfo.counter。
———————————————————————————————————————
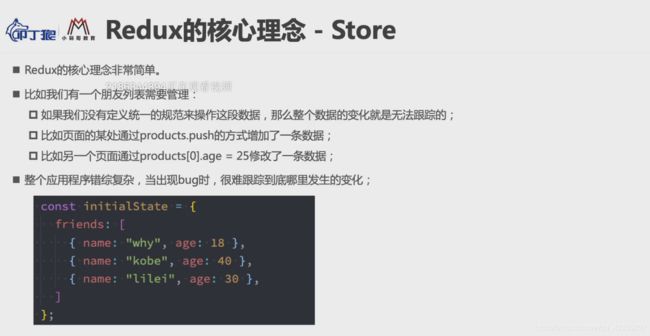
个人理解redux:
- 为什么使用redux?
随着javascript开发趋向复杂化,所以javascript需要管理更多的state(状态),这些庄涛可能来自服务器响应数据,缓存数据,本地生成数据,(也包括一些UI状态,激活的路由,选中的标签等等)而redux的出现就是为了我们更加方便地管理state,让state的变化变得可以预测。 - redux核心概念
store就是普通的对象,就是一些数据
{
bookList:[
{
"name":"三国演义"},
{
"name":"西游记"}
]
}
action 如果你想要修改store中的数据,只有通过action来修改state
{
type: 'ADD_TODO', text: 'Go to swimming pool' }
{
type: 'TOGGLE_TODO', index: 1 }
{
type: 'SET_VISIBILITY_FILTER', filter: 'SHOW_ALL' }
reducer 为了把state和action串联起来((state,action) => state)
function visibilityFilter(state = 'SHOW_ALL', action) {
if (action.type === 'SET_VISIBILITY_FILTER') {
return action.filter;
} else {
return state;
}
}
再开发一个 reducer 调用这两个 reducer,进而来管理整个应用的 state:
function todoApp(state = {
}, action) {
return {
todos: todos(state.todos, action),
visibilityFilter: visibilityFilter(state.visibilityFilter, action)
};
}
实际开发中,我们会将某一个要求或者说某一个请求的数据拆分为一个完整的redux,及属于其自己的actionCreators.js, constants.js,index.js,reducer.js.
第一次接触redux,感觉比vuex较难吧,或许是我没有认真的去看过vuex的原理吧。