2019独角兽企业重金招聘Python工程师标准>>> ![]()
Future,在Netty中所有的IO操作都是异步的,因此,你不能立刻得知消息是否被正确处理,但是我们可以过一会等它执行完成或者直接注册一个监听,具体的实现就是通过Future和ChannelFuture,他们可以注册一个监听,当操作执行成功或失败时监听会自动触发。总之,所有的操作都会返回一个ChannelFuture。
Netty中的异步,就不得不提ChannelFuture。Netty中的IO操作是异步的,包括bind、write、connect等操作会简单的返回一个ChannelFuture,调用者并不能立刻获得结果。
在netty中所有的io操作都是异步的,也就是说我们在发送完消息后,netty内部是采用线程池去处理,方法立即返回了,但有时候我们需要外部方法等待服务器的响应,整个过程需要同步处理,那么就需要将异步调用转为同步调用,原理很简单,就是在调用异步方法后,主线程阻塞,直到异步方法返回结果
在netty中所有的I/O操作都是异步,这意味着netty提供的I/O方法调用都将立即返回,会返回一个ChannelFuture对象的实像,它将会给你一些信息,关于I/O执行状态的结果,但此时不能保证真正的I/O操作已经完成。
推荐使用addListener(ChannelFutureListener)异步得到通知当一个I/O操作完成后,做任何后续任务,而不是通过调用await方法(降低吞吐量)。但如果你想要业务场景是必须先执行A,然后同步执行B(异步通知不合适的场景),使用await是比较方便的。但await有一个限制,调用await方法的线程不能是I/O 线程(work线程),否则会抛出一个异常,避免死锁。
作为一个异步NIO框架,Netty的所有IO操作都是异步非阻塞的,通过Future-Listener机制,用户可以方便的主动获取或者通过通知机制获得IO操作结果。
比如:
/**
* Connect a {@link Channel} to the remote peer.
*/
public ChannelFuture connect(String inetHost, int inetPort) {
return connect(new InetSocketAddress(inetHost, inetPort));
}/**
* Create a new {@link Channel} and bind it.
*/
public ChannelFuture bind(int inetPort) {
return bind(new InetSocketAddress(inetPort));
}/**
* Request to write a message via this {@link Channel} through the {@link ChannelPipeline}.
* This method will not request to actual flush, so be sure to call {@link #flush()}
* once you want to request to flush all pending data to the actual transport.
*/
ChannelFuture write(Object msg);判断Future状态的方法
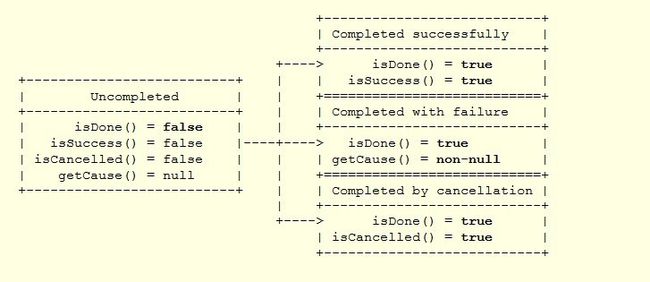
Future状态图
ChannelFuture对象状态只有uncompleted和completed。当一个I/O操作开始时,一个ChannelFuture实例被创建(我知道的暂时除close方法),刚开始时,future对象的实例即不是succeeded,failed,cancelled。因为真正的I/O操作还没有完成。如果正的I/O操作已经完成,那么future的状态将是completed,无论结果是succeeded,failed,cancelled。
netty中Future接口中的方法
netty的Future是继承自java.util.concurrent.Future接口
/**
* Returns {@code true} if and only if the I/O operation was completed
* successfully.
*/
boolean isSuccess();
/**
* returns {@code true} if and only if the operation can be cancelled via {@link #cancel(boolean)}.
*/
boolean isCancellable();java.util.concurrent.Future接口中的方法:
/**
* Waits for this future until it is done, and rethrows the cause of the failure if this future
* failed.
