Dialog、Toast的Window和ViewRootImpl
文章目录
- 前言
- Dialog
- Dialog的构造
- Dialog添加View
- Dialog的展现
- Toast
- Toast的构造
- Toast添加View
- Toast的展示
- Toast的消失
- Dialog和Toast在异步线程的展现
- 总结
前言
文章Activity中的Window的setContentView、遇见LayoutInflater&Factory、ViewRootImpl的独白,我不是一个View(布局篇) 分别讲述了Activity的setContentView添加View、LayoutInflater布局解析以及添加Window。文章内容都是站在Activity的角度来进行代码解析的,因此我们不再对Dialog和Toast与Activity做具体分析,主要来看看它们与Activity有什么不同之处源码:android-22。
Dialog
Dialog的构造
public class Dialog implements DialogInterface, Window.Callback,
KeyEvent.Callback, OnCreateContextMenuListener,Window.OnWindowDismissedCallback{
//只有Activity的Context可以启动Dialog,因为Dialog展示的时候需要主题资源也就是ContextThemeWrapper。
Dialog(Context context, int theme, boolean createContextThemeWrapper) {
if (createContextThemeWrapper) {
if (theme == 0) {
TypedValue outValue = new TypedValue();
context.getTheme().resolveAttribute(com.android.internal.R.attr.dialogTheme,
outValue, true);
theme = outValue.resourceId;
}
mContext = new ContextThemeWrapper(context, theme);
} else {
mContext = context;
}
//因为每个上下文环境获取的系统服务都是相同的实例,这里获取的WindowManager是Activity的WindowManager。
mWindowManager = (WindowManager)context.getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE);
//创建Dialog的PhoneWindow对象。
Window w = PolicyManager.makeNewWindow(mContext);
mWindow = w;
w.setCallback(this);
w.setOnWindowDismissedCallback(this);
w.setWindowManager(mWindowManager, null, null);
w.setGravity(Gravity.CENTER);
//Handler中的Looper默认为当前线程的Looper
mListenersHandler = new ListenersHandler(this);
}
}
Dialog添加View
和Activity相同通过setContentView初始化 Window 中的 DecorView,并对页面 View 进行add。详细讲述请移动到Activity中的Window的setContentView
public class Dialog implements DialogInterface, Window.Callback,
KeyEvent.Callback, OnCreateContextMenuListener,Window.OnWindowDismissedCallback{
/**
* Set the screen content from a layout resource. The resource will be
* inflated, adding all top-level views to the screen.
*
* @param layoutResID Resource ID to be inflated.
*/
public void setContentView(int layoutResID) {
mWindow.setContentView(layoutResID);
}
}
Dialog的展现
Dialog 的展现和 Activity 不同是因为两者的声明周期不同,Activity 的声明周期是有 AMS 调用而 Dialog 是应用程序自己调用的。ViewRootImpl的初始化在 Activity 会在onResume()方法之后,而是 Dialog 被调用show方法时触发的。
public class Dialog implements DialogInterface, Window.Callback,
KeyEvent.Callback, OnCreateContextMenuListener,Window.OnWindowDismissedCallback{
/**
* Start the dialog and display it on screen. The window is placed in the
* application layer and opaque. Note that you should not override this
* method to do initialization when the dialog is shown, instead implement
* that in {@link #onStart}.
