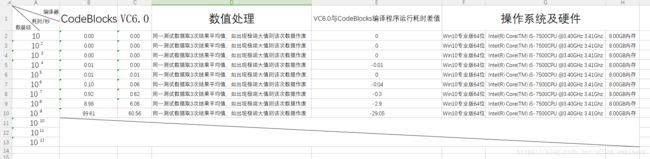
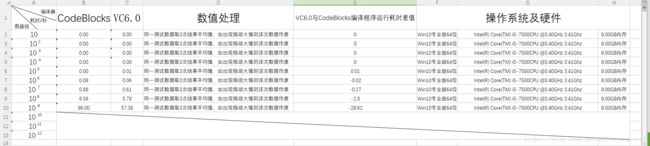
比较BF、KMP和BM算法的性能(纯C语言实现,而且……VC6.0编译的程序跑得比codeblocks 17.12编译的快)
首先声明:BF和KMP算法是刁肥宅自己实现的,BM算法源自此处,刁肥宅未曾妄加改动,只是作测试用。操作系统及硬件配置信息如图6所示,刁肥宅所用编译环境为:Code::Blocks 17.12、VC6.0(完整绿色版)。所用源代码与测试数据都已上传到百度云盘(提取密码:dhu0)与CSDN“我的资源-下载”上,各位看官可以免费下载亲测。
话不多说,先贴出三个算法的C语言实现:
一、算法实现
1.BF模式匹配算法
头文件BF.c:
/*Bf.h*/
#ifndef BF_H_INCLUDED
#define BF_H_INCLUDED
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
int Find( char *T, int T_Length,char *P, int P_Length );
#endif /* BF_H_INCLUDED*/ 源文件BF.c:
/*BF.c*/
#include "BF.h"
int Find( char *T, int T_Length,char *P, int P_Length )
{
/*在目标串T中从第0个字符开始寻找模式串P在T中匹配的位置。若在T中找不到与
串P匹配的子串, 则函数返回-1, 否则返回P在T中第一次匹配的位置。*/
int i, j, k; /*last为在T中最后可比对位置*/
/*printf( "In Find,T_Length = %d, P_Length = %d\n", T_Length, P_Length );*/
/*for ( i = 0; i <= strlen(T) - strlen(P); i++)*/
for ( i = 0; i <= T_Length - P_Length; i++ )/*逐趟比对*/
{
for ( k = i, j = 0; j < P_Length; k++, j++ ) /*从T.ch[i]开始与P.ch进行比对*/
if ( *( T + k ) != *( P + j ) )
break; /*比对不等跳出循环*/
if ( j == P_Length )
return i + 1; /*P已扫描完, 匹配成功*/
}
return -1; /*匹配失败*/
}源文件test.c:
/*test.c*/
#include "BF.h"
int main()
{
/*freopen("x1.out","w",stdout);*/
srand( time(NULL) );
char *T = NULL,*P = NULL;
FILE *fp1 = fopen("x1.in","r");
if( fp1 == NULL )
{
printf("Opening Error.\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
int i,d,ChoosingKey = 0,Value = 0,T_Length,P_Length,RandomSize = 1000001430;
T = ( char * )malloc( sizeof(char) * RandomSize );
P = ( char * )malloc( sizeof(char) * 34 );
/*strcpy(P,"wOvT5jN9154gQ751sK9eH1I1l0Hgf9d");*/
strcpy(P,"fsf8QQCNlL80s1ouGx2TeANoH2jxx9SYQ");
for( i = 0;!feof(fp1);i ++ )
fscanf( fp1,"%c",(T + i) );
P_Length = ( strlen(P) );
T_Length = ( strlen(T) );
/*
for( i = 0;i < RandomSize;i ++ )
{
ChoosingKey = rand() % 3 + 1;
switch(ChoosingKey)
{
case 1:
Value = rand() % ( 90 - 65 + 1 ) + 65;
*( T + i ) = (char)Value;
break;
case 2:
Value = rand() % ( 122 - 97 + 1 ) + 97;
*( T + i ) = (char)Value;
break;
case 3:
Value = rand() % ( 57 - 48 + 1 ) + 48;
*( T + i ) = (char)Value;
break;
default:
*( T + i ) = 'Q';
}
}
i = 0;
while( *(T + i) != '\0' )
{
printf("%c",*(T + i));
i ++;
}
*/
d = Find ( T,T_Length,P,P_Length );
if( d == -1 )
printf("匹配位置失败!\n");
else
printf("匹配位置为%d\n",d);
printf("Time used = %.2f seconds.\n",(double)clock() / CLOCKS_PER_SEC);
system("pause");
//return 0;
}2.KMP模式匹配算法
头文件KMP.h:
/*KMP.h*/
#ifndef KMP_H_INCLUDED
#define KMP_H_INCLUDED
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#define DefaultSize 40
void GetNext ( char *P, int P_Length, int next[] );
int FastFind ( char *T, int T_Length,char *P, int P_Length,int next[ ] );
#endif /* KMP_H_INCLUDED*/ 源文件KMP.c:
/*KMP.c*/
#include "KMP.h"
/*
/*P和T的长度必须以参数的形式从主函数传递給被调用的 GEtNext 和 FastFind 函数,
否则当T长度较大时匹配结果必然错误!!!或者d的返回值为 -1 (预设匹配失败时的值)
在这两个函数中,直接用 strlen( P ) 、strlen( T ) 求P、T的长度,且似乎主要是因为 strlen( T )
最终匹配结果错误。为什么?!