*/
Future sync() throws InterruptedException;
/**
* Waits for this future until it is done, and rethrows the cause of the failure if this future
* failed.
*/
Future syncUninterruptibly();
/**
* Waits for this future to be completed.
*
* @throws InterruptedException
* if the current thread was interrupted
*/
Future await() throws InterruptedException;
/**
* Waits for this future to be completed without
* interruption. This method catches an {@link InterruptedException} and
* discards it silently.
*/
Future awaitUninterruptibly();
/**
* Waits for this future to be completed within the
* specified time limit.
*
* @return {@code true} if and only if the future was completed within
* the specified time limit
*
* @throws InterruptedException
* if the current thread was interrupted
*/
boolean await(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException;
/**
* Waits for this future to be completed within the
* specified time limit.
*
* @return {@code true} if and only if the future was completed within
* the specified time limit
*
* @throws InterruptedException
* if the current thread was interrupted
*/
boolean await(long timeoutMillis) throws InterruptedException;
/**
* Waits for this future to be completed within the
* specified time limit without interruption. This method catches an
* {@link InterruptedException} and discards it silently.
*
* @return {@code true} if and only if the future was completed within
* the specified time limit
*/
boolean awaitUninterruptibly(long timeout, TimeUnit unit);
/**
* Waits for this future to be completed within the
* specified time limit without interruption. This method catches an
* {@link InterruptedException} and discards it silently.
*
* @return {@code true} if and only if the future was completed within
* the specified time limit
*/
boolean awaitUninterruptibly(long timeoutMillis); 维持netty中Future的生命周期的方法
sync()
syncUninterruptibly()
await()
await(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
awaitUninterruptibly(long timeout, TimeUnit unit):
awaitUninterruptibly(long timeoutMillis);
示例DEMO
服务器端代码
package hello.netty.lyx.com;
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
public class HelloServer {
public void start(int port) throws Exception {
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap();
b.group(bossGroup, workerGroup).channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer() {
@Override
public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch)
throws Exception {
// 注册handler
ch.pipeline().addLast(new HelloServerInHandler());
}
}).option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 128)
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true);
long t1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
ChannelFuture f = b.bind(port).sync();
f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
long t2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.print("diff in seconds:" + (t2 - t1) / 1000 + "\n");
} finally {
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
HelloServer server = new HelloServer();
server.start(9090);
}
} package hello.netty.lyx.com;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter;
// 该handler是InboundHandler类型
public class HelloServerInHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public boolean isSharable() {
System.out.println("==============handler-sharable==============");
return super.isSharable();
}
@Override
public void channelRegistered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
System.out.println("==============channel-register==============");
}
@Override
public void channelUnregistered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
System.out.println("==============channel-unregister==============");
}
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
System.out.println("==============channel-active==============");
}
@Override
public void channelInactive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
System.out.println("==============channel-inactive==============");
}
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
System.out.println("==============channel-read==============");
ByteBuf result = (ByteBuf) msg;
byte[] result1 = new byte[result.readableBytes()];
// msg中存储的是ByteBuf类型的数据,把数据读取到byte[]中
result.readBytes(result1);
String resultStr = new String(result1);
// 接收并打印客户端的信息
System.out.println("Client said:" + resultStr);
// 释放资源,这行很关键
result.release();
// 向客户端发送消息
String response = "I am ok!";
// 在当前场景下,发送的数据必须转换成ByteBuf数组
ByteBuf encoded = ctx.alloc().buffer(4 * response.length());
encoded.writeBytes(response.getBytes());
ctx.writeAndFlush(encoded);
Thread.sleep(10000);
System.out.println("thread sleep end");
ctx.close();
// Thread.sleep(10000);
// System.out.println("thread sleep end");
}
@Override
public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
System.out.println("==============channel-read-complete==============");
ctx.flush();
}
}客户端代码
package hello.netty.lyx.com;
import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
/**
* 1、Client向Server发送消息:Are you ok?
