ruby学习
交互式命令
irb
instance_methods(false),列出对象(类)内部的可用方法,用于调查解析对象的使用。
respond_to? 调查对象的方法/属性是否可用。
send 执行对象的方法。
class Game
def initialize(title = "aaaa", price = 200)
@title = title
@price = price
end
def show()
puts "biaoti:#{
@title}"
puts "jiage: #{
@price}"
end
def show2()
end
def show3()
end
puts Game.instance_method(false)
mari = Game.new("chaojimaliao", 350);
if mari.respond_to?("show")
mari.send("show")
end
attr_accessor:定义可存取对象的属性
提供了可供对象外部使用的属性。
class Game
attr_accessor :price #, :title
def initialize(title = "bbbb", price = 200)
@title = title
@price = price
end
def show()
puts "biaoti: #{
@title}"
puts "jiage: #{
@price}"
end
end
mygame = Game.new()
mygame.show()
puts "title is" + mygame.respond_to?("title").to_s
puts "price is" + mygame.respond_to?("price").to_s
# mygame.title = "Super Mario world"
mygame.price = 150
mygame.show()
判断是否是一个数组
if games.respond_to?("each")
end
如果games示例有each方法,那就是数组;
之后全备注
END
字符串运算:
+字符连接
<<字符带入
*字符循环
数据结构
mvp_rank = {
"curry" => 28.1,
"harden" => 30.3,
"lebron" => 26
}
puts mvp_rank["harden"]
player = {
name: "harden",
age: 28,
}
puts player[:name]
to_i 和 to_s 区别
静态方法,不能用实例去调用,直接用类点方法名调用
class Game
def self.toStr
puts "I love this game!"
end
end
module与class区别
module BaseFunc
Version = "0.0.1"
def v
return Version
end
def add(a,b)
return a + b
end
def self.showVersion
return Version
end
# 将v方法定义范围静态方法
module_function :v
end
puts BaseFunc::Version
puts BaseFunc.showVersion
puts BaseFunc.v
#puts BaseFunc.add(10, 30)
class BaseClass include BaseFunc
end
puts "================================"
puts BaseClass::Version
# puts BaseClass.showVersion
# puts BaseClass.v
myCls = BaseClass.new
puts myCls.add(10,20)
foo = "str"
foo.instance_f?(String)
ruby中的库都叫Gems
fixum 和 bignum 区别
a = 3
a.class
b = 1_000000000000.class
3.even? # 判断偶数
3.odd? # 判断奇数
字符串可以改变值
a = 'asdf'
a.object_id
a[1] = 'c'
a.object_id
Symbol
:foo
:foo.class # Symbol
a.to_sym # 把字符串a变成symbol
看一下ruby中内存位置
a = Array.new(3, 'asdf')
a[0][0] = 'b'
a # 发现三个位置都变成bsdf
a = Array.new(3) {
'asdf'}
a[0][0] = 'b'
a # 发现只有第一个位置变了
还有一种定义字符串方法
arr = %w(foo bar wut wat)
fetch用法
arr.fetch(0) # 取下标0位置的值
arr.fetch(5, 'asdf') # 取下标5位置的值,要是取不到,就返回默认值 asdf
uniq
arr.uniq # 去重,跟set一样
shuffle
arr.shuffle # 打乱
遍历数组
arr.each {
|e| p e}
判断
arr.any? {
|e| e < 0}
Hash
h = {
a: 3, b: 4}
=> {
:a=>3, :b=>4}
里面的key都是symbol,因为symbol都是unitable,静态的不会变,所以key用symbol;
除此之外,key也可以用字符串做,虽然字符串是muteable,但是ruby私底下,都给每个字符串做了备份,虽然字符串改变了,但是备份的字符串没有改变;
h = Hash.new {
|h, k| h[k] = []}
h[:a] << 1
h
h[:b]
h[:c] = 3
h.delete(:a)
h.assoc(:b) # 把key的b和value都取出来
起别名
alias :new_name :old_name
运算符重新定义,运算符就是一个方法
arr = [1,2,3]
def arr.+(num)
self.dup << num
end
arr + 5
*b
def foo(a, *b, c)
p a
p b
p c
end
foo(1,2,3,4,5)
&
把proc转成block
arr = %w(a b c)
arr.map(&:capitalize)
等于下面这个
arr.map {
|x| x.capitalize}
proc和lambda区别
proc的行为更像Proc,lambda行为更像方法
p = Proc.new {
|x, y| p x, y}
p.call(1)
p.call(2)
p.call(1,2)
p.call(1,2,3)
l = lambda {
|x,y| p x, y}
l.call(1) # 会报错
l.call(1,2)
l.call(1,2,3) # 会报错
p = Proc.new {
|x| return if x > 0}
p.call(1)
# 会报错,因为没有函数把它包起来,return的时候会报错
l = lambda {
|x| return if x > 0}
l.call(1)
# 不会报错
ancestors
Point.ancestors
p.methods
p.class
methods class 都是introspection反省自己
attr_accessor和attr_reader
attr_accessor 就是 getter and setter
attr_reader 就是 getter
class Point
attr_accessor :x
attr_reader :y
@@origin = 0
ORIGIN = 2
def initialize(x = 0, y = 0)
@x, @y = x, y
end
def first_quadrant? # 这是instant的method
x > 0 && y > 0
# self.x > 0 && self.y > 0
end
def +(p2)
Point.new(x + p2.x, y + p2.y)
# self ,这里的self是指对象
end
def self.second_quadrant?(x,y) # 这里是class的method
x < 0 && y > 0
# self,这里的self是指类
end
class << self # 在这里面可以定义很多class的method,并不需要加self.
