LeetCode刷题笔记(Java)---第221-240题
文章目录
-
-
- 笔记导航
- 221. 最大正方形
- 222. 完全二叉树的节点个数
- 223. 矩形面积
- 224. 基本计算器
- 225. 用队列实现栈
- 226. 翻转二叉树
- 227. 基本计算器 II
- 228. 汇总区间
- 229. 求众数 II
- 230. 二叉搜索树中第K小的元素
- 231. 2的幂
- 232. 用栈实现队列
- 233. 数字 1 的个数
- 234. 回文链表
- 235. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
- 236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先
- 237. 删除链表中的节点
- 238. 除自身以外数组的乘积
- 239. 滑动窗口最大值
- 240. 搜索二维矩阵 II
-
笔记导航
点击链接可跳转到所有刷题笔记的导航链接
221. 最大正方形
在一个由 0 和 1 组成的二维矩阵内,找到只包含 1 的最大正方形,并返回其面积。

- 解答
public static int maximalSquare(char[][] matrix) {
int res = 0;
int height = matrix.length;
int width = matrix[0].length;
int[][] dp = new int[height][width];
for(int i=0;i<height;i++){
dp[i][0] = matrix[i][0]-48;
}
for(int i=0;i<width;i++){
dp[0][i] = matrix[0][i]-48;
}
for(int i = 1;i < height;i++){
for(int j = 1; j<width;j++){
if((matrix[i][j]-48)!=0){
dp[i][j] = Math.min(Math.min(dp[i-1][j-1],dp[i-1][j]),dp[i][j-1])+1;
if(dp[i][j] * dp[i][j] > res)
res = dp[i][j]*dp[i][j];
}
}
}
return res;
}
}
-
分析
1.动态规划实现
动态转移方程为
dp[i][j] = Math.min(Math.min(dp[i-1][j-1],dp[i-1][j]),dp[i][j-1])+1;
2.用于记录当前方格所属最大的正方形边长。(i,j之前的部分,即左边) -
提交结果
222. 完全二叉树的节点个数
给出一个完全二叉树,求出该树的节点个数。
说明:
完全二叉树的定义如下:在完全二叉树中,除了最底层节点可能没填满外,其余每层节点数都达到最大值,并且最下面一层的节点都集中在该层最左边的若干位置。若最底层为第 h 层,则该层包含 1~ 2h 个节点。

- 解答
//方法一
public int countNodes(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null)return 0;
List<List<TreeNode>> list = new ArrayList<>();
tb(list,root,1);
int depth = list.size();
int lastLayerNumber = list.get(depth-1).size();
return (int)Math.pow(2,depth-1) - 1 + lastLayerNumber;
}
public void tb(List<List<TreeNode>> list,TreeNode root,int depth){
if(root==null)return;
if(list.size()<depth){
list.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
List<TreeNode> layer = list.get(depth-1);
layer.add(root);
tb(list,root.left,depth+1);
tb(list,root.right,depth+1);
}
//方法二
public int countNodes(TreeNode root){
return root == null? 0: 1 + countNodes(root.left)+ countNodes(root.right);
}
//方法三
public int computeDepth(TreeNode node) {
int d = 0;
while (node.left != null) {
node = node.left;
++d;
}
return d;
}
public boolean exists(int idx, int d, TreeNode node) {
int left = 0, right = (int)Math.pow(2, d) - 1;
int pivot;
for(int i = 0; i < d; ++i) {
pivot = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (idx <= pivot) {
node = node.left;
right = pivot;
}
else {
node = node.right;
left = pivot + 1;
}
}
return node != null;
}
public int countNodes(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
int d = computeDepth(root);
if (d == 0) return 1;
int left = 1, right = (int)Math.pow(2, d) - 1;
int pivot;
while (left <= right) {
pivot = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (exists(pivot, d, root)) left = pivot + 1;
else right = pivot - 1;
}
return (int)Math.pow(2, d) - 1 + left;
}
-
分析
1.利用递归层次遍历,遍历完完全二叉树
2.可以得到完全二叉树的高度和最后一层的个数
3.(int)Math.pow(2,depth-1) - 1 + lastLayerNumber;利用这个公式即可得到完全二叉树结点的数量
