Netty源码分析(五)—ByteBuf源码分析
Netty源码分析(五)—ByteBuf源码分析
在进行数据传输时往往需要使用缓冲区,Java NIO中使用Buffer作为缓冲区;七种基本数据类型都有自己的缓冲区实现,最常使用的是ByteBuffer,但是ByteBuffer也有局限性;
Netty实现了缓冲区的池化技术,在一定程度上减少了频繁内存分配和GC带来的性能损耗
个人主页:tuzhenyu’s page
原文地址:Netty源码分析(五)—ByteBuf源码分析
(0) ByteBuffer和ByteBuffer
ByteBuffer的缺点
ByteBuffer长度固定,通过ByteBuffer.allocate()方法或者ByteBuffer.wrap()方法分配后容量不能动态的扩展和收缩;
ByteBuffer只有一个标识位置的指针position,读写数据时候需要调用flip()方法或者rewind()方法调整指针位置;
ByteBuffer的API功能有限,一些高级和实用的性能不支持
ByteBuf的优点
每次写入数据会判断容量是否足够,如果不够则重新创建缓冲区并进行数据复制,实现缓冲区的容量大小可以随着需求动态改变
使用读指针和写指针代替position指针,实现在读写模式之间切换不需要调用ByteBuffer的flip()方法
从内存分配来看,ByteBuf分为堆内存和直接内存两类UnpooledHeapByteBuf和UnpooledDirectByteBuf,上层使用相同的封装;
从内存使用上分为基于对象池的ByteBuf和普通的ByteBuf,基于对象池的ByteBu会重用池中的ByteBuf对象,提高内存的实用率,避免由高负载导致的频繁的触发GC;
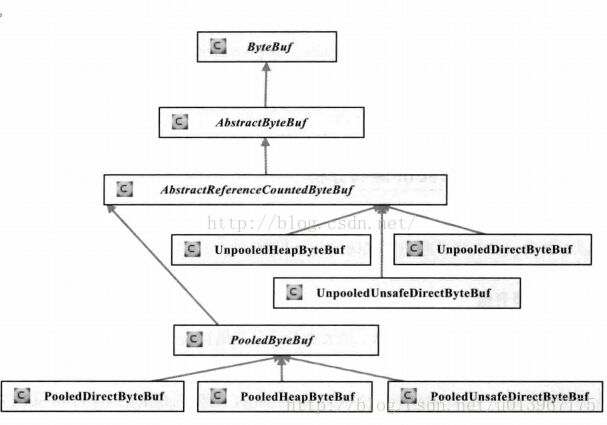
(1) ByteBuffer的继承结构
ByteBuf是Netty缓存区的顶层抽象类,定义了缓存区操作的所有API;
ByteBuf的直接间接实现类有AbstractByteBuf和AbstractReferenceCountedByteBuf,在这两个类中实现了一些公共功能的函数,AbstractReferenceCountedByteBuf按照内存实用情况分为基于内存池的PooledByteBuf和普通的UnPooledHeapByteBufer等;
普通的不基于内存池的缓冲区按照内存分配情况分为UnPooledHeapByteBuf堆缓存区,UnPooledDirectByteBuf直接缓存区和UnPooledUnsafeDirectByteBuf等
基于内存池的缓冲区PooledByteBuf根据内存分配的情况分为PooledDirectByteBuf,PooledHeapByteBuf和PooledUnsafeDirectByteBuf等;
(2) ByteBuf的功能
- 顺序读操作(ByteBuf.readXxx()),类似于ByteBuffer的get()方法
int readInt(); //从readerIndex开始读取4个字节转换成整型数值返回,将readerIndex值增加4
long readLong(); //从readerIndex开始读取8个字节转换成长整型数值返回,将readerIndex值增加8
ByteBuf readBytes(byte[] bytes) //从readerIndex开始读取bytes.length长度的字节数,并封装成ByteBuf类型返回
- 顺序写操作(ByteBuf.writeXxx()),类似于ByteBuffer的put()方法
ByteBuf writeInt(int value) //将参数写入到当前ByteBuf中,操作成功后writeIndex+=4
ByteBuf writeLong(long value) //将参数写入到当前ByteBuf,操作成功后writeIndex+=8
ByteBuf writeBytes(byte[] bytes) //将字节数组写入到当前的ByteBuf中,操作成功后writeIndex+=bytes.length
- 随机读操作(ByteBuf.getXxx())
int getInt(int index) //从index索引处读取4个字节转换成整型数值返回
long getLong(int index) //从index索引处读取8个字节转换成整型数值返回
ByteBuf getBytes(int index,byte[] bytes) //从index索引处读取bytes.length个字节封装成ByteBuf返回;
- 随机写操作(ByteBuf.setXxx())
ByteBuf setInt(int index,int value) //将value写入到从readerIndex开始的4个字节中
ByteBuf setLong(int index,long value) //将value写入到从readerIndex开始的8个字节中;
ByteBuf setBytes(int index,byte[] bytes) //将bytes字节数组写入到从readerIndex开始的bytes.length长度的字节中;
- 复制操作(duplicate和copy)
Bytebuf byteBuf.duplicate() //返回一个复制的ByteBuf对象,该对象和被复制的ByteBuf共享一块缓冲区内存,只是维护着自己独立的读写索引,修改一个另外一个也会变化;
ByteBuf byteBuf.copy() //复制一个新的ByteBuf对象,内容和索引都是独立的不会相互影响;
- 查找操作(indexOf和bytesBefore)
int indexOf(int fromIndex,int toIndex,byte value) //从当前ByteBuf对象中查找value首次出现的位置,查找起始索引是fromIndex,终点索引是toIndex,如果没查找到则返回-1;
int bytesBefore(byte value) //从当前ByteBuf对象中查找value首次出现的位置,查找起始索引是readerIndex,终点索引是writerIndex,如果没查找到则返回-1;
