【连载】Dijkstra求最短路径算法设计—Java实现
Dijkstra求最短路径算法设计
1. Dijkstra简介
What’s the shortest path?
最短路径指两顶点之间经过的边上权值之和最少的路径,并且称路径上的第一个顶点为源点,最后一个顶点为终点。
Thought line of algorithm:
How to realize Dijkstra algorithm:
2. Let’s coding
注:该代码的实现是基于Java的,也运用了设计模式在里面。所以,如果个人Java基础和设计模式思想不过关,接下来看代码会比较费解,望谅解!
数据结构的构建:
- Vertex.java
package zychaowill.datastructure.graph.vo;
public class Vertex implements Comparable {
/**
*
*/
private String name;
/**
* 最短路径长度
*/
private int path;
/**
* 节点是否已经出列(是否已经处理完毕)
*/
private boolean isMarked;
public Vertex(String name) {
this.name = name;
this.path = Integer.MAX_VALUE; // 初始设置为无穷大
this.setMarked(false);
}
public Vertex(String name, int path) {
this.name = name;
this.path = path;
this.setMarked(false);
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Vertex o) {
return o.path > path ? -1 : 1;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getPath() {
return path;
}
public void setPath(int path) {
this.path = path;
}
public boolean isMarked() {
return isMarked;
}
public void setMarked(boolean isMarked) {
this.isMarked = isMarked;
}
} - Graph.java
package zychaowill.datastructure.graph.vo;
import java.util.List;
import zychaowill.datastructure.graph.algo.ShortestPathStrategy;
public class Graph {
/*
* 顶点
*/
private final List vertexs;
/*
* 边
*/
private final int[][] edges;
/**
* 求最短路径的策略
*/
private ShortestPathStrategy shortestPathStrategy;
public Graph(List vertexs, int[][] edges) {
this.vertexs = vertexs;
this.edges = edges;
}
/*
* 打印图
*/
public void printGraph() {
int verNums = vertexs.size();
for (int row = 0; row < verNums; row++) {
for (int col = 0; col < verNums; col++) {
if (Integer.MAX_VALUE == edges[row][col]) {
System.out.print("X");
System.out.print(" ");
continue;
}
System.out.print(edges[row][col]);
System.out.print(" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
/**
* Get shortest path from v
* @see
* @param v
*/
public void getShortestPath(Vertex v) {
shortestPathStrategy.shortestPath(this, v).printResult();
}
/**
* Export access method
*/
public void setShortestPathStrategy(ShortestPathStrategy shortestPathStrategy) {
this.shortestPathStrategy = shortestPathStrategy;
}
public List getVertexs() {
return vertexs;
}
public int[][] getEdges() {
return edges;
}
} 算法接口设计
- ShortestPathStrategy.java
package zychaowill.datastructure.graph.algo;
import zychaowill.datastructure.graph.vo.Graph;
import zychaowill.datastructure.graph.vo.Vertex;
public interface ShortestPathStrategy {
ShortestResult shortestPath(Graph graph, Vertex v);
}- 抽象层实现: AbstractShortestPathStrategy.java
package zychaowill.datastructure.graph.algo;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
import java.util.Queue;
import zychaowill.datastructure.graph.vo.Graph;
import zychaowill.datastructure.graph.vo.Vertex;
public abstract class AbstractShortestPathStrategy implements ShortestPathStrategy {
protected final int MAX_VALUE = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
protected List vertexs; // all vertexs of graph
protected int[][] edges; // weight between two vertexs
protected Queue S;
protected Queue U;
/**
* get shortest path length
* @see
* @return
*/
protected int getShortestPathLength() {
int path = 0;
List list = new ArrayList<>(S);
for (int i = 1; i < list.size(); i++) {
path += getDistance(list.get(i - 1), list.get(i));
}
return path;
}
/*
* 获取顶点所有(未访问的)邻居
*/
protected List getNeighbors(Vertex v) {
List neighbors = new ArrayList<>();
int position = vertexs.indexOf(v);
Vertex neighbor = null;
int distance;
for (int i = 0; i < vertexs.size(); i++) {
if (i == position) {
continue;
}
distance = edges[position][i];
if (distance < MAX_VALUE) {
neighbor = vertexs.get(i);
if (U.contains(neighbor)) {
neighbors.add(neighbor);
}
}
}
return neighbors;
}
/*
* 获取顶点到目标顶点的距离
*/
protected int getDistance(Vertex source, Vertex destination) {
int sourceIndex = vertexs.indexOf(source);
int destinationIndex = vertexs.indexOf(destination);