*/
public void show() {
if (mShowing) {
if (mDecor != null) {
if (mWindow.hasFeature(Window.FEATURE_ACTION_BAR)) {
mWindow.invalidatePanelMenu(Window.FEATURE_ACTION_BAR);
}
mDecor.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
}
return;
}
mCanceled = false;
//判断是否调用onCreate方法
if (!mCreated) {
dispatchOnCreate(null);
}
//调用onStart方法
onStart();
//获取DecorView对象实例
mDecor = mWindow.getDecorView();
if (mActionBar == null && mWindow.hasFeature(Window.FEATURE_ACTION_BAR)) {
final ApplicationInfo info = mContext.getApplicationInfo();
mWindow.setDefaultIcon(info.icon);
mWindow.setDefaultLogo(info.logo);
mActionBar = new WindowDecorActionBar(this);
}
//更新Window属性参数
WindowManager.LayoutParams l = mWindow.getAttributes();
if ((l.softInputMode
& WindowManager.LayoutParams.SOFT_INPUT_IS_FORWARD_NAVIGATION) == 0) {
WindowManager.LayoutParams nl = new WindowManager.LayoutParams();
nl.copyFrom(l);
nl.softInputMode |=
WindowManager.LayoutParams.SOFT_INPUT_IS_FORWARD_NAVIGATION;
l = nl;
}
try {
//Windowmanger添加Window、ViewRootImpl初始化并绑定Window
mWindowManager.addView(mDecor, l);
mShowing = true;
//OnShowListener监听回调
sendShowMessage();
} finally {
}
}
}
Toast
Toast的构造
public class Toast {
final Context mContext;
final TN mTN;//
int mDuration;//展示时间
View mNextView;//所展示的View
/**
* Construct an empty Toast object. You must call {@link #setView} before you
* can call {@link #show}.
*
* @param context The context to use. Usually your {@link android.app.Application}
* or {@link android.app.Activity} object.
*/
//Context可以为Application也可以为Activity,
public Toast(Context context) {
mContext = context;
mTN = new TN();
mTN.mY = context.getResources().getDimensionPixelSize(
com.android.internal.R.dimen.toast_y_offset);
mTN.mGravity = context.getResources().getInteger(
com.android.internal.R.integer.config_toastDefaultGravity);
}
//NotificationManagerService的客户端IBinder对
private static INotificationManager sService;
private static class TN extends ITransientNotification.Stub {
/***部分代码省略***/
private final WindowManager.LayoutParams mParams = new WindowManager.LayoutParams();
//Handler中的Looper默认为当前线程的Looper
final Handler mHandler = new Handler();
TN() {
// XXX This should be changed to use a Dialog, with a Theme.Toast
// defined that sets up the layout params appropriately.
final WindowManager.LayoutParams params = mParams;
params.height = WindowManager.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT;
params.width = WindowManager.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT;
params.format = PixelFormat.TRANSLUCENT;
params.windowAnimations = com.android.internal.R.style.Animation_Toast;
//设置Window类型为Toast
params.type = WindowManager.LayoutParams.TYPE_TOAST;
params.setTitle("Toast");
params.flags = WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_KEEP_SCREEN_ON
| WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_NOT_FOCUSABLE
| WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_NOT_TOUCHABLE;
}
}
}
transient_notification.xml
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:background="?android:attr/toastFrameBackground">
<TextView
android:id="@android:id/message"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:textAppearance="@style/TextAppearance.Toast"
android:textColor="@color/bright_foreground_dark"
android:shadowColor="#BB000000"
android:shadowRadius="2.75"
/>
LinearLayout>
Toast添加View
从Toast的调用我们开始分析Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this , "Hello World" , Toast.LENGTH_SHORT);我们主要看makeText方法。
public class Toast {
/**
* Make a standard toast that just contains a text view.
*
* @param context The context to use. Usually your {@link android.app.Application}
* or {@link android.app.Activity} object.
* @param text The text to show. Can be formatted text.