*/
/*void GetNext ( char *P, int next[] )*/
void GetNext ( char *P, int P_Length, int next[] )
{
/*对模式串P, 计算next失配函数*/
int j = 0, k = -1;
next[0] = -1; /*j已经在最左边了,不可能再移动了,这时候要应该是i指针后移*/
/*while ( j < strlen( P ) )
直接用 strlen( P ) 求P的长度,最终匹配结果错误。为什么?!
*/
while ( j < P_Length )/*计算next[j]*/
{
/*while ( k >= 0 && P->ch[j] != P->ch[k] )*/
while ( k >= 0 && *(P + j) != *(P + k) )
k = next[k];
j++;
k++;
if ( *(P + j) == *(P + k) )
next[j] = next[k];
else
next[j] = k;
}
/*printf( "In GetNext,strlen( P ) = %d\n",strlen( P ) );*/
}
/*int FastFind ( char *T, char *P, int next[ ] )*/
int FastFind ( char *T, int T_Length,char *P, int P_Length,int next[ ] )
{
/*在目标串T中寻找模式串P的匹配位置。若找到,则函数返回P在T中开始字符
下标,否则函数返回-1。数组nex存放P的失配函数next[j]值。*/
int j = 0, i = 0; /*串P与串T的扫描指针*/
/*while ( j < strlen( P ) && i < strlen( T ) )
直接用 strlen( P ) 、strlen( T ) 求P、T的长度,最终匹配结果错误。为什么?!
*/
while ( j < P_Length && i < T_Length ) /*对两串扫描*/
/*while ( j < 31 && i < 1000050 )*/
{
/*printf ( "i=%d, j=%d\n", i, j );*/
if ( j == -1 || *(P + j) == *(T + i) )/*对应字符匹配,比对位置加一*/
{
j++;
i++;
}
else
j = next[j]; /*第j位失配,找下一对齐位置*/
}
/*printf( "In FastFind,strlen( T ) = %d,strlen( P ) = %d\n",strlen( T ),strlen( P ) );*/
/*if ( j < strlen( P ) )
直接用 strlen( P ) 求P的长度,最终匹配结果错误。为什么?!
