一起学springboot(三)
springboot数据访问概述
SpringData是spring提供的一个用于简化数据库访问,支持云反服务的开元框架。它是一个伞形项目,包含了大量关系型数据库和非关系型数据库的访问解决方案。
Spring Boot默认采用整合SpringData的方式统一处理数据访问层,通过添加大量自动配置,引入各种数据访问模板xxxTemplate以及统一的Repository接口,从而达到简化数据访问层的操作。下图Spring Boot提供的常见数据库依赖启动器 
其中没有mybatis的。应为springboot没有提供mybatis 场景依赖,但是mybatis开发团队适配了springboot。提供了mybatis-spring-boot-starter依赖启动器
----环境搭建
①数据准备:创建数据库、数据表并插入一定的数据,(这里就省略建库建表插入数据的步骤)
②创建项目,引入相应的启动器:使用Spring Initializr的方式构建项目,选择MySQL和MyBatis依赖,编写实体类。(这里就省去新建一个项目的步骤)
③编写配置文件:在配置文件中进行数据库连接配置以及进行第三方数据源的默认参数覆盖
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springbootdata?serverTimezone=UTC
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=root
tips:数据源类型选择--springboot1.x版本默认的是tomcat.jdbc数据源,springboot2.x默认的是hikari数据源.如果需要其他数据源需要重新配置
我选择了druid数据源,因此,需要在pom.xml引入阿里巴巴为springboot适配的依赖启动器
com.alibaba
druid-spring-boot-starter
1.1.10
引入后,无需其他额外配置,springboot自动识别。但是这样是使用了默认参数,如果需要修改一些参数,那么需要在全局配置文件重新定义修改,如下:
#添加并配置第三方数据源druid
spring.datasource.type = com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.datasource.initialSize=20
spring.datasource.minIdle=10
spring.datasource.maxActive=100还需写一个自定义配置文件,将上述属性注入到druid数据源属性中
package com.rainnie.config;
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
@Configuration
public class DataSourceConfig {
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource")
public DataSource getDruid(){
return new DruidDataSource();
}
}最后就是 Spring Boot 整合MyBatis。此时有两种方法
①使用注解的方式MyBatis
package com.rainnie.mapper;
import com.rainnie.domain.Comment;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.*;
@Mapper
public interface CommentMapper {
@Select("SELECT * FROM t_comment WHERE id =#{id}")
public Comment findById(Integer id);
@Insert("INSERT INTO t_comment(content,author,a_id) " +
"values (#{content},#{author},#{aId})")
public int insertComment(Comment comment);
@Update("UPDATE t_comment SET content=#{content} WHERE id=#{id}")
public int updateComment(Comment comment);
@Delete("DELETE FROM t_comment WHERE id=#{id}")
public int deleteComment(Integer id);
}
如上所示。整合步骤是 a.创建Mapper接口文件:@Mapper b.编写测试方法进行接口方法测试及整合测试
package com.rainnie.chapter3;
import com.rainnie.domain.Article;
import com.rainnie.domain.Comment;
import com.rainnie.mapper.ArticleMapper;
import com.rainnie.mapper.CommentMapper;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class Chapter3ApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private CommentMapper commentMapper;
@Test
public void selectComment() {
Comment comment = commentMapper.findById(1);
System.out.println(comment);
}
②使用配置文件方式整合mybatis
步骤如下:
a.创建Mapper接口文件:@Mapper
b.创建XML映射文件:编写对应的SQL语句
c.在全局文件中配置XML映射文件路径以及实体类别名映射路径
d.编写测试方法进行接口方法测试及整合测试
UPDATE t_article
title=#{title},
content=#{content}
WHERE id=#{id}
#开启驼峰命名匹配映射
#mybatis.configuration.map-underscore-to-camel-case=true
#配置mybatis的xml配置文件路径
mybatis.mapper-locations=classpath:mapper/*.xml
#配置xml映射文件中指定的实体类别名路径
mybatis.type-aliases-package=com.rainnie.domain @Autowired
private ArticleMapper articleMapper;
@Test
public void selectArticle() {
Article article = articleMapper.selectArticle(1);
System.out.println(article);
}总结和比较:对于springboot支持与mybatis整合的两种方式而言,使用注解的方式比较适合简单的增删改查,使用配置文件的方式稍微复杂,但是对于复杂的数据操作更加实用。实际开发中,一般两者会混用使用。
Spring Boot 整合JPA
Spring Data JPA是Spring基于ORM框架、JPA规范的基础上封装的一套JPA应用框架,它提供了增删改查等常用功能,使开发者可以用较少的代码实现数据操作,同时还易于扩展。
Spring Data JPA基本使用
a.编写ORM实体类:实体类与数据表进行映射,并且配置好映射关系。
package com.rainnie.domain;
import javax.persistence.*;
@Entity(name = "t_comment") // 设置ORM实体类,并指定映射的表名,默认情况下,数据表的名称就是首字母小写的类名
//@Table(name="t_comment")
public class Discuss {
@Id // 表明映射对应的主键id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY) // 设置主键自增策略
private Integer id;
private String content;
private String author;
@Column(name = "a_id") //指定映射的表字段名,当时类属性与表名字段不同的时候,能够配置name属性表示类属性对应的表字段名
private Integer aId;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getContent() {
return content;
}
public void setContent(String content) {
this.content = content;
}
public String getAuthor() {
return author;
}
public void setAuthor(String author) {
this.author = author;
}
public Integer getaId() {
return aId;
}
public void setaId(Integer aId) {
this.aId = aId;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Discuss{" +
"id=" + id +
", content='" + content + '\'' +
