前言
这篇是很久之前学习Spring Security整理的博客,发现浏览量都1000多了,一个赞都没有,那说明写得确实不怎么样,哈哈。应该很多初学者对这个接口存在疑问,特别是如果学习这个框架之前还了解过Shiro,可能会因为这两个框架角色、权限的表示方式,产生困惑。现在重新整理一下。
GrantedAuthority接口
我们知道UserDeitails接口里面有一个getAuthorities()方法。这个方法将返回此用户的所拥有的权限。这个集合将用于用户的访问控制,也就是Authorization。
所谓权限,就是一个字符串。一般不会重复。
所谓权限检查,就是查看用户权限列表中是否含有匹配的字符串。
package org.springframework.security.core; import java.io.Serializable; public interface GrantedAuthority extends Serializable { String getAuthority(); }
"角色"如何表示?与Shiro有何不同?
在Security中,角色和权限共用GrantedAuthority接口,唯一的不同角色就是多了个前缀"ROLE_",而且它没有Shiro的那种从属关系,即一个角色包含哪些权限等等。在Security看来角色和权限时一样的,它认证的时候,把所有权限(角色、权限)都取出来,而不是分开验证。
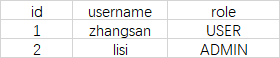
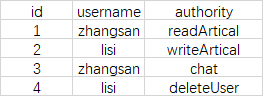
所以,在Security提供的UserDetailsService默认实现JdbcDaoImpl中,角色和权限都存储在auhtorities表中。而不是像Shiro那样,角色有个roles表,权限有个permissions表。以及相关的管理表等等。
GrantedAuthority接口的默认实现SimpleGrantedAuthority
package org.springframework.security.core.authority; import org.springframework.security.core.GrantedAuthority; import org.springframework.util.Assert; public final class SimpleGrantedAuthority implements GrantedAuthority { private static final long serialVersionUID = 500L; private final String role; public SimpleGrantedAuthority(String role) { Assert.hasText(role, "A granted authority textual representation is required"); this.role = role; } public String getAuthority() { return this.role; } public boolean equals(Object obj) { if (this == obj) { return true; } else { return obj instanceof SimpleGrantedAuthority ? this.role.equals(((SimpleGrantedAuthority)obj).role) : false; } } public int hashCode() { return this.role.hashCode(); } public String toString() { return this.role; } }
注意,在构建SimpleGrantedAuthority对象的时候,它没有添加任何前缀。所以表示"角色"的权限,在数据库中就带有"ROLE_"前缀了。所以authorities表中的视图可能是这样的。
角色和权限能否分开存储?角色能不能不带"ROLE_"前缀
当然可以分开存储,你可以定义两张表,一张存角色,一张存权限。但是你自定义UserDetailsService的时候,需要保证把这两张表的数据都取出来,放到UserDails的权限集合中。当然你数据库中存储的角色也可以不带"ROLE_"前缀,就像这样。
但是前面说到了,Security才不管你是角色,还是权限。它只比对字符串。
比如它有个表达式hasRole("ADMIN")。那它实际上查询的是用户权限集合中是否存在字符串"ROLE_ADMIN"。如果你从角色表中取出用户所拥有的角色时不加上"ROLE_"前缀,那验证的时候就匹配不上了。
所以角色信息存储的时候可以没有"ROLE_"前缀,但是包装成GrantedAuthority对象的时候必须要有。
权限检查/访问控制方式
权限检查有两种方式,一种是在配置类中,指定粗粒度的访问控制,另一种是使用注解细粒度的控制访问。
粗粒度访问控制,所有URL以"/admin"开头的用户必须拥有角色"ADMIN"才能访问。实际上操作的时候hasRole表达式,会判断参数是否包含"ROLE_"前缀,如果没有则加上去,然后再去校验。有这个前缀则直接校验。
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception { http.authorizeRequests() .antMatchers("/admin/**").access("hasRole('ADMIN')") .antMatchers("/user/**").access("hasRole('USER')") .anyRequest().authenticated(); }
细粒度的访问控制
注:需要使用注解@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled=true) 开启
@PreAuthoritze("hasAuthority('readArtical')")
public List getAll() {
//...
}
这个注解,会从SecurityContext中取出Authencation对象,然后再取出Collection