*/
if ( j < P_Length ) /*j未比完失配,匹配失败*/
/*if ( j < 31 )*/
return -1;
else
/*return i - strlen( P ); */
return i - P_Length + 1; /*匹配成功*/
}源文件test.c:
/*test.c*/
#include "KMP.h"
int main()
{
/*freopen( "x1.out","w",stdout );*/
srand( time(NULL) );
char *T = NULL,*P = NULL;
FILE *fp1 = fopen("x1.in","r");
if( fp1 == NULL )
{
printf("Opening Error.\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
int i,T_Length = 0,P_Length = 0,d = 0,ChoosingKey = 0,Value = 0,RandomSize = 1000001430;
/*int Fail[10000120];*/
int *Fail = (int *)malloc( sizeof(int) * DefaultSize );
T = ( char * )malloc( sizeof(char) * RandomSize );
P = ( char * )malloc( sizeof(char) * 34 );
/*strcpy(P,"wOvT5jN9154gQ751sK9eH1I1l0Hgf9d");*/
strcpy(P,"fsf8QQCNlL80s1ouGx2TeANoH2jxx9SYQ");
P_Length = ( strlen(P) );
for( i = 0;!feof(fp1);i ++ )
fscanf( fp1,"%c",(T + i) );
T_Length = ( strlen(T) );
/*printf( "In main,T_Length = %d, P_Length = %d\n", T_Length, P_Length );
system("pause");*/
/*for( i = 0;i < 10000120;i ++ )
Fail[i] = 0;*/
memset( Fail,0,sizeof(Fail) );
/*GetNext ( P, Fail );*/
GetNext ( P, P_Length, Fail );
/*d = FastFind ( T, P, Fail );*/
d = FastFind ( T, T_Length, P, P_Length, Fail );
if( d == -1 )
printf("匹配位置失败!\n");
else
printf("匹配位置为%d\n",d);/*-(d + 45) - 2*/
/*Sleep(1000 * 60);*/
printf("Time used = %.2f seconds.\n",(double)clock() / CLOCKS_PER_SEC);
system("pause");
/*return 0;*/
}3.BM模式匹配算法
头文件BM.h:
/*BM.h*/
#ifndef BM_H_INCLUDED
#define BM_H_INCLUDED
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
int *MakeSkip(char* ptrn,int pLen);
int *MakeShift(char *ptrn,int pLen);
int BMSearch(char *buf,int blen,char *ptrn,int plen,int *skip,int *shift);
#endif // BM_H_INCLUDED 源文件BM.c:
/*BM.c*/
#include "BM.h"
/*
函数:int* MakeSkip(char*,int)
目的:根据坏字符规则做预处理,建立一张坏字符表
表的长度由字符的规模而定,
如果只有字母则长度只有26,
如果是字母加数字长度就是26+10
参数:
ptrn=>模式串P
pLen=>模式串P长度
返回:
int* - 坏字符表
*/
int *MakeSkip(char* ptrn,int pLen)
{
int i;
int len=pLen;
char *p=ptrn;
//为建立坏字符表,申请256个int的空间
int *skip=(int*)malloc(256*sizeof(int));
if(skip==NULL)
{
printf("malloc failed!");
return 0;
}
//初始化坏字符表,256个单元全部初始化为pLen
for(i=0;i<256;i++)
{
*(skip+i)=pLen;
}
//赋值,从左到右遍历ptrn,这样如果一个字符出现两次,后面的覆盖前面的,
//不在模式中出现的字符不用再赋值,它们使用默认值pLen。
while(pLen!=0)
{
*(skip+(int)*ptrn++)=--pLen;
}
return skip;
}
/*
函数:int *MakeShift(char*,int)
目的:根据好后缀原则做预处理,建立一张好后缀表
参数:
ptrn=>模式串P
pLen=>模式串P的长度
返回:
int* :好后缀表
*/
int *MakeShift(char *ptrn,int pLen)
{
//为好后缀表申请pLen个int的空间
//这样,第一个位置放置长度为1的后缀
int *shift=(int *)malloc(pLen*sizeof(int));
int *sptr=shift+pLen-1;//方便为好后缀表进行赋值的指针
char *pptr=ptrn+pLen-1;//记录好后缀表边界位置的指针
char c;
//int i;
if(shift==NULL)
{
fprintf(stderr,"malloc failed!");
return 0;
}
c=*(ptrn+pLen-1);//保存模式串中最后一个字符,因为要反复用到它
*sptr=1;//以最后一个字符为边界时,移动距离设为1(因为要与坏字符规则比较,所以这个是个假设,1也是最小的移动距离)
pptr--;//边界移动到倒数第二个字符
while(--sptr>=shift)//该最外层循环完成给好后缀表中的每一个单元进行赋值的工作
{
char *p1=ptrn+pLen-2,*p2,*p3;
//该do...while循环完成以当前pptr所指向的字符为边界时,要移动的距离
do
{
