【python画图】——数据注释ax.test()/plot.test()
ax.test()
plot.test()
作用一直,主要是区分一下作用区域
话不多说举例说名一下
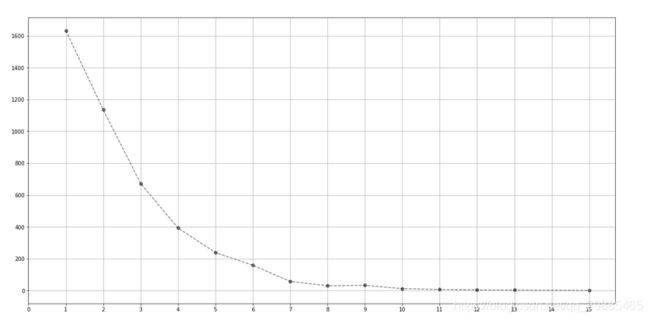
画了一个图干干巴巴麻麻勒勒的不方便查看
#调用包略
#代码不用看太细举例说明而已
fig,ax=plt.subplots(1,1,figsize=(20, 10))
ax.grid()
x=total.index
y=total['var1']
ax.plot(x,y,'k--o',alpha=0.5)
ax.set_xticks(range(0,16))
#法一:
for a, b in zip(x, y): #不了解zip()函数去百度一下,就是对应关系,a对应x;b对应y
plt.text(a, b, b, ha='center', va='bottom', fontsize=20)
#法二:
for a, b in data:
#plt.text(a, b, b, ha='center', va='bottom', fontsize=20)
plt.text(x, y, s, fontdict=None, withdash=False, **kwargs)
x:x轴对应的数据
y:y轴对应的数据
s:要备注的数据
Help on function text in module matplotlib.pyplot:
text(x, y, s, fontdict=None, withdash=False, **kwargs)
Add text to the axes.
Add the text *s* to the axes at location *x*, *y* in data coordinates.
Parameters
----------
x, y : scalars
The position to place the text. By default, this is in data
coordinates. The coordinate system can be changed using the
*transform* parameter.
s : str
The text.
fontdict : dictionary, optional, default: None
A dictionary to override the default text properties. If fontdict
is None, the defaults are determined by your rc parameters.
withdash : boolean, optional, default: False
Creates a `~matplotlib.text.TextWithDash` instance instead of a
`~matplotlib.text.Text` instance.
Returns
-------
text : `.Text`
The created `.Text` instance.
Other Parameters
----------------
**kwargs : `~matplotlib.text.Text` properties.
Other miscellaneous text parameters.
Examples
--------
Individual keyword arguments can be used to override any given
parameter::
>>> text(x, y, s, fontsize=12)
The default transform specifies that text is in data coords,
alternatively, you can specify text in axis coords (0,0 is
lower-left and 1,1 is upper-right). The example below places
text in the center of the axes::
>>> text(0.5, 0.5, 'matplotlib', horizontalalignment='center',
... verticalalignment='center', transform=ax.transAxes)
You can put a rectangular box around the text instance (e.g., to
set a background color) by using the keyword `bbox`. `bbox` is
a dictionary of `~matplotlib.patches.Rectangle`
properties. For example::
>>> text(x, y, s, bbox=dict(facecolor='red', alpha=0.5))
喜欢可以关注【小猪课堂】公众号了解更多内容