(3) AbstractByteBuf抽象类
AbstractByteBuf抽象类继承自ByteBuf,一些公共属性和功能会在AbstractByteBu中实现
1. 公共成员变量
- AbstractByteBuf中维护着读索引readerIndex,写索引writerIndex,mark指针和最大容量maxCapacity等
static final ResourceLeakDetector leakDetector;
int readerIndex;
int writerIndex;
private int markedReaderIndex;
private int markedWriterIndex;
private int maxCapacity; - 读写索引将ByteBuf缓冲区分为了三个区域:丢弃区域,可读区域,可写区域
+-------------------+------------------+------------------+
| discardable bytes | readable bytes | writable bytes |
| | (CONTENT) | |
+-------------------+------------------+------------------+
| | | |
0 <= readerIndex <= writerIndex <= capacity- 通过调用ByteBuf.discardReadBytes()来回收已经读取过的字节,discardReadBytes()将回收从索引0到readerIndex之间的字节;byteBuf.discardReadBytes()会执行数据的拷贝,覆盖已经读过的丢弃区域释放ByteBuf的内存;
+------------------+------------------+
| readable bytes | writable bytes |
| (CONTENT) | |
+------------------+------------------+
| | |
readerIndex <= writerIndex <= capacity2. 读操作
- AbstractByteBuf类实现了读操作函数
public ByteBuf readBytes(byte[] dst) {
this.readBytes((byte[])dst, 0, dst.length);
return this;
}public ByteBuf readBytes(byte[] dst, int dstIndex, int length) {
this.checkReadableBytes(length);
this.getBytes(this.readerIndex, dst, dstIndex, length);
this.readerIndex += length;
return this;
}- 首先对缓冲区可读空间长度进行校验,如果读取的长度超过可读的长度则抛出错误
protected final void checkReadableBytes(int minimumReadableBytes) {
if(minimumReadableBytes < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("minimumReadableBytes: " + minimumReadableBytes + " (expected: >= 0)");
} else {
this.checkReadableBytes0(minimumReadableBytes);
}
}
private void checkReadableBytes0(int minimumReadableBytes) {
this.ensureAccessible();
if(this.readerIndex > this.writerIndex - minimumReadableBytes) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(String.format("readerIndex(%d) + length(%d) exceeds writerIndex(%d): %s", new Object[]{Integer.valueOf(this.readerIndex), Integer.valueOf(minimumReadableBytes), Integer.valueOf(this.writerIndex), this}));
}
}- 校验通过后调用getBytes()方法从当前的readerIndex读索引开始复制length个字节到目标byte数组中,不同的子类复制操作的实现不同,getBytes()方法由子类实现;
3. 写操作
- AbstractByteBuf实现了写操作的具体函数writeBytes(byte[] bytes)
public ByteBuf writeBytes(byte[] src) {
this.writeBytes((byte[])src, 0, src.length);
return this;
}public ByteBuf writeBytes(byte[] src, int srcIndex, int length) {
this.ensureAccessible();
this.ensureWritable(length);
this.setBytes(this.writerIndex, src, srcIndex, length);
this.writerIndex += length;
return this;
}- 首先对写入字节数组的长度进行写可行性校验,如果写入数组的长度小于0则抛出错误;如果写入字节数组长度小于当前ByteBuf可写的字节数,则写入成功;如果写入数组的长度大于当前ByteBuf可写的字节数组,则动态拓展可写字节数;
public ByteBuf ensureWritable(int minWritableBytes) {
