spring-security入门9---记住我功能
文章目录
- 1.基本原理
- 2 代码开发
-
- 2.1 数据库连接相关
- 2.2 页面增加“记住我”按钮
- 2.3 记住我的时间配置
- 2.4 配置TokenRepository
- 2.5 Remember相关配置
- 2.4和2.5其实写在了一个配置类里,里面有很多前面文章的信息,这里也贴一下
- 3 源码解析---以表单登陆认证方式为例(http.formLogin()…)
-
- 3.1 登陆认证时
-
- 3.1.1登陆认证成功后
- 3.1.2 追踪rememberMeServices.loginSuccess方法
- 3.2 用户在规定的时间以内(这里一般指session已经超时或者重启会话时)再次访问我们的服务时
- 4.测试
-
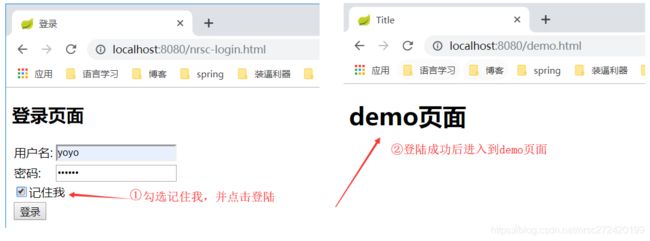
- 4.1 勾选记住我,并点击登陆进入demo页面
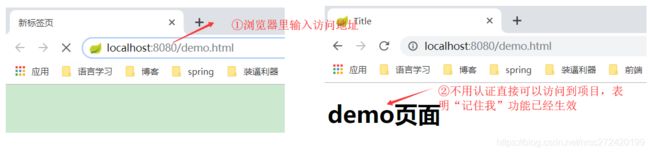
- 4.2 关闭项目,再重启项目,这时候会话已经结束,如果在同一浏览器(Cookie中存有token)重新访问项目可以直接访问,表面“记住我”功能已经生效
项目源码地址 https://github.com/nieandsun/security
1.基本原理
注意1: 图中UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter不是很准确,通过看源码我们可以知道,当我们在配置文件里指定认证方式为http.formLogin()… 时,UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter位置对应的Filter实际应为AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter,当配置的为 http.httpBasic()… 时,该位置应为BasicAuthenticationFilter,即这个位置的Filter就是我在spring-security入门7—浅析spring-security原理那篇文章里讲的FilterA1,A2…
注意2: 可以看我spring-security入门7—浅析spring-security原理这篇文章讲的RememberMeAuthenticationFilter所处的位置。
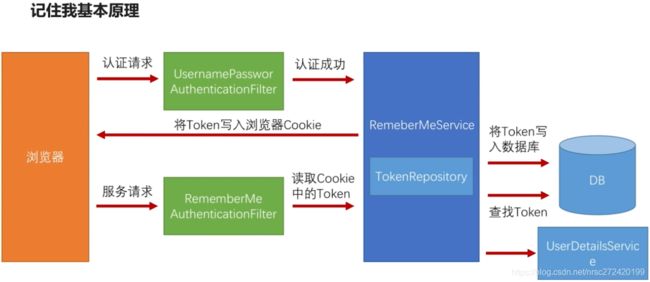
- 记住我基本原理讲解------结合上图
用户发起认证请求,当认证成功之后会在执行认证成功后的逻辑(如直接返回一个与认证成功相关的json字符串或者重定向到促发认证的请求上去)之前RememberMeService将认证成功的用户信息Token写入到数据库,同时将这个Token写入到浏览器的Cookie。当用户隔了一段时间(指定的时间范围之内),再来请求我们的服务,请求会经过RememberMeAuthenticationFiler,这个filter会读取Cookie中的Token,然后去数据库中查找是否有相应的Token,然后再通过UserDetailsService进行用户信息认证校验,如果可以认证通过,用户便可以访问到我们的服务,而不用重新进行登陆认证。
2 代码开发
2.1 数据库连接相关
- 新增jar包
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbcartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysqlgroupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-javaartifactId>
dependency>
- 连接池相关信息
spring:
datasource:
#mysql版本为8.0.13
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/nrsc-security?characterEncoding=utf-8&serverTimezone=GMT&useSSL=false
username: root
password: 123456
2.2 页面增加“记住我”按钮
<tr>
<td colspan='2'><input name="remember-me" type="checkbox" value="true" />记住我td>
tr>
2.3 记住我的时间配置
package com.nrsc.security.core.properties;
import lombok.Data;
/**
* Created By: Sun Chuan
* Created Date: 2019/6/20 22:13
*/
@Data
public class BrowserProperties {
//指定默认的登陆页面
private String loginPage = "/nrsc-login.html";
//指定默认的处理成功与处理失败的方法
private LoginType loginType = LoginType.JSON;
//