return edges[sourceIndex][destinationIndex];
}
/*
* 更新所有邻居的最短路径
*/
protected void updateDistance(Vertex vertex, List neighbors) {
for (Vertex neighbor : neighbors) {
updateDistance(vertex, neighbor);
}
}
/*
* 更新邻居的最短路径
*/
protected void updateDistance(Vertex vertex, Vertex neighbor) {
int distance = getDistance(vertex, neighbor) + vertex.getPath();
if (distance < neighbor.getPath()) {
neighbor.setPath(distance);
}
}
/*
* 根据顶点位置获取顶点
*/
protected Vertex getVertex(int index) {
return vertexs.get(index);
}
/**
* 初始化
*/
protected void init(Graph graph, Vertex v) {
this.vertexs = graph.getVertexs();
this.edges = graph.getEdges();
initUnVisited();
S = new LinkedList<>();
}
/**
* 初始化未访问顶点集合
* @see
*/
private void initUnVisited() {
U = new PriorityQueue<>();
for (Vertex v : vertexs) {
U.add(v);
}
}
} - 结果集构建: ShortestResult.java
package zychaowill.datastructure.graph.algo;
import java.util.Queue;
import zychaowill.datastructure.graph.vo.Vertex;
public class ShortestResult {
Queue vertexs;
int path;
public ShortestResult(Queue vertexs, int path) {
this.vertexs = vertexs;
this.path = path;
}
public void printResult() {
final String separator = " -> ";
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder("");
while (!vertexs.isEmpty()) {
builder.append(vertexs.poll().getName() + separator);
}
String shortestPath = builder.substring(0, builder.lastIndexOf(separator));
System.out.println(shortestPath + ", length: " + path);
}
} Dijkstra算法实现
- Dijkstra.java
package zychaowill.datastructure.graph.algo.impl;
import java.util.List;
import zychaowill.datastructure.graph.algo.AbstractShortestPathStrategy;
import zychaowill.datastructure.graph.algo.ShortestResult;
import zychaowill.datastructure.graph.vo.Graph;
import zychaowill.datastructure.graph.vo.Vertex;
public class Dijkstra extends AbstractShortestPathStrategy {
@Override
public ShortestResult shortestPath(Graph graph, Vertex v) {
init(graph, v);
Vertex w;
while (!U.isEmpty()) {
w = U.element();
List neighbors = getNeighbors(w);
updateDistance(w, neighbors);
S.add(U.poll());
}
return new ShortestResult(S, getShortestPathLength());
}
} 算法测试
- ShortestPath.java
package zychaowill.datastructure.graph.examples;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import zychaowill.datastructure.graph.algo.impl.Dijkstra;
import zychaowill.datastructure.graph.vo.Graph;
import zychaowill.datastructure.graph.vo.Vertex;
public class DijkstraShortestPath {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List vertexs = new ArrayList();
Vertex a = new Vertex("0", 0);
Vertex b = new Vertex("1");
Vertex c = new Vertex("2");
Vertex d = new Vertex("3");
Vertex e = new Vertex("4");
Vertex f = new Vertex("5");
Vertex g = new Vertex("6");
vertexs.add(a);
vertexs.add(b);
vertexs.add(c);
vertexs.add(d);
vertexs.add(e);
vertexs.add(f);
vertexs.add(g);
int[][] edges = { { 0, 4, 6, 6, Integer.MAX_VALUE, Integer.MAX_VALUE, Integer.MAX_VALUE },
{ Integer.MAX_VALUE, 0, 1, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 7, Integer.MAX_VALUE, Integer.MAX_VALUE },
{ Integer.MAX_VALUE, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 0, 2, 6, 4, Integer.MAX_VALUE },
{ Integer.MAX_VALUE, Integer.MAX_VALUE, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 0, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 5, Integer.MAX_VALUE },
{ Integer.MAX_VALUE, Integer.MAX_VALUE, Integer.MAX_VALUE, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 0, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 6 },
{ Integer.MAX_VALUE, Integer.MAX_VALUE, Integer.MAX_VALUE, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 1, 0, 8 },
{ Integer.MAX_VALUE, Integer.MAX_VALUE, Integer.MAX_VALUE, Integer.MAX_VALUE, Integer.MAX_VALUE, Integer.MAX_VALUE, Integer.MAX_VALUE }
};
Graph graph = new Graph(vertexs, edges);
graph.setShortestPathStrategy(new Dijkstra());
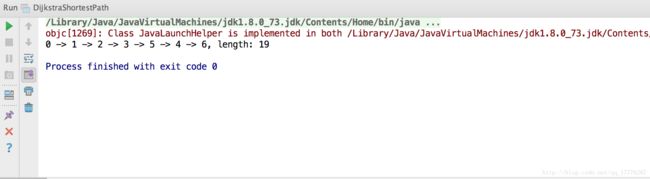
graph.getShortestPath(a);
}
}