", author='" + author + '\'' +
", aId=" + aId +
'}';
}
}
b.编写Repository接口:针对不同的表数据操作编写各自对应的Repositor接口,并根据需要编写对应的数据操作方法
public interface DiscussRepository extends JpaRepository {
// 1、查询author非空的Discuss评论集合
public List findByAuthorNotNull();
// 2、根据文章id分页查询Discuss评论集合
@Query("SELECT c FROM t_comment c WHERE c.aId = ?1")
public List getDiscussPaged(Integer aid,Pageable pageable);
// 3、使用元素SQL语句,根据文章id分页查询Discuss评论集合
@Query(value = "SELECT * FROM t_comment WHERE a_Id = ?1",nativeQuery = true)
public List getDiscussPaged2(Integer aid, Pageable pageable);
//注:与getDiscussPaged()方法的参数和作用完全一样。区别是该方法上方的@Query注解将
//nativeQuery属性设置为了true,用来编写原生SQL语句。
//4、 根据评论id修改评论作者author
@Transactional
@Modifying
@Query("UPDATE t_comment c SET c.author = ?1 WHERE c.id = ?2")
public int updateDiscuss(String author,Integer id);
// 5、根据评论id删除评论
@Transactional
@Modifying
@Query("DELETE t_comment c WHERE c.id = ?1")
public int deleteDiscuss(Integer id);
}
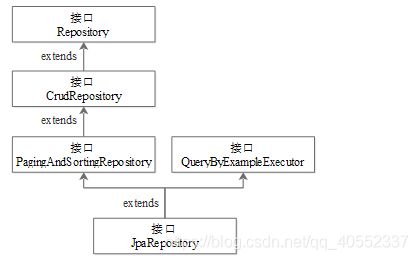
tips:Repository继承关系--使用Spring Data JPA自定义Repository接口,必须继承XXRepository
整合步骤:
①在pom文件中添加Spring Data JPA依赖启动器
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-data-jpa
②编写ORM实体类
@Entity(name = "t_comment")
public class Discuss {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Integer id;
private String content;
private String author;
@Column(name = "a_id")
private Integer aId;
}
③编写Repository接口DiscussRepository
public interface DiscussRepository extends JpaRepository {
// 1、查询author非空的Discuss评论集合
public List findByAuthorNotNull();
// 2、根据文章id分页查询Discuss评论集合
@Query("SELECT c FROM t_comment c WHERE c.aId = ?1")
public List getDiscussPaged(Integer aid,Pageable pageable);
// 3、使用元素SQL语句,根据文章id分页查询Discuss评论集合
@Query(value = "SELECT * FROM t_comment WHERE a_Id = ?1",nativeQuery = true)
public List getDiscussPaged2(Integer aid, Pageable pageable);
//4、 根据评论id修改评论作者author
@Transactional
@Modifying
@Query("UPDATE t_comment c SET c.author = ?1 WHERE c.id = ?2")
public int updateDiscuss(String author,Integer id);
// 5、根据评论id删除评论
@Transactional
@Modifying
@Query("DELETE t_comment c WHERE c.id = ?1")
public int deleteDiscuss(Integer id);
}
④编写测试方法
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class JpaTests {
@Autowired
private DiscussRepository repository;
// 1、使用JpaRepository内部方法进行数据操作
@Test
public void selectComment() {
Optional optional = repository.findById(1);
if(optional.isPresent()){
System.out.println(optional.get());
}
System.out.println();
}
// 2、使用方法名关键字进行数据操作
@Test
public void selectCommentByKeys() {
List list = repository.findByAuthorNotNull();
System.out.println(list);
}
// 3、使用@Query注解进行数据操作
@Test
public void selectCommentPaged() {
Pageable pageable = PageRequest.of(0,3);
List allPaged = repository.getDiscussPaged(1, pageable);
System.out.println(allPaged);
}
// 4、使用Example封装参数进行数据查询操作
@Test
public void selectCommentByExample() {
Discuss discuss =new Discuss();
discuss.setAuthor("张三");
Example example = Example.of(discuss);
List list = repository.findAll(example);
System.out.println(list);
}
@Test
public void selectCommentByExampleMatcher() {
Discuss discuss =new Discuss();
discuss.setAuthor("张");
ExampleMatcher matcher = ExampleMatcher.matching()
.withMatcher("author",startsWith());
Example example = Example.of(discuss, matcher);
List list = repository.findAll(example);
System.out.println(list);
}
springboot整合redis
Redis 是一个开源(BSD许可)的、内存中的数据结构存储系统,它可以用作数据库、缓存和消息中间件,并提供多种语言的API,优点有下面几点:
a.存取速度快:Redis速度非常快,每秒可执行大约110000次的设值操作,或者执行81000次的读取操作。
b.支持丰富的数据类型:Redis支持开发人员常用的大多数数据类型,例如列表、集合、排序集和散列等。
c.操作具有原子性:所有Redis操作都是原子操作,这确保如果两个客户端并发访问,Redis服务器能接收更新后的值。
d.提供多种功能:Redis提供了多种功能特性,可用作非关系型数据库、缓存中间件、消息中间件等。
整合步骤如下
①在pom文件中添加Spring Data Redis依赖启动器
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-data-redis
②编写实体类,如下三个
package com.rainnie.domain;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.index.Indexed;
public class Address {
@Indexed
private String city;
@Indexed
private String country;
public Address() {
}
public Address(String city, String country) {
this.city = city;
this.country = country;
}
public String getCity() {
return city;
}
public void setCity(String city) {
this.city = city;
}
public String getCountry() {
return country;
}
public void setCountry(String country) {