* @param duration How long to display the message. Either {@link #LENGTH_SHORT} or
* {@link #LENGTH_LONG}
*
*/
public static Toast makeText(Context context, CharSequence text, @Duration int duration) {
Toast result = new Toast(context);
//获取布局解析器
LayoutInflater inflate = (LayoutInflater)
context.getSystemService(Context.LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE);
//解析transient_notification.xml生成对应的View
View v = inflate.inflate(com.android.internal.R.layout.transient_notification, null);
//找到View中的id为message的TextView
TextView tv = (TextView)v.findViewById(com.android.internal.R.id.message);
//对Textview进行文字赋值
tv.setText(text);
//展示的Toast所用的View
result.mNextView = v;
//设置间隔时间
result.mDuration = duration;
return result;
}
}
主要是对Toast内部成员变量mNextView和mDuration进行初始化。
Toast的展示
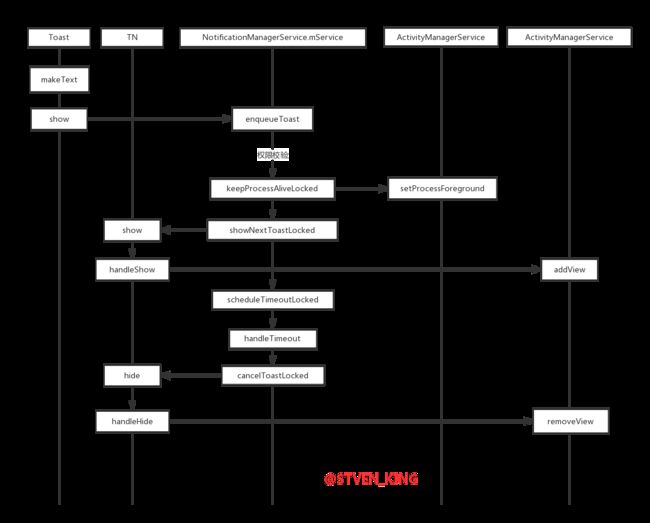
将 Toast 内部的 TN ( ITransientNotification 客户端对象)加入到 INotificationManager 服务端的 Binder 兑现的 mToastQueue 队列中。再由服务端循环遍历 mToastQueue 队列中ToastRecord对象,处理一个移除一个,每次处理的都是 List 的第一个ToastRecord对象。
public class Toast {
//INotificationManager的客户端的Binder对象
private static INotificationManager sService;
static private INotificationManager getService() {
if (sService != null) {
return sService;
}
//获取INotificationManager的客户端的Binder对象
sService = INotificationManager.Stub.asInterface(ServiceManager.getService("notification"));
return sService;
}
/**
* Show the view for the specified duration.
*/
public void show() {
//mNextView不能为空
if (mNextView == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("setView must have been called");
}
//service初始哈
INotificationManager service = getService();
//获取当前Context对应的包名
String pkg = mContext.getOpPackageName();
TN tn = mTN;
tn.mNextView = mNextView;
try {
//将TN加入INotificationManager中的mToastQueue队列
service.enqueueToast(pkg, tn, mDuration);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
// Empty
}
}
}
NotificationManagerService在服务端处理ITransientNotification客户端传过来的enqueueToast事件。
public class NotificationManagerService extends SystemService {
//是否是系统调用
private static boolean isCallerSystem() {
return isUidSystem(Binder.getCallingUid());
}
private final IBinder mService = new INotificationManager.Stub() {
@Override
public void enqueueToast(String pkg, ITransientNotification callback, int duration){
if (DBG) {
Slog.i(TAG, "enqueueToast pkg=" + pkg + " callback=" + callback
+ " duration=" + duration);
}
if (pkg == null || callback == null) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Not doing toast. pkg=" + pkg + " callback=" + callback);
return ;
}
//判断是否是系统调动或者是Android系统应用程序进行调用
final boolean isSystemToast = isCallerSystem() || ("android".equals(pkg));
//Toast或者通知权限被禁用
if (ENABLE_BLOCKED_TOASTS && !noteNotificationOp(pkg, Binder.getCallingUid())) {
if (!isSystemToast) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Suppressing toast from package " + pkg + " by user request.");
return;
}
}
//mToastQueue加锁
synchronized (mToastQueue) {
int callingPid = Binder.getCallingPid();
long callingId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
try {
ToastRecord record;
//寻找当前callback在mToastQueue中的索引,没找到则返回-1
int index = indexOfToastLocked(pkg, callback);
// If it's already in the queue, we update it in place, we don't
// move it to the end of the queue.
//index>=0表示mToastQueue中有该callback的索引,record进行更新展示时间
if (index >= 0) {
record = mToastQueue.get(index);
record.update(duration);
} else {
// Limit the number of toasts that any given package except the android
// package can enqueue. Prevents DOS attacks and deals with leaks.