4.方法二直接遍历树,计算遍历过的结点
5.方法三二分查找,先计算层数,然后根据最后一层的范围,进行二分查找,判断二分后的中间结点是否存在,移动左右的指针,找到最后一个结点。 -
提交结果
223. 矩形面积
在二维平面上计算出两个由直线构成的矩形重叠后形成的总面积。
- 解答
public int computeArea(int A, int B, int C, int D, int E, int F, int G, int H) {
int res = 0;
int leftx = Math.max(A,E);
int lefty = Math.max(B,F);
int rightx = Math.min(C,G);
int righty = Math.min(D,H);
if(E>=C || F>=D || G <= A || H <= B) res = (C-A)*(D-B) + (G-E)*(H-F);
else res = (C-A)*(D-B) + (G-E)*(H-F) - (rightx-leftx)*(righty-lefty);
return res;
}
-
分析
1.两个矩形叠加的面积 = 两个矩形的面积-公共面积
2.叠加部分的矩形可以根据如下得出int leftx = Math.max(A,E); int lefty = Math.max(B,F); int rightx = Math.min(C,G); int righty = Math.min(D,H);3.若E>=C || F>=D || G <= A || H <= B则表示没有公共部分
则面积就是两个矩形的面积
4.否则减去公共部分的面积
224. 基本计算器
实现一个基本的计算器来计算一个简单的字符串表达式的值。
字符串表达式可以包含左括号 ( ,右括号 ),加号 + ,减号 -,非负整数和空格 。
- 解答
public int evaluateExpr(Stack<Object> stack) {
int res = 0;
if (!stack.empty()) {
res = (int) stack.pop();
}
while (!stack.empty() && !((char) stack.peek() == ')')) {
char sign = (char) stack.pop();
if (sign == '+') {
res += (int) stack.pop();
} else {
res -= (int) stack.pop();
}
}
return res;
}
public int calculate(String s) {
int operand = 0;
int n = 0;
Stack<Object> stack = new Stack<Object>();
for (int i = s.length() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
char ch = s.charAt(i);
if (Character.isDigit(ch)) {
operand = (int) Math.pow(10, n) * (int) (ch - '0') + operand;
n += 1;
} else if (ch != ' ') {
if (n != 0) {
stack.push(operand);
n = 0;
operand = 0;
}
if (ch == '(') {
int res = evaluateExpr(stack);
stack.pop();
stack.push(res);
} else {
stack.push(ch);
}
}
}
if (n != 0) {
stack.push(operand);
}
return evaluateExpr(stack);
}
-
分析
1.用栈来实现计算操作。
2.一开始想的是从左到右遍历,但发现这样计算的顺序是从右到左计算的;
比如 1 +2 +3 入栈 计算的顺序是 3+2+1 倒过来的。
所以如果是减法操作 则会出错
例如 1- 2 +3 本来的结果应该是 2。而实际的结果会得到3+2-1 = 4
所以可以从右到左的遍历字符串
3 + 2 - 1 倒过来计算就是 1-2+3 和实际的结果一致
3.从右到左遍历,需要两个辅助的变量,一是保存当前的数字,二是记录当前是否存在数字。
通过 operand = (int) Math.pow(10, n) * (int) (ch - ‘0’) + operand; 计算当前的数字
4.遍历到的当前字符不为空,则先判断当前是否有数字。有的话将数字压栈,再判断当前是不是遇到了"(",遇到了则进行栈内的计算。否则直接将其压栈
5.最后还需要判断当前是否有数字有的话压栈,最后计算栈内的结果。
225. 用队列实现栈
使用队列实现栈的下列操作:
push(x) – 元素 x 入栈
pop() – 移除栈顶元素
top() – 获取栈顶元素
empty() – 返回栈是否为空
注意:
-
你只能使用队列的基本操作-- 也就是 push to back, peek/pop from front, size, 和 is empty 这些操作是合法的。
-
你所使用的语言也许不支持队列。 你可以使用 list 或者 deque(双端队列)来模拟一个队列 , 只要是标准的队列操作即可。
-
你可以假设所有操作都是有效的(例如, 对一个空的栈不会调用 pop 或者 top 操作)。
-
解答
class MyStack {
private List<Integer> list;
public MyStack() {
list = new ArrayList<>();
}
public void push(int x) {
list.add(x);
}
public int pop() {
return list.remove(list.size()-1);
}
public int top() {
return list.get(list.size() - 1);
}
public boolean empty() {
return list.size() == 0;
}
}
226. 翻转二叉树
翻转一棵二叉树。
示例:

备注:
这个问题是受到 Max Howell 的 原问题 启发的 :
谷歌:我们90%的工程师使用您编写的软件(Homebrew),但是您却无法在面试时在白板上写出翻转二叉树这道题,这太糟糕了。
- 解答
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null || (root.left == null && root.right == null))return root;