this.country = country;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Address{" +
"city='" + city + '\'' +
", country='" + country + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
package com.rainnie.domain;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.index.Indexed;
public class Family {
@Indexed
private String type;
@Indexed
private String username;
public Family() {
}
public Family(String type, String username) {
this.type = type;
this.username = username;
}
public String getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Family{" +
"type='" + type + '\'' +
", username='" + username + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
package com.rainnie.domain;
import org.springframework.data.annotation.Id;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisHash;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.index.Indexed;
import java.util.List;
@RedisHash("persons")//指定操作实体类对象在redis数据库中的存储空间
public class Person {
@Id //标识实体类主键
private String id;
@Indexed // 标识对应属性在Redis数据库中生成二级索引
private String firstname;
@Indexed
private String lastname;
private Address address;
private List familyList;
public Person() {
}
public Person(String firstname, String lastname) {
this.firstname = firstname;
this.lastname = lastname;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getFirstname() {
return firstname;
}
public void setFirstname(String firstname) {
this.firstname = firstname;
}
public String getLastname() {
return lastname;
}
public void setLastname(String lastname) {
this.lastname = lastname;
}
public Address getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(Address address) {
this.address = address;
}
public List getFamilyList() {
return familyList;
}
public void setFamilyList(List familyList) {
this.familyList = familyList;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"id='" + id + '\'' +
", firstname='" + firstname + '\'' +
", lastname='" + lastname + '\'' +
", address=" + address +
", familyList=" + familyList +
'}';
}
}
上面的注解@RedisHash("person")用于指定操作实体类对象在redis中存储空间,此处说明person实体类的数据操作都存储在redis中名为person的存储空间下。
@Id用户表示实体类主键。在redis中会默认生成字符串形式的hashkey表示唯一的实体类对象,当然也可在数据存储时手动指定id
@Indexed用户表示对应属性在redis生成的二级索引。使用该注解后会在redis数据库中生成属性对应的二级索引,索引名就是属性名,可以方便进行数据条件查询
③编写Repository接口
package com.rainnie.repository;
import com.rainnie.domain.Person;
import org.springframework.data.domain.Page;
import org.springframework.data.domain.Pageable;
import org.springframework.data.repository.CrudRepository;
import java.util.List;
public interface PersonRepository extends CrudRepository {
List findByLastname(String lastname);
Page findPersonByLastname(String lastname, Pageable page);
List findByFirstnameAndLastname(String firstname, String lastname);
List findByAddress_City(String city);
List findByFamilyList_Username(String username);
}
④在全局配置文件application.properties中添加Redis数据库连接配置
# Redis服务器地址
spring.redis.host=127.0.0.1
# Redis服务器连接端口
spring.redis.port=6379
# Redis服务器连接密码(默认为空)
spring.redis.password=
⑤编写单元测试进行接口方法测试以及整合测试
package com.itheima;
import com.itheima.domain.Address;
import com.itheima.domain.Family;
import com.itheima.domain.Person;
import com.itheima.repository.PersonRepository;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class RedisTests {
@Autowired
private PersonRepository repository;
@Test
public void savePerson() {
Person person =new Person("张","有才");
Person person2 =new Person("James","Harden");
// 创建并添加住址信息
Address address=new Address("北京","China");
person.setAddress(address);
// 创建并添加家庭成员
List list =new ArrayList<>();
Family dad =new Family("父亲","张良");
Family mom =new Family("母亲","李香君");
list.add(dad);
list.add(mom);
person.setFamilyList(list);
// 向Redis数据库添加数据
Person save = repository.save(person);
Person save2 = repository.save(person2);
System.out.println(save);
System.out.println(save2);
}
@Test
public void selectPerson() {
List list = repository.findByAddress_City("北京");
System.out.println(list);
}
@Test
public void updatePerson() {
Person person = repository.findByFirstnameAndLastname("张","有才").get(0);
person.setLastname("小明");
Person update = repository.save(person);
System.out.println(update);
}
@Test
public void deletePerson() {
Person person = repository.findByFirstnameAndLastname("张","小明").get(0);
repository.delete(person);
}
}