读懂老板的暗语,你需要知道解释器模式!
看过《大明王朝1566》吗?这是Jungle所看过的历史剧当中最最喜欢和推崇的一部剧。看过这部剧的小伙伴们都知道,嘉靖皇帝说话从来不会明明白白说出来,而是喜欢绕着说,或者说暗语,若不细细揣测,根本不知道嘉靖说的真实含义是什么。比如他跟陈洪说“行到水穷处,坐看云起时”,陈洪就意会到皇上是让他除草;太子喜获儿子,嘉靖给了枣和栗……要是Jungle生活在那时候,脑壳真得变大啊,整天揣测皇帝的意图都够了。要是有个解释器就好了,能够把皇帝的话解释为明明白白的语言!
1.解释器模式概述
解释器模式用于描述一个简单的语言解释器,主要应用于使用面向对象语言开发的解释器的设计。当需要开发一个新的语言是,可以使用解释器模式。
解释器模式:
给定一个语言,定义它的文法的一种表示,并定义一个解释器,这个解释器使用该表示来解释语言中的句子。
解释器模式需要解决的是,如果一种特定类型的问题发生的频率足够高,那么可能就值得将该问题的各个实例表述为一个简单语言中的句子。这样就可以构件一个解释器,该解释器通过解释这些句子,来解决该问题。解释器模式描述了如何为简单的语言定义一个文法,如何在该语言中表示一个句子,以及如何解释这些句子。
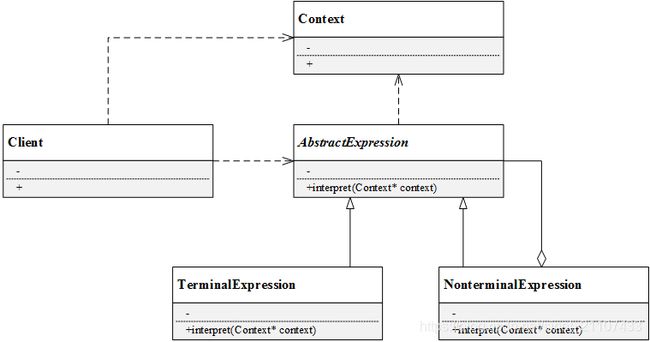
2.解释器模式结构
解释器模式的结构由抽象表达式、终结符表达式、非终结符表达式和环境类组成:
- AbstractExpression(抽象表达式):声明了抽象的解释操作interpret(),是所有终结符表达式和非终结符表达式的基类;
- TerminalExpression(终结符表达式):终结符是文法规则的组成元素中最基本的语言单位,不能再分解。终结符表达式实现了与文法规则中终结符相关的解释操作,句子中的每一个终结符都是该类的一个实例。
- NonterminalExpression(非终结符表达式):实现了文法规则中非终结符的解释操作,因为非终结符表达式同样可以包含终结符表达式,所以终结符表达式可以是非终结符表达式的成员。
- Context(环境类):即上下文类,用于存储解释器之外的一些全局信息,通常临时存储需要解释的语句。
解释器模式的UML图如上所示。抽象表达式声明了抽象接口interpret(),终结符表达式和非终结符表达式式具体实现了该接口。其中,终结符表达式的interpret()接口实现了具体的解释操作,而非终结符表达式中可能包含终结符表达式或者非终结符表达式,所以非终结符表达式的interpret()接口中可能是递归调用每一个组成部分的interpret()方法。
3.解释器模式代码实例
本节Jungle使用解释器模式实现下面一个小功能:
设计一个简单的解释器,使得系统可以解释0和1的或运算和与运算(不考虑或运算和与运算的优先级,即从左往右依次运算),语句表达式和输出结果的几个实例如下表:
表达式及输出结果部分实例表 表达式 输出结果 表达式 输出结果 1 and 1 1 0 or 0 0 1 or 1 1 1 and 1 or 0 1 1 or 0 1 0 or 1 and 0 0 1 and 0 0 0 or 1 and 1 or 1 1 0 and 0 0 1 or 0 and 1 and 0 or 0 0
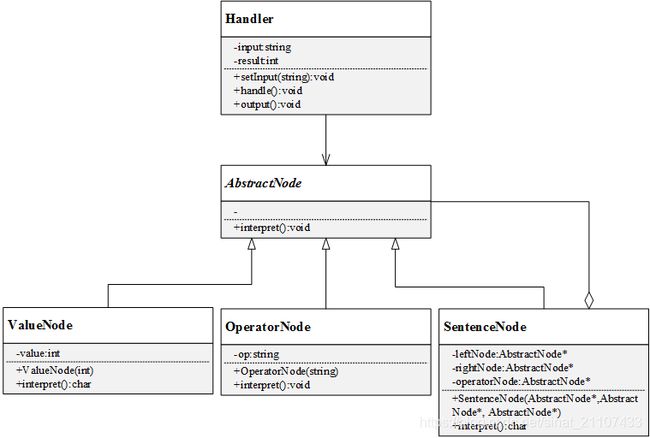
结合前面叙述的解释器模式的结构和本例,可以划分出以下角色:
- 终结符表达式角色——值节点(ValueNode):0、1,因为它们是表达式的基本组成元素,不可再细分
- 终结符表达式角色——运算符节点(OperatorNode):运算符号“and”和“or” ,同样也是表达式的基本组成元素
- 非终结符表达式角色——句子节点(SentenceNode):类似于“1 and 1”这样的表达式或者更长的组合表达式
- 上下文类角色——处理者(Handler):保存输入的表达式和输出的结果
由此,本例的UML实例图如下:
3.1.抽象表达式
// 抽象表达式类
class AbstractNode
{
public:
AbstractNode(){}
// 声明抽象接口
virtual char interpret() = 0;
};3.2.终结符表达式角色——值节点
// 终结符表达式:ValueNode
class ValueNode :public AbstractNode
{
public :
ValueNode(){}
ValueNode(int iValue){
this->value = iValue;
}
// 实现解释操作
char interpret(){
return value;
}
private:
int value;
};3.3.终结符表达式角色——运算符节点
// 终结符表达式:OperationNode
class OperatorNode :public AbstractNode
{
public:
OperatorNode(){}
OperatorNode(string iOp){
this->op = iOp;
}
// 实现解释操作
char interpret(){
if (op == "and"){
return '&';
}
else if (op == "or"){
return '|';
}
return 0;
}
private:
string op;
};3.4.非终结符表达式角色——句子节点
每一个句子节点由“左值节点+运算符节点+右值节点”组成。
// 非终结符表达式:SentenceNode
class SentenceNode :public AbstractNode
{
public:
SentenceNode(){}
SentenceNode(AbstractNode *iLeftNode,
AbstractNode *iRightNode, AbstractNode* iOperatorNode){
this->leftNode = iLeftNode;
this->rightNode = iRightNode;
this->operatorNode = iOperatorNode;
}
char interpret(){
if (operatorNode->interpret() == '&'){
return leftNode->interpret()&rightNode->interpret();
}
else{