//不是系统的Toast
if (!isSystemToast) {
int count = 0;
final int N = mToastQueue.size();
for (int i=0; i<N; i++) {
final ToastRecord r = mToastQueue.get(i);
//判断当前的Toast是不是同一个包发出的
if (r.pkg.equals(pkg)) {
count++;
//当前包的需要展示的Toast缓存数量>=50
if (count >= MAX_PACKAGE_NOTIFICATIONS) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Package has already posted " + count
+ " toasts. Not showing more. Package=" + pkg);
return;
}
}
}
}
//根据callback等信息构造ToastRecord对象
record = new ToastRecord(callingPid, pkg, callback, duration);
//将新的ToastRecord对象加入到队列总
mToastQueue.add(record);
//加入之后当前的索引是lenth-1
index = mToastQueue.size() - 1;
//将当前包对应的线程切换为前台线程
keepProcessAliveLocked(callingPid);
}
// If it's at index 0, it's the current toast. It doesn't matter if it's
// new or just been updated. Call back and tell it to show itself.
// If the callback fails, this will remove it from the list, so don't
// assume that it's valid after this.
//如果之前队列中没有正在处理的消息,那么处理当前这个ToastRecord
if (index == 0) {
showNextToastLocked();
}
} finally {
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(callingId);
}
}
}
}
}
NotificationManagerService使用先进先出(FIFO)的方式处理 mToastQueue 队列中的消息。
- 服务端的处理
public class NotificationManagerService extends SystemService {
void showNextToastLocked() {
//获取队列第一个ToastRecord
ToastRecord record = mToastQueue.get(0);
while (record != null) {
if (DBG) Slog.d(TAG, "Show pkg=" + record.pkg + " callback=" + record.callback);
try {
//调用客户端Binder对应的TN.show方法。
record.callback.show();
scheduleTimeoutLocked(record);
return;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Object died trying to show notification " + record.callback
+ " in package " + record.pkg);
// remove it from the list and let the process die
//当前Toast客户端Binder方法调用抛出异常
//移除当前ToastRecord
int index = mToastQueue.indexOf(record);
if (index >= 0) {
mToastQueue.remove(index);
}
//切换当前ToastRecord进程
keepProcessAliveLocked(record.pid);
//遍历对象变为列表下一个oastRecord对象
if (mToastQueue.size() > 0) {
record = mToastQueue.get(0);
} else {
record = null;
}
}
}
}
}
- 客户端的处理
private static class TN extends ITransientNotification.Stub {
/**
* schedule handleShow into the right thread
*/
@Override
public void show() {
if (localLOGV) Log.v(TAG, "SHOW: " + this);
mHandler.post(mShow);//利用Handler执行mShow
}
final Runnable mShow = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
handleShow();
}
};
//展示Toast
public void handleShow() {
if (localLOGV) Log.v(TAG, "HANDLE SHOW: " + this + " mView=" + mView
+ " mNextView=" + mNextView);
//判断mNextView是否展示过
if (mView != mNextView) {
// remove the old view if necessary
//移除当前展示的Toast
handleHide();
mView = mNextView;
//获取当前的应用程序的上下文环境
Context context = mView.getContext().getApplicationContext();
//获取当前包名
String packageName = mView.getContext().getOpPackageName();
if (context == null) {
context = mView.getContext();
}
//获取上下文环境的WindowManagerImpl
mWM = (WindowManager)context.getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE);
// We can resolve the Gravity here by using the Locale for getting
// the layout direction
final Configuration config = mView.getContext().getResources().getConfiguration();
final int gravity = Gravity.getAbsoluteGravity(mGravity, config.getLayoutDirection());
//设置参数的重力防线
mParams.gravity = gravity;
if ((gravity & Gravity.HORIZONTAL_GRAVITY_MASK) == Gravity.FILL_HORIZONTAL) {
mParams.horizontalWeight = 1.0f;
}
