MemoryManager
一、MemoryManager
//spark 内存管理器, 默认false: 1.6之前使用StaticMemoryManager ;
val useLegacyMemoryManager = conf.getBoolean("spark.memory.useLegacyMode", false)
val memoryManager: MemoryManager =
if (useLegacyMemoryManager) {
new StaticMemoryManager(conf, numUsableCores)
} else {
UnifiedMemoryManager(conf, numUsableCores)
}
1.1、StaticMemoryManager
spark.shuffle.memoryFraction: 该参数代表了Executor内存中,分配给shuffle read task进行聚合操作的内存比例,默认是20%。
spark.storage.memoryFraction: 决定存储区域的大小
两部分内存是相互隔离的, 无法借用对方的内存
/**
* A [[MemoryManager]] that statically partitions the heap space into disjoint regions.
*
* The sizes of the execution and storage regions are determined through
* `spark.shuffle.memoryFraction` and `spark.storage.memoryFraction` respectively.
* The two regions are cleanly separated such that neither usage can borrow memory from the other.
*/
1.2、UnifiedMemoryManager
在spark1.6引入了动态内存管理, 如下图
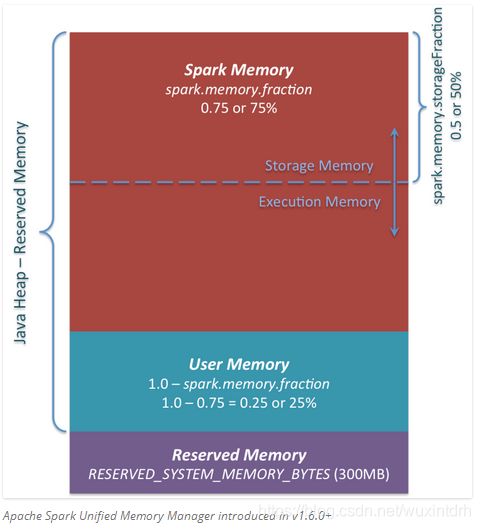
1.2.1、系统预留内存300M(除非重新编译源码)
// Set aside a fixed amount of memory for non-storage, non-execution purposes.
// This serves a function similar to `spark.memory.fraction`, but guarantees that we reserve
// sufficient memory for the system even for small heaps. E.g. if we have a 1GB JVM, then
// the memory used for execution and storage will be (1024 - 300) * 0.6 = 434MB by default.
private val RESERVED_SYSTEM_MEMORY_BYTES = 300 * 1024 * 1024
1.2.2、系统总内存
//spark.testing.memory测试使用
val systemMemory = conf.getLong("spark.testing.memory", Runtime.getRuntime.maxMemory)
系统总内存不能够小于450M
val minSystemMemory = (reservedMemory * 1.5).ceil.toLong
//如果dirver的内存小于预留的1.5倍(450M),将会报错"Please increase heap size"
if (systemMemory < minSystemMemory) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(s"System memory $systemMemory must " +
s"be at least $minSystemMemory. Please increase heap size using the --driver-memory " +
s"option or spark.driver.memory in Spark configuration.")
}
// SPARK-12759 Check executor memory to fail fast if memory is insufficient
if (conf.contains("spark.executor.memory")) {
val executorMemory = conf.getSizeAsBytes("spark.executor.memory")
//不能小于450M, 需要增加executor内存
if (executorMemory < minSystemMemory) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(s"Executor memory $executorMemory must be at least " +
s"$minSystemMemory. Please increase executor memory using the " +
s"--executor-memory option or spark.executor.memory in Spark configuration.")
}
}
1.2.3、可用内存
//可用内存
val usableMemory = systemMemory - reservedMemory
1.2.4、User Memory(这个还不算理解)
User Memory.这部分内存是分配Spark Memory内存之后的部分,而且这部分用来干什么完全取决于你。你可以用来存储RDD transformations过程使用的数据结构。例如,你可以通过mapPartitions transformation 重写Spark aggregation,mapPartitions transformations 保存hash表保证aggregation运行。这部分数据就保存在User Memory。再次强调,这是User Memory它完全由你决定存什么、如何使用,Spark完全不会管你拿这块区域用来做什么,怎么用,也不会考虑你的代码在这块区域是否会导致内存溢出。
1.2.5、spark可用资源,为storeageMemory和executionMemory共用,
//spark可用资源由spark.memory.fraction, 默认是0.6
val memoryFraction = conf.getDouble("spark.memory.fraction", 0.6)
(usableMemory * memoryFraction).toLong
1.2.5、storage可用内存, 由spark.memory.storageFraction决定, 默认0.5, 初始化storageMemory和executionMemory各占一半
所以为(totalMemory - ReversedMemory) * spark.memory.fraction * spark.memory.storageFraction = 0.3 * usableMemory
onHeapStorageRegionSize = (maxMemory * conf.getDouble("spark.memory.storageFraction", 0.5)).toLong,