def foo
end
def bar
end
def wat
end
end
# self,这里的self也是指类
def self.get_origin
@@origin
end
end
p = Point.new(1,2)
p.x
p = Point.new(-1,0)
p1 = Point.new(2, 3)
p2 = Point.new(3, 4)
p1 + p2
Point.second_quadrant?(2,3)
Point.foo
Point.bar
Point.get_origin
Point::ORIGIN
子类可以继承父类的所有method
Mixin Ruby Module
include : mixin module instance method as class’ instance method
extend : mixin module instance methods as class’ class methods
module Helper
def self.distance(obj1, obj2)
Math.sqrt((obj1.x - obj2.x) ** 2 + (obj1.y - obj2.y) ** 2)
end
def shift_right(x,y,z = 0)
return x + 3, y, z
end
end
module里面不能生成instance
class Point
include Helper
end
p1 = Point.new(1,2)
p2 = Point.new(1,4)
p1.shift_right(p1.x, p1.y)
Point.distance # 会报错,不能调用 class instance
class Point
extend Helper
end
Point.shift_right(1,2)
同时变成instant method和class method
module Helper
def shift_right(x,y,z=0)
return x + 3, y, z
end
module ClassMethod
def distance(obj1, obj2)
Math.sqrt((obj1.x - obj2.x) ** 2 + (obj1.y - obj2.y) ** 2)
end
end
def self.include(klass) # 这个相当于回调,表示当前module被include,这个就会被调用
klass.extend ClassMethods
end
end
class Point
include Helper
end
Point.included_modules
Point.is_a? Module
singleton
str = 'hello world'
def str.foo
puts 'foo'
end
str.singleton_class
str.singleton_class.instance_methods(false)
=> [:foo]
An object’s singleton method == its singleton class’ instance method
Enumerable and Comparable
可列举的,可比较的
Enumerable.instance_methods
Fixnumber.included_moduless
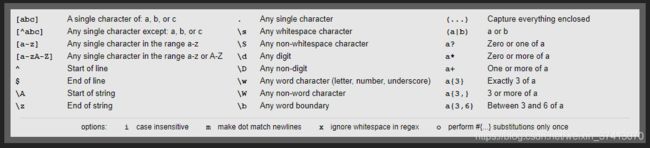
Regex正则
?是匹配0个或者1个
*可以是0个,也可以是无穷个
+一个或者多个
.是任意字符,但是不包括换行
i是大小写不分
m包含换行
[abc]可以匹配a或b或c,[a-z]
r[^a-z]+y # 在这里^反而是取反的意思
多线程
Thread.current hash
count = 0
arr = []
10.times do |i|
arr[i] = Thread.new {
sleep(rand(0)/10.0)
Thread.current["count"] = count
count += 1
}
end
arr.each {
|t| t.join; print t["count"], ", "}
puts "count = #{
count}"
Thread priority
count1 = count2 = 0
a = Thread.new do
loop {
count1 += 1 }
end
a.priority = -1
b = Thread.new do
loop {
count2 += 1 }
end
b.priority = -2
sleep 1
count1
count2