if ((gravity & Gravity.VERTICAL_GRAVITY_MASK) == Gravity.FILL_VERTICAL) {
mParams.verticalWeight = 1.0f;
}
//设置参数的坐标和偏移量
mParams.x = mX;
mParams.y = mY;
mParams.verticalMargin = mVerticalMargin;
mParams.horizontalMargin = mHorizontalMargin;
mParams.packageName = packageName;
//如果mView添加过,那么先把mView从WindowManager中移除。
if (mView.getParent() != null) {
if (localLOGV) Log.v(TAG, "REMOVE! " + mView + " in " + this);
mWM.removeView(mView);
}
if (localLOGV) Log.v(TAG, "ADD! " + mView + " in " + this);
//把需要展示的View添加在WindowManager中
mWM.addView(mView, mParams);
trySendAccessibilityEvent();
}
}
}
Toast的消失
系统的 Toast 的 hide 都是在 INotificationManager 的服务端 Binder 中发起的,但最终的执行都是在 INotificationManager 的客户端 Binder 中执行的。
- 服务端
public class NotificationManagerService extends SystemService {
private final class WorkerHandler extends Handler{
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg){
switch (msg.what){
case MESSAGE_TIMEOUT:
//调用当前的Toast的hide
handleTimeout((ToastRecord)msg.obj);
break;
case MESSAGE_SAVE_POLICY_FILE:
handleSavePolicyFile();
break;
case MESSAGE_SEND_RANKING_UPDATE:
handleSendRankingUpdate();
break;
case MESSAGE_LISTENER_HINTS_CHANGED:
handleListenerHintsChanged(msg.arg1);
break;
case MESSAGE_LISTENER_NOTIFICATION_FILTER_CHANGED:
handleListenerInterruptionFilterChanged(msg.arg1);
break;
}
}
}
//让当前Toast展示一段时间后消失
private void scheduleTimeoutLocked(ToastRecord r){
//移除mHandler关于这个TaostRecord的所有Message
mHandler.removeCallbacksAndMessages(r);
Message m = Message.obtain(mHandler, MESSAGE_TIMEOUT, r);
long delay = r.duration == Toast.LENGTH_LONG ? LONG_DELAY : SHORT_DELAY;
//发送一个delayed=duration的MESSAGE_TIMEOUT事件
mHandler.sendMessageDelayed(m, delay);
}
//使Toast消失
private void handleTimeout(ToastRecord record){
if (DBG) Slog.d(TAG, "Timeout pkg=" + record.pkg + " callback=" + record.callback);
synchronized (mToastQueue) {
//找当前ToastRecord在mToastQueue队列中的索引
int index = indexOfToastLocked(record.pkg, record.callback);
if (index >= 0) {
cancelToastLocked(index);
}
}
}
//调用当前索引=index的ToastRecord.callback.hide
void cancelToastLocked(int index) {
ToastRecord record = mToastQueue.get(index);
try {
调用客户端Binder对应的TN.hide方法。
record.callback.hide();
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Object died trying to hide notification " + record.callback
+ " in package " + record.pkg);
// don't worry about this, we're about to remove it from
// the list anyway
}
//移除处理完的ToastRecord
mToastQueue.remove(index);
keepProcessAliveLocked(record.pid);
if (mToastQueue.size() > 0) {
// Show the next one. If the callback fails, this will remove
// it from the list, so don't assume that the list hasn't changed
// after this point.
//处理队列中的下一个ToastRecord
showNextToastLocked();
}
}
}
- 客户端
private static class TN extends ITransientNotification.Stub {
/**
* schedule handleHide into the right thread
*/
@Override
public void hide() {
if (localLOGV) Log.v(TAG, "HIDE: " + this);
mHandler.post(mHide);//利用Handler执行mHide
}
final Runnable mHide = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
handleHide();
// Don't do this in handleHide() because it is also invoked by handleShow()
mNextView = null;
}
};
public void handleHide() {
if (localLOGV) Log.v(TAG, "HANDLE HIDE: " + this + " mView=" + mView);
if (mView != null) {
// note: checking parent() just to make sure the view has
// been added... i have seen cases where we get here when
// the view isn't yet added, so let's try not to crash.