TreeNode tmp = root.right;
root.right = root.left;
root.left = tmp;
if(root.left !=null){
root.left = invertTree(root.left);
}
if(root.right != null){
root.right = invertTree(root.right);
}
return root;
}
227. 基本计算器 II
实现一个基本的计算器来计算一个简单的字符串表达式的值。
字符串表达式仅包含非负整数,+, - ,*,/ 四种运算符和空格 。 整数除法仅保留整数部分。
- 解答
public int calculate2(String s) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
int sign = 1; // 表示正负号 2-3*3 = 2+(-3)*3
int msign = 0; // 1表示相乘 -1 表示相除 0 表示无操作
for(int i=0; i<s.length(); i++){
char ch = s.charAt(i);
if(Character.isDigit(ch)){
// 如果是数字
int num = ch - '0';
while(i+1<s.length() && Character.isDigit(s.charAt(i+1))){
num = num*10 + (s.charAt(i+1) - '0');
i++;
}
if(msign == 1){
//相乘
stack.push(stack.pop() * num);
msign = 0;
}else if(msign == -1){
// 相除
stack.push(stack.pop() / num);
msign = 0;
}else{
stack.push(num * sign);
}
}else if(ch == '+'){
sign = 1;
}else if(ch == '-'){
sign = -1;
}else if(ch == '*'){
msign = 1;
sign = 1;
}else if(ch == '/'){
msign = -1;
sign = 1;
}
}
int res = 0;
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
res += stack.pop();
}
return res;
}
228. 汇总区间
- 解答
public List<String> summaryRanges(int[] nums) {
List<String> res = new ArrayList<>();
if(nums.length==0) return res;
int start = nums[0];
int end = start;
for(int i = 1;i < nums.length;i++){
if(nums[i] - 1 == end){
end = nums[i];
}else{
if(start != end){
String tmp = "" + start + "->" + end;
res.add(tmp);
}else
res.add(""+start);
start = nums[i];
end = start;
}
}
if(start != end){
String tmp = "" + start + "->" + end;
res.add(tmp);
}else
res.add(""+start);
return res;
}
-
分析
1.遍历数组,记录连续数字的首尾。
2.当遇到不连续的数字的时候,判断首尾是否相同,相同的话 表示当前区间只有一个数字,直接插入,若不相同则说明是一段区间,根据要求插入。
3.最后的一个区间在遍历完之后并没有插入到答案中,要记得插入 -
提交结果

229. 求众数 II
给定一个大小为 n 的数组,找出其中所有出现超过 ⌊ n/3 ⌋ 次的元素。
说明: 要求算法的时间复杂度为 O(n),空间复杂度为 O(1)。

- 解答
public List<Integer> majorityElement(int[] nums) {
// 创建返回值
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
if (nums == null || nums.length == 0) return res;
// 初始化两个候选人candidate,和他们的计票
int cand1 = nums[0], count1 = 0;
int cand2 = nums[0], count2 = 0;
// 摩尔投票法,分为两个阶段:配对阶段和计数阶段
// 配对阶段
for (int num : nums) {
// 投票
if (cand1 == num) {
count1++;
continue;
}
if (cand2 == num) {
count2++;
continue;
}
// 第1个候选人配对
if (count1 == 0) {
cand1 = num;
count1++;
continue;
}
// 第2个候选人配对
if (count2 == 0) {
cand2 = num;
count2++;
continue;
}
count1--;
count2--;
}
// 计数阶段
// 找到了两个候选人之后,需要确定票数是否满足大于 N/3
count1 = 0;
count2 = 0;
for (int num : nums) {
if (cand1 == num) count1++;
else if (cand2 == num) count2++;
}
if (count1 > nums.length / 3) res.add(cand1);
if (count2 > nums.length / 3) res.add(cand2);
return res;
}
230. 二叉搜索树中第K小的元素
给定一个二叉搜索树,编写一个函数 kthSmallest 来查找其中第 k 个最小的元素。
说明:
你可以假设 k 总是有效的,1 ≤ k ≤ 二叉搜索树元素个数。
- 解答
// 方法一
public int kthSmallest(TreeNode root, int k) {
int n = 0;
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode p = root;
while(p!=null){
stack.push(p);
p = p.left;
}