if(minWritableBytes < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format("minWritableBytes: %d (expected: >= 0)", new Object[]{Integer.valueOf(minWritableBytes)}));
} else {
this.ensureWritable0(minWritableBytes);
return this;
}
}
private void ensureWritable0(int minWritableBytes) {
if(minWritableBytes > this.writableBytes()) {
if(minWritableBytes > this.maxCapacity - this.writerIndex) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(String.format("writerIndex(%d) + minWritableBytes(%d) exceeds maxCapacity(%d): %s", new Object[]{Integer.valueOf(this.writerIndex), Integer.valueOf(minWritableBytes), Integer.valueOf(this.maxCapacity), this}));
} else {
int newCapacity = this.alloc().calculateNewCapacity(this.writerIndex + minWritableBytes, this.maxCapacity);
this.capacity(newCapacity);
}
}
}如果写入数组长度超过ByteBuf可写入的长度,通过calculateNewCapacity()方法动态拓展ByteBuf的长度,再调用底层ByteBuf具体实现如UnpooledHeapByteBuf的capacity()方法分配新的内存;
在容量动态扩展时设有容量阀值,当满足要求的最小容量小于阀值4M时采用倍增的方式扩展容量值,当满足要求的最小容量大于阀值4M时采用递进的方法扩展容量;
当minNewCapacity大于容量值阀值,采用每次增加4M的递进的方式
当minNewCapacity小于容量阀值,采用每次翻倍的倍增模式,动态拓展的其市值是64byte字节,采用左移的方式倍增
public int calculateNewCapacity(int minNewCapacity, int maxCapacity) {
if (minNewCapacity < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("minNewCapacity: " + minNewCapacity + " (expectd: 0+)");
}
if (minNewCapacity > maxCapacity) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format(
"minNewCapacity: %d (expected: not greater than maxCapacity(%d)",
minNewCapacity, maxCapacity));
}
final int threshold = CALCULATE_THRESHOLD; // 4 MiB page
if (minNewCapacity == threshold) {
return threshold;
}
// If over threshold, do not double but just increase by threshold.
if (minNewCapacity > threshold) {
int newCapacity = minNewCapacity / threshold * threshold;
if (newCapacity > maxCapacity - threshold) {
newCapacity = maxCapacity;
} else {
newCapacity += threshold;
}
return newCapacity;
}
// Not over threshold. Double up to 4 MiB, starting from 64.
int newCapacity = 64;
while (newCapacity < minNewCapacity) {
newCapacity <<= 1;
}
return Math.min(newCapacity, maxCapacity);
}(4) AbstractReferenceCountedByteBuf抽象类
- AbstractReferenceCountedByteBuf抽象类主要是用来对引用进行计数,用于跟踪对象的分配和销毁等;AbstractReferenceCountedByteBuf类中维护着一个volatile类型的变量用来表示被引用的次数;
private volatile int refCnt = 1;- 通过retain()方法计数器加一,通过CAS解决并发多线程安全问题
public ByteBuf retain(int increment) {
return retain0(checkPositive(increment, "increment"));
}
private ByteBuf retain0(int increment) {
for (;;) {
int refCnt = this.refCnt;
final int nextCnt = refCnt + increment;
// Ensure we not resurrect (which means the refCnt was 0) and also that we encountered an overflow.