* 2、Server接收客户端发送的消息,并打印出来。
* 3、Server端向客户端发送消息:I am ok!
* 4、Client接收Server端发送的消息,并打印出来,通讯结束。
*/
public class HelloClient {
public void connect(String host, int port) throws Exception {
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
Bootstrap b = new Bootstrap();
b.group(workerGroup);
b.channel(NioSocketChannel.class);
b.option(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true);
b.handler(new ChannelInitializer() {
@Override
public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new HelloClientIntHandler());
}
});
// Start the client.
/**
* wait()方法:Waits for this future to be completed.
* Waits for this future until it is done, and rethrows the cause of the failure if this future
* failed.
*/
long t1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
ChannelFuture f = b.connect(host, port).await();
// Wait until the connection is closed.
f.channel().closeFuture().await(); //closeFuture方法返回通道关闭的结果
long t2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.print("diff in seconds:" + (t2 - t1) / 1000 + "\n");
} finally {
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
HelloClient client = new HelloClient();
client.connect("127.0.0.1", 9090);
}
} package hello.netty.lyx.com;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter;
//InboundHandler类型
public class HelloClientIntHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelRegistered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
System.out.println("==============channel--register==============");
}
@Override
public void channelUnregistered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
System.out.println("==============channel--unregistered==============");
}
@Override
public void channelInactive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
System.out.println("==============channel--inactive==============");
}
// 连接成功后,向server发送消息
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
System.out.println("==============channel--active==============");
String msg = "Are you ok?";
/**
* 分配ByteBuf
* Return the assigned {@link io.netty.buffer.ByteBufAllocator} which will be used to allocate {@link ByteBuf}s.
*/
ByteBuf encoded = ctx.alloc().buffer(4 * msg.length());
encoded.writeBytes(msg.getBytes());
ctx.write(encoded);
ctx.flush();
}
// 接收server端的消息,并打印出来
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
System.out.println("==============channel--read==============");
//先等待两秒
Thread.sleep(2000);
ByteBuf result = (ByteBuf) msg;
byte[] result1 = new byte[result.readableBytes()];
result.readBytes(result1);
System.out.println("Server said:" + new String(result1));
result.release();
}
}客户端的异步IO
让这个demo异步方式运行则客户端的代码应该是这样的:
long t1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
ChannelFuture f = b.connect(host, port).await();
long t2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.print("diff in seconds:" + (t2 - t1) / 1000 + "\n");看运行结果:
==============channel--register==============
diff in seconds:0
==============channel--active==============
==============channel--inactive==============
==============channel--unregistered==============
和原来的代码相比,通过运行结果可以分析出没有read服务器的数据。
在看一段异步的代码:
long t1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
ChannelFuture f = b.connect(host, port).await();
f = f.channel().closeFuture();
f.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {
System.out.println("success complete!!ok!!");
}
});
long t2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.print("diff in seconds:" + (t2 - t1) / 1000 + "\n");运行结果:
==============channel--register==============
==============channel--active==============
diff in seconds:0
success complete!!ok!!
==============channel--inactive==============
==============channel--unregistered==============
给通道的关闭Future注册了监听事件,监听事件等这个关闭Future完成后打印了字符串,而客户端没有读取服务器的数据。
在看一段代码
long t1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
ChannelFuture f = b.connect(host, port).await();
f = f.channel().closeFuture().await();
f.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {
System.out.println("success complete!!ok!!");
}
});
long t2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.print("diff in seconds:" + (t2 - t1) / 1000 + "\n");运行结果:
==============channel--register==============
==============channel--active==============
==============channel--read==============
Server said:I am ok!
==============channel--inactive==============
==============channel--unregistered==============
diff in seconds:2
success complete!!ok!!
可以读取服务器的数据,并且监听事件也起了作用,但这不是一个异步调用。
=============END=============