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
TreeNode node = stack.pop();
n++;
if(n==k)return node.val;
if(node.right!=null){
p = node.right;
while(p!=null){
stack.push(p);
p = p.left;
}
}
}
return -1;
}
//方法二
public ArrayList<Integer> inorder(TreeNode root, ArrayList<Integer> arr){
if (root == null) return arr;
inorder(root.left, arr);
arr.add(root.val);
inorder(root.right, arr);
return arr;
}
public int kthSmallest(TreeNode root, int k) {
ArrayList<Integer> nums = inorder(root, new ArrayList<Integer>());
return nums.get(k - 1);
}
//方法三
int count = 0;
public int kthSmallest(TreeNode root, int k) {
if(root==null) return -1;
int rtn = kthSmallest(root.left, k);
if(rtn != -1) return rtn;
count ++;
if(count == k) return root.val;
int rrtn = kthSmallest(root.right, k);
if(rrtn != -1) return rrtn;
return -1;
}
-
分析
1.方法一用栈来实现中序遍历,遍历到第k个结点
2.方法二用递归实现中序遍历,返回第k个
3.方法三在方法二的基础上的改进,不用遍历完整个树,用一个全局变量,在记录已经遍历到第几个结点。
231. 2的幂
给定一个整数,编写一个函数来判断它是否是 2 的幂次方。
- 解答
public boolean isPowerOfTwo(int n) {
if(n == 0)return false;
while(n!=1){
if(n%2 != 0)return false;
n /= 2;
}
return true;
}
232. 用栈实现队列
使用栈实现队列的下列操作:
push(x) – 将一个元素放入队列的尾部。
pop() – 从队列首部移除元素。
peek() – 返回队列首部的元素。
empty() – 返回队列是否为空。
- 解答
class MyQueue {
Stack<Integer> inStack;
Stack<Integer> outStack;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
public MyQueue() {
inStack = new Stack<>();
outStack = new Stack<>();
}
/** Push element x to the back of queue. */
public void push(int x) {
while(!outStack.isEmpty())
inStack.push(outStack.pop());
inStack.push(x);
}
/** Removes the element from in front of queue and returns that element. */
public int pop() {
while(!inStack.isEmpty())
outStack.push(inStack.pop());
return outStack.pop();
}
/** Get the front element. */
public int peek() {
while(!inStack.isEmpty())
outStack.push(inStack.pop());
return outStack.peek();
}
/** Returns whether the queue is empty. */
public boolean empty() {
return inStack.isEmpty() && outStack.isEmpty();
}
}
233. 数字 1 的个数
给定一个整数 n,计算所有小于等于 n 的非负整数中数字 1 出现的个数。

- 解答
public int countDigitOne(int n) {
if(n<=0) return 0;
if(n<10) return 1;
int len = getLenOfNum(n);
int power = (int) Math.pow(10,len-1);
int high = n/power; // 最高位
int last = n - high*power;//其余位
if(high == 1)
return countDigitOne(last) + countDigitOne(power-1) + last + 1; // 如果最高位为1 最高位贡献了 last+1 个1 递归判断最高位以外的剩余位 以及 power-1的数贡献的1
else
return power + high * countDigitOne(power-1) + countDigitOne(last); // 如果最高位不位1 最高位贡献了power个1,例如 2100 贡献了 1000个1; 其余位贡献的位数 + high*(power-1)的数贡献的1
}
public int getLenOfNum(int n) {
int len = 0;
while (n != 0) {
len++;
n /= 10;
}
return len;
}
-
分析
1.用递归实现,分位最高位和剩余位
例如1234。分位 最高位位1。剩余位234 最高位的位数4位 即1000
2.若最高位位1,则最高位为1的数字贡献1的个数为剩余位的+1 即234+1 = 235
然后递归的判断剩余位贡献一的个数 以及 小于1000的数贡献1的个数
即countDigitOne(234) + countDigitOne(999)
3.若最高位不是1,例如 2234,则最高位贡献1的个数为1000个 1000-1999
然后递归的判断剩余位中1 的个数 即countDigitOne(last),以及小于1000的数贡献1的个数 因为这里high大于1 所以为high *(power-1) power这里指1000.