return leftNode->interpret()|rightNode->interpret();
}
return 0;
}
private:
AbstractNode *leftNode;
AbstractNode *rightNode;
AbstractNode *operatorNode;
};
3.5.上下文角色——处理者
处理者将处理输入的表达式,并解释出表达式最终的结果。
// 处理者
class Handler
{
public:
Handler(){}
void setInput(string iInput){
this->input = iInput;
}
void handle(){
AbstractNode *left = NULL;
AbstractNode *right = NULL;
AbstractNode *op = NULL;
AbstractNode *sentence = NULL;
string iInput = this->input;
vectorinputList;
char* inputCh = const_cast(iInput.c_str());
char *token = strtok(inputCh, " ");
while (token != NULL){
inputList.push_back(token);
token = strtok(NULL, " ");
}
for (int i = 0; i < inputList.size() - 2; i += 2){
left = new ValueNode(*(inputList[i].c_str()));
op = new OperatorNode(inputList[i + 1]);
right = new ValueNode(*(inputList[i+2].c_str()));
sentence = new SentenceNode(left, right, op);
inputList[i + 2] = string(1, sentence->interpret());
}
string tmpRes = inputList[inputList.size() - 1];
if (tmpRes == "1"){
result = 1;
}
else if (tmpRes == "0"){
result = 0;
}
else{
result = -1;
}
this->output();
}
void output(){
printf("%s = %d\n", input.c_str(), result);
}
private:
string input;
char result;
}; 3.6.客户端代码示例和结果
#include
#include "InterpreterPattern.h"
int main()
{
Handler *handler = new Handler();
string input_1 = "1 and 1";
string input_2 = "1 and 0";
string input_3 = "0 and 1";
string input_4 = "0 and 0";
string input_5 = "0 or 0";
string input_6 = "0 or 1";
string input_7 = "1 or 0";
string input_8 = "1 or 1";
string input_9 = "1 and 0 or 1";
string input_10 = "0 or 0 and 1";
string input_11 = "1 or 1 and 1 and 0";
string input_12 = "0 and 1 and 1 and 1";
string input_13 = "0 and 1 and 1 and 1 or 1 or 0 and 1";
handler->setInput(input_1); handler->handle();
handler->setInput(input_2); handler->handle();
handler->setInput(input_3); handler->handle();
handler->setInput(input_4); handler->handle();
handler->setInput(input_5); handler->handle();
handler->setInput(input_6); handler->handle();
handler->setInput(input_7); handler->handle();
handler->setInput(input_8); handler->handle();
handler->setInput(input_9); handler->handle();
handler->setInput(input_10); handler->handle();
handler->setInput(input_11); handler->handle();
handler->setInput(input_12); handler->handle();
handler->setInput(input_13); handler->handle();
printf("\n\n");
system("pause");
return 0;
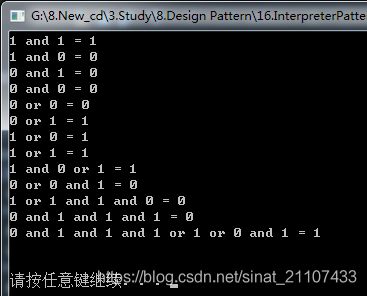
} 运行结果如下:
4.总结
优点:
- 易于改变和扩展文法,在解释器中使用类表示语言的文法规则,可以通过继承等机制类改变或扩展文法;
- 每一条文法规则都可以表示为一个类,因此可以方便地实现一个简单的语言;
- 如果要增加新的解释表达式,只需增加一个新的终结符表达式或非终结符表达式类,无需修改原有代码,符合开闭原则。
缺点:
- 对于复杂文法难以维护。在解释器模式中每一条规则至少需要定义一个类,因此如果一个语言包含太多文法规则,类的个数将会大量增加,导致系统难以管理和维护;
- 执行效率低,因为解释器模式中有大量循环和递归调用。
适用环境:
- 一些重复出现的问题可以用一种简单的语言进行表达;
- 一个语言的文法较为简单;
- 不考虑执行效率的问题时可以使用解释器模式。
欢迎关注知乎专栏:Jungle是一个用Qt的工业Robot
欢迎关注Jungle的微信公众号:Jungle笔记