if (nextCnt <= increment) {
throw new IllegalReferenceCountException(refCnt, increment);
}
if (refCntUpdater.compareAndSet(this, refCnt, nextCnt)) {
break;
}
}
return this;
}- 通过release()方法将计数器减一,通过CAS解决并发多线程安全问题
public boolean release(int decrement) {
return release0(checkPositive(decrement, "decrement"));
}
private boolean release0(int decrement) {
for (;;) {
int refCnt = this.refCnt;
if (refCnt < decrement) {
throw new IllegalReferenceCountException(refCnt, -decrement);
}
if (refCntUpdater.compareAndSet(this, refCnt, refCnt - decrement)) {
if (refCnt == decrement) {
deallocate();
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
}(5) UnpooledHeapByteBuf实现类
- UnpooledHeapByteBuf是基于堆内存进行内存分配的字节缓冲区,没有基于对象池技术实现每次调用都会创建一个新的对象;
1. 成员变量
- 成员变量中定义了一个ByteBufAllocator类型的alloc用来分配堆内存,定义一个byte字节数组用作缓冲区,定义一个ByteBuffer类型的tmpNioBuf用作Netty的ByteBuf到JDK ByteBuffer转换;
private final ByteBufAllocator alloc;
byte[] array;
private ByteBuffer tmpNioBuf;2. 动态扩展缓冲区容量
在父类AbstractByteBuf写数据时对容量是否满足进行判断,如果不满足则进行扩容通过calculate()方法计算新容量的大小,然后通过AbstractByteBuf的实现类的capacity()方法分配具体内存;
- capacity()方法动态扩容的过程是:先判断新的容量是否大于当前缓冲区的容量,如果大于则进行动态扩容;通过byte[] newArray = new byte[newCapacity]创建新容量的字节数组,然后通过System.arrayCopy()方法进行数据复制,最后通过setArray()方法替换旧的缓冲区数组;
public ByteBuf capacity(int newCapacity) {
checkNewCapacity(newCapacity);
int oldCapacity = array.length;
byte[] oldArray = array;
if (newCapacity > oldCapacity) {
byte[] newArray = allocateArray(newCapacity);
System.arraycopy(oldArray, 0, newArray, 0, oldArray.length);
setArray(newArray);
freeArray(oldArray);
} else if (newCapacity < oldCapacity) {
byte[] newArray = allocateArray(newCapacity);
int readerIndex = readerIndex();
if (readerIndex < newCapacity) {
int writerIndex = writerIndex();
if (writerIndex > newCapacity) {
writerIndex(writerIndex = newCapacity);
}
System.arraycopy(oldArray, readerIndex, newArray, readerIndex, writerIndex - readerIndex);
} else {
setIndex(newCapacity, newCapacity);
}
setArray(newArray);
freeArray(oldArray);
}
return this;
}3. 字节数组复制
- 在AbstractByteBuf中通过setBytes()方法实现数组数据的复制,通过调用System.copy方法实现数组数据的复制
public ByteBuf setBytes(int index, ByteBuf src, int srcIndex, int length) {
checkSrcIndex(index, length, srcIndex, src.capacity());
if (src.hasMemoryAddress()) {
PlatformDependent.copyMemory(src.memoryAddress() + srcIndex, array, index, length);
} else if (src.hasArray()) {