234. 回文链表
- 解答
//方法一
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
if(head==null || head.next == null)return true;
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
ListNode p = head;
int len = 0;
while(p!=null){
len++;
p = p.next;
}
p = head;
int number = 0;
if(len % 2 == 0){
while(number < len / 2){
stack.push(p.val);
p = p.next;
number++;
}
}else{
while(number < len / 2){
stack.push(p.val);
p = p.next;
number++;
}
p = p.next;
}
while(p!=null){
if(stack.pop() != p.val)return false;
p = p.next;
}
return true;
}
//方法二
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
List<Integer> vals = new ArrayList<>();
// Convert LinkedList into ArrayList.
ListNode currentNode = head;
while (currentNode != null) {
vals.add(currentNode.val);
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
// Use two-pointer technique to check for palindrome.
int front = 0;
int back = vals.size() - 1;
while (front < back) {
// Note that we must use ! .equals instead of !=
// because we are comparing Integer, not int.
if (!vals.get(front).equals(vals.get(back))) {
return false;
}
front++;
back--;
}
return true;
}
//方法三
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) return true;
ListNode firstHalfEnd = endOfFirstHalf(head);
ListNode secondHalfStart = reverseList(firstHalfEnd.next);
ListNode p1 = head;
ListNode p2 = secondHalfStart;
boolean result = true;
while (result && p2 != null) {
if (p1.val != p2.val) result = false;
p1 = p1.next;
p2 = p2.next;
}
firstHalfEnd.next = reverseList(secondHalfStart);
return result;
}
private ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode prev = null;
ListNode curr = head;
while (curr != null) {
ListNode nextTemp = curr.next;
curr.next = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = nextTemp;
}
return prev;
}
private ListNode endOfFirstHalf(ListNode head) {
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return slow;
}
-
分析
方法一
1.用栈来记录前半段
2.继续遍历后半段和栈顶元素比较,若不相同则说明不是回文
方法二
1.复制到数组中,用双指针,头尾遍历,比较是否是回文
方法三
1.使用额外空间O(1),将链表的后半段反转
2.然后同时遍历前半段和后半段 观察是否一致
235. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
给定一个二叉搜索树, 找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先。
百度百科中最近公共祖先的定义为:“对于有根树 T 的两个结点 p、q,最近公共祖先表示为一个结点 x,满足 x 是 p、q 的祖先且 x 的深度尽可能大(一个节点也可以是它自己的祖先)。”
例如,给定如下二叉搜索树: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5]
- 解答
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
TreeNode node1 = root;
TreeNode node2 = root;
TreeNode res = root;
while(node1 != p && node2 != q){
if(node1 == node2)res = node1;
if(node1 != node2)break;
if(node1.val < p.val)
node1 = node1.right;
else node1 = node1.left;
if(node2.val < q.val)
node2 = node2.right;
else node2 = node2.left;
}
if(node1 == node2)
res = node1;
return res;
}
-
分析
1.用两个指针分别的去寻找p和q
2.在寻找的过程中,遇到相同的结点,则将其记录下来
遇到不同的结点,说明已经出现了分叉,直接停止寻找
3.最后的一个if是为了避免p和q是在一条搜索路径上,例如 若p为2的结点 q为4的结点
在while循环结束之后,res 指向值为6的结点,不满足要求。
236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先
给定一个二叉树, 找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先。
百度百科中最近公共祖先的定义为:“对于有根树 T 的两个结点 p、q,最近公共祖先表示为一个结点 x,满足 x 是 p、q 的祖先且 x 的深度尽可能大(一个节点也可以是它自己的祖先)。”