while(p1>=ptrn&&*p1--!=c);//该空循环,寻找与最后一个字符c匹配的字符所指向的位置
if(p1=ptrn&&*p3--==*p2--&&p2>=pptr);//该空循环,判断在边界内字符串匹配到什么位置
if(p2=ptrn);
pptr--;//边界继续向前移动
}
return shift;
}
/*
函数:int* BMSearch(char*,int ,char*,int,int*,int*)
目的:判断文本串是否包含模式串P
参数:
buf->文本串T
blen->文本串T长度
ptrn->模式串P长度
plen->模式串P长度
skip->坏字符表
shift->好后缀表
返回:
int->1表示成功(文本串包含模式串),0表示失败(文本串不包含模式串)
*/
int BMSearch(char *buf,int blen,char *ptrn,int plen,int *skip,int *shift)
{
int b_idx=plen;
if(plen==0)
{
return 1;
}
while(b_idx<=blen)//计算字符串是否匹配到了尽头
{
int p_idx=plen,skip_stride,shift_stride;
int i=0;
int temp=b_idx;//是为了不改动b_idx的值,b_idx将来用于计算移动的距离
while(buf[--temp]==ptrn[--p_idx])//开始匹配
{
i++;
if(p_idx==0)
{
fprintf(stderr,"match at %d!\n",b_idx - plen + 1);
return 1;
}
}
/*printf("i:%d\tbad:%c\n",i,buf[temp]);*/
skip_stride=skip[(unsigned char)buf[temp]]-i;//根据坏字符规则计算跳跃的距离
shift_stride=shift[p_idx];
/*printf("b_idx:%d 1:%d 2:%d\n",b_idx,skip_stride,shift_stride);*/
b_idx+=(skip_stride>shift_stride)?skip_stride:shift_stride;//取最大者
}
return 0;
} 源文件test.c:
/*test.c*/
#include "BM.h"
int main()
{
FILE *fp1 = fopen( "E:/document/²âÊÔÊý¾Ý/100503.in","r" );
if( !fp1 )
{
printf( "Opening data failed.\n" );
Sleep( 1000 * 60 );
exit( EXIT_FAILURE );
}
int BLength = 100503,PLength = 60,i;
char *buf = ( char * )malloc( sizeof(char) * BLength );
char *ptrn = ( char * )malloc( sizeof(char) * PLength );
for( i = 0;!feof(fp1);i ++ )
fscanf( fp1,"%c",(buf + i) );
/*strcpy(ptrn,"6qc48TlVIvb482XM07Y4isP6X89a7WYi948579f1HR1Avsp2Qok5n2T0z9I");*/
strcpy(ptrn,"fsf8QQCNlL80s1ouGx2TeANoH2jxx9SYQ");
int *skip = NULL;
int *shift = NULL;
fprintf(stderr,"plen=%d!\n",strlen(ptrn));
skip=MakeSkip(ptrn,strlen(ptrn));
shift=MakeShift(ptrn,strlen(ptrn));
BMSearch(buf,strlen(buf),ptrn,strlen(ptrn),skip,shift);
/*printf( "%d\n",strlen("6qc48TlVIvb482XM07Y4isP6X89a7WYi948579f1HR1Avsp2Qok5n2T0z9I") );*/
/*return 0;*/
printf("Time used = %.2f seconds.\n",(double)clock() / CLOCKS_PER_SEC);
system( "pause" );
}4.生成测试用随机字符串C代码
/*生成测试用随机字符串*/
#include
#include
int main()
{
freopen("10000000050.out","w",stdout);
srand( time(NULL) );
char *T = NULL,*P = NULL;
int i,d,ChoosingKey = 0,Value = 0,RandomSize = 10000000050;
T = ( char * )malloc( sizeof(char) * RandomSize );
/*P = ( char * )malloc( sizeof(char) * 32 );
strcpy(P,"wOvT5jN9154gQ751sK9eH1I1l0Hgf9d");*/
for( i = 0;i < RandomSize;i ++ )
{
ChoosingKey = rand() % 3 + 1;
switch(ChoosingKey)
{
case 1:
Value = rand() % ( 90 - 65 + 1 ) + 65;
*( T + i ) = (char)Value;
break;
case 2:
Value = rand() % ( 122 - 97 + 1 ) + 97;
*( T + i ) = (char)Value;
break;
case 3:
Value = rand() % ( 57 - 48 + 1 ) + 48;
*( T + i ) = (char)Value;
break;
default:
*( T + i ) = 'Q';
break;
}
}
i = 0;
while( *(T + i) != '\0' )
{
printf("%c",*(T + i));
i ++;
}
/*printf("\n%s",P);*/
return 0;
} 二、测试结果
一言难尽,暂且放下结论,改天详谈,算法运行效率:BM>BF>KMP。而且刁肥宅发现,VC6.0编译的程序跑的结果耗时永远比CodeBlocks 17.12编译的短。
有图有真相,各位可以去下载刁肥宅上传的源代码与测试数据,自行验证。