if (mView.getParent() != null) {
if (localLOGV) Log.v(TAG, "REMOVE! " + mView + " in " + this);
//调用WindowManager的removeView移除mView
mWM.removeView(mView);
}
mView = null;
}
}
}
Dialog和Toast在异步线程的展现
ViewRootImpl的独白,我不是一个View(布局篇) 这篇文章说明了为什么我们一般禁止在非 UI线程 中刷新 View ,以及怎么安全的在异步线程操作UI。
发生了对任务执行线程的校验,而且当前执行任务的线程与创建
ViewRootImpl的线程不一样;。
那么 Toast 、 Dialog 和 View 的异步展现,与异步操作UI是否一致呢?
首先测试一下异步展现 Dialog 和 Toast :
//Toast展现
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
//Looper.prepare();
Toast.makeText(TestActivity.this, "test", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
//Looper.loop();
}
}).start();
//Dialog的展现
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
//Looper.prepare();
new MyDialog(TestActivity.this, "test").show();
//Looper.loop();
}
}).start();
崩溃日志:
//Toast崩溃日志
17:30:04.211#[androidcode@]#30824#E#AndroidRuntime #FATAL EXCEPTION: Thread-2
Process: com.tzx.androidcode, PID: 30513
java.lang.RuntimeException: Can't toast on a thread that has not called Looper.prepare()
at android.widget.Toast$TN.<init>(Toast.java:394)
at android.widget.Toast.<init>(Toast.java:114)
at android.widget.Toast.makeText(Toast.java:277)
at android.widget.Toast.makeText(Toast.java:267)
at com.tzx.androidcode.activity.TestActivity$1.run(TestActivity.java:72)
at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:764)
//Dialog的崩溃日志
17:33:07.961#[androidcode@]#31514#E#AndroidRuntime #FATAL EXCEPTION: Thread-2
Process: com.tzx.androidcode, PID: 31438
java.lang.RuntimeException: Can't create handler inside thread that has not called Looper.prepare()
at android.os.Handler.<init>(Handler.java:203)
at android.os.Handler.<init>(Handler.java:117)
at android.app.Dialog.<init>(Dialog.java:123)
at android.app.Dialog.<init>(Dialog.java:149)
at com.tzx.rollaction.test.BaseDailog.<init>(BaseDailog.java:23)
at com.tzx.rollaction.test.MyDialog.<init>(MyDialog.java:20)
at com.tzx.androidcode.activity.TestActivity$2.run(TestActivity.java:86)
at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:764)
我们可以看到都是提示 当前的Handler的Looper没有调用prepare。
我们在上面进行源码阅读的时候都看到了 Toast.TN 和 Dialog 构造的时候的 Handler 都是默认当前线程的 Looper 。
如果当前线程的 Looper 没有 prepare 那么必定会抛异常,如果仅仅执行了 prepare 那么崩溃不会产生了,但是依旧不展示。因为整个 Looper 还没有开始,里面的 Message 都未进行处理。最后我们将代码中注释的 Looper.prepare(); 和 Looper.loop(); 打开就可以正常在异步线程进行 Toast 和 Dialog 的展现。
所以 Toast 和 Dialog 的异步展现其实主要是与其线程的 Looper 队列有关。 Toast 和 Dialog 展示的时候进行的 ViewRootImpl 的创建,这个执行UI操作的也是这个线程,所以展现不会发现异常。如果对 Dialog 进行异步刷新UI ,那么他的限制和 View 的异步刷新是相同的。
总结
通过分析Activity、Dialog、Toast通过对 ViewRootImpl 的更细节的分析,所有添加在窗口上的 View 都有一个 ViewRootImpl 作为它的 Parent ,处理View的布局、事件处理等。
文章到这里就全部讲述完啦,若有其他需要交流的可以留言哦!!
想阅读作者的更多文章,可以查看我 个人博客 和公共号:
![]()