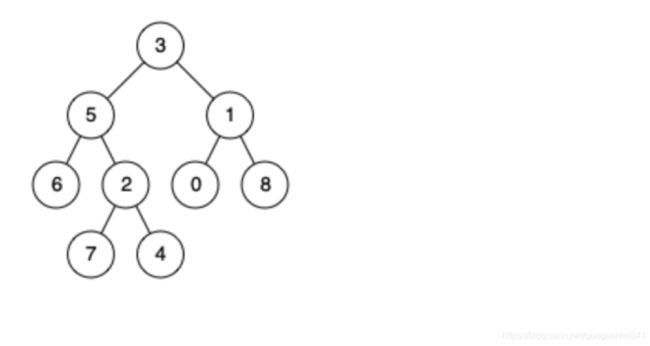
例如,给定如下二叉树: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4]
- 解答
// 方法一
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
List<TreeNode> path1 = new ArrayList<>();
List<TreeNode> path2 = new ArrayList<>();
TreeNode node1 = root;
backTrack(node1,path1,p);
TreeNode node2 = root;
backTrack(node2,path2,q);
int len = Math.min(path1.size(),path2.size());
TreeNode res = root;
for(int i = 0;i < len;i++){
if(path1.get(i) == path2.get(i))
res = path1.get(i);
else break;
}
return res;
}
public void backTrack(TreeNode node,List<TreeNode> res,TreeNode target){
if(node == null || (res.size() != 0 && res.get(res.size()-1) == target)){
return;
}
res.add(node);
backTrack(node.left,res,target);
backTrack(node.right,res,target);
if(res.get(res.size()-1) != target)
res.remove(res.size()-1);
}
//方法二
Map<Integer, TreeNode> parent = new HashMap<Integer, TreeNode>();
Set<Integer> visited = new HashSet<Integer>();
public void dfs(TreeNode root) {
if (root.left != null) {
parent.put(root.left.val, root);
dfs(root.left);
}
if (root.right != null) {
parent.put(root.right.val, root);
dfs(root.right);
}
}
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
dfs(root);
while (p != null) {
visited.add(p.val);
p = parent.get(p.val);
}
while (q != null) {
if (visited.contains(q.val)) {
return q;
}
q = parent.get(q.val);
}
return null;
}
//方法三
private TreeNode ans = null;
private boolean dfs(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if (root == null) return false;
boolean lson = dfs(root.left, p, q);
boolean rson = dfs(root.right, p, q);
if ((lson && rson) || ((root.val == p.val || root.val == q.val) && (lson || rson))) {
ans = root;
}
return lson || rson || (root.val == p.val || root.val == q.val);
}
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
this.dfs(root, p, q);
return this.ans;
}
-
分析
方法一
1.先利用回溯找到两个结点从根结点开始途径的结点路径。
2.然后同时遍历两条路径,寻找最近的公共结点
方法二
1.先找到所有结点的父亲结点并记录下来
2.然后从p开始 往上找父亲结点直到根结点,设为访问过
3.接着从q开始 往上找父结点,找到第一个访问过的结点表示最近的公共祖先结点。
方法三
1.深度搜索遍历 返回当前结点是不是路径上的点 判断条件
lson || rson || (root.val == p.val || root.val == q.val);
左孩子是路径上的点或 右孩子是路径上的点 或当前点是p或q
2.当前结点的左右孩子都是路径上的点,则说明当前结点是公共祖先
或 或者当前结点是p或q中的一个 并且左右孩子中有一个是路径上的点,则说明当前的点是公共祖先。
237. 删除链表中的节点
请编写一个函数,使其可以删除某个链表中给定的(非末尾)节点,你将只被给定要求被删除的节点。
现有一个链表 – head = [4,5,1,9],它可以表示为:
说明:
链表至少包含两个节点。
链表中所有节点的值都是唯一的。
给定的节点为非末尾节点并且一定是链表中的一个有效节点。
不要从你的函数中返回任何结果。
- 解答
public void deleteNode(ListNode node) {
node.val = node.next.val;
node.next = node.next.next;
}
238. 除自身以外数组的乘积
给你一个长度为 n 的整数数组 nums,其中 n > 1,返回输出数组 output ,其中 output[i] 等于 nums 中除 nums[i] 之外其余各元素的乘积。
- 解答
public int[] productExceptSelf(int[] nums) {
int len = nums.length;
int[] output = new int[len];
int left =1;
int right = 1;
for(int i = 0;i<len;i++){
output[i] = left; //1,1,2,6
left *= nums[i];
}
for(int i = len-1;i>=0;i--){
output[i] *= right;
right *= nums[i];
}
return output;
}
-
分析
1.第一个for循环是得到每一位之前的乘积
2.第二个for循环是乘以每一位之后的乘积,得到最终的乘积 -
提交结果
239. 滑动窗口最大值
给定一个数组 nums,有一个大小为 k 的滑动窗口从数组的最左侧移动到数组的最右侧。你只可以看到在滑动窗口内的 k 个数字。滑动窗口每次只向右移动一位。
返回滑动窗口中的最大值。
进阶:
你能在线性时间复杂度内解决此题吗?