setBytes(index, src.array(), src.arrayOffset() + srcIndex, length);
} else {
src.getBytes(srcIndex, array, index, length);
}
return this;
}
public ByteBuf setBytes(int index, byte[] src, int srcIndex, int length) {
checkSrcIndex(index, length, srcIndex, src.length);
System.arraycopy(src, srcIndex, array, index, length);
return this;
}(6) PooledByteBuf内存池实现
内存池数据结构
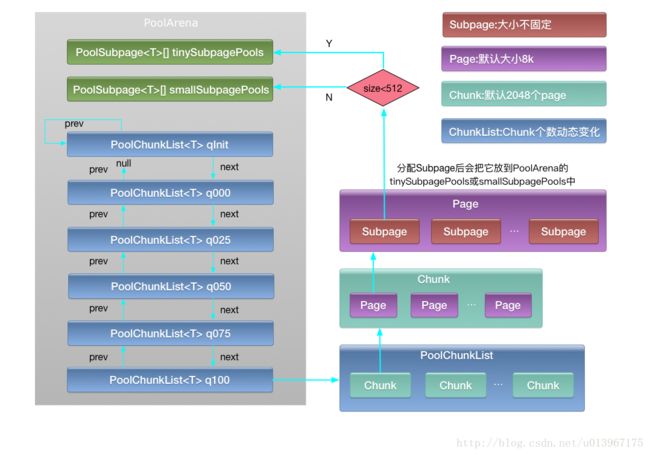
- 内存分级从上到下主要分为:Arena,ChunkList,Chunk,Page,SubPage五级;
PooledArena是一块连续的内存块,为了优化并发性能在Netty内存池中存在一个由多个Arena组成的数组,在多个线程进行内存分配时会按照轮询策略选择一个Arena进行内存分配;
一个PoolArena内存块是由两个PoolSubPage(用来存储零碎内存)和多个ChunkList组成,两个PoolSubpage数组分别为tinySubpagePools和smallSubpagePools。每个ChunkList里包含多个Chunk按照双向链表排列,每个Chunk里包含多个Page(默认2048个),每个Page(默认大小为8k字节)由多个Subpage组成。
每个ChunkList里包含的Chunk数量会动态变化,比如当该chunk的内存利用率变化时会向其它ChunkList里移动。
final PooledByteBufAllocator parent;
private final int maxOrder;
final int pageSize;
final int pageShifts;
final int chunkSize;
final int subpageOverflowMask;
final int numSmallSubpagePools;
final int directMemoryCacheAlignment;
final int directMemoryCacheAlignmentMask;
private final PoolSubpage[] tinySubpagePools;
private final PoolSubpage[] smallSubpagePools;
private final PoolChunkList q050;
private final PoolChunkList q025;
private final PoolChunkList q000;
private final PoolChunkList qInit;
private final PoolChunkList q075;
private final PoolChunkList q100; 内存池内存分配规则
对于小于PageSize大小的内存分配,会在tinySubPagePools和smallSubPagePools中分配,tinySubPagePools用来分配小于512字节的内存,smallSubPagePools用来分配大于512字节小于PageSize的内存;
对于大于PageSize小于ChunkSize的内存分配,会在PoolChunkList中的Chunk中分配
对于大于ChunkSize的内存分配,会之间直接创建非池化的Chunk来分配,并且该Chunk不会放在内存池中重用。
Netty内存池实现
对于缓冲区Buffer,Netty的池化对象分为PooledDirectByteBuf和PooledHeapByteBuf两种,PooledDirectByteBuf的构造方法是私有的,通过newInstance()方法创建Buf缓冲区实例;
- 从Recycler中获取一个PooledDirectByteBuf实例,通过reuse()方法重新分配内存大小;
static PooledDirectByteBuf newInstance(int maxCapacity) {
PooledDirectByteBuf buf = RECYCLER.get();
buf.reuse(maxCapacity);
return buf;
}Recycler是内存池的核心,是一个轻量级的对象池用于重用对象的获取;Recycler是一个基于ThreadLocal栈的轻量级的对象池,在实现上,线程内部的threadLocal保存Stack对象,Stack内部保存了Handler;
在使用PooledDirectByteBuf时会初始化一个Recycler实例,需要重写Recycler的newObject方法,该方法会在get时使用,如果本地线程池没有可重复使用的对象则调用newObject返回一个新对象。
private static final Recycler RECYCLER = new Recycler() {
@Override
protected PooledDirectByteBuf newObject(Handle handle) {
return new PooledDirectByteBuf(handle, 0);
}
}; - 从对象池Recycler对象池中获取对象后通过PoolArena分配内存;