- 解答
ArrayDeque<Integer> deq = new ArrayDeque<Integer>();
int [] nums;
public void clean_deque(int i, int k) {
if (!deq.isEmpty() && deq.getFirst() == i - k)//队中的首位已经超出滑动窗口范围
deq.removeFirst();
while (!deq.isEmpty() && nums[i] > nums[deq.getLast()])// 从队尾开始删除比新加入的结点小的数
deq.removeLast();
}
public int[] maxSlidingWindow(int[] nums, int k) {
int n = nums.length;
if (n * k == 0) return new int[0];
if (k == 1) return nums;
this.nums = nums;
int max_idx = 0; // 记录下最大值的下标
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
clean_deque(i, k); // 调整队列
deq.addLast(i);// 尾部插入
if (nums[i] > nums[max_idx]) max_idx = i;//更新最大值下标
}
int [] output = new int[n - k + 1];
output[0] = nums[max_idx];//第一个滑动窗口内的最大值
for (int i = k; i < n; i++) {
//滑动窗口最右侧的值 即每次移动新加入的值的下标为i
clean_deque(i, k);// 调整队列
deq.addLast(i);// 尾部插入
output[i - k + 1] = nums[deq.getFirst()];//第(i-k+1)个滑动窗口内的最大值 即队列中的首个
}
return output;
}
-
分析
1.使用双端队列来记录滑动窗口内的数值,队头总是最大的。新插入的值从队尾插入,从后往前删除比队尾小的数值。这样当滑动窗口移动后,若队伍中的第一位不在滑动窗口内而移除的时候,之后顶替队头的元素也是当前队伍中最大的元素下标。
2.先判断第一个窗口内的元素,按照上述规则依次入队,根据条件出队。得出第一个窗口的最大值。
3.然后从k开始,即滑动窗口最右侧,即每次移动新加入的值的下标。根据1,进行队伍调整。第(i-k+1)个滑动窗口内的最大值 即队列中的首个元素对应的值。
240. 搜索二维矩阵 II
编写一个高效的算法来搜索 m x n 矩阵 matrix 中的一个目标值 target。该矩阵具有以下特性:
每行的元素从左到右升序排列。
每列的元素从上到下升序排列。
示例:
- 解答
方法一
public boolean searchMatrix(int[][] matrix, int target) {
int m = matrix.length;
if(m == 0)return false;
int n = matrix[0].length;
if(n == 0)return false;
for(int i = 0;i < m;i++){
int left = 0;
int right = n-1;
while(left<=right){
int mid = (left+right)/2;
if(matrix[i][mid] > target){
right = mid -1;
}else if(matrix[i][mid] < target)
left = mid +1;
else return true;
}
}
return false;
}
方法二
public boolean searchMatrix(int[][] matrix, int target) {
int m = matrix.length;
if(m == 0)return false;
int n = matrix[0].length;
if(n == 0)return false;
int row = m-1;
int column = 0;
while(true){
if(row < 0 || row == m || column < 0 || column == n)break;
if(matrix[row][column] > target)
row--;
else if(matrix[row][column] < target)
column++;
else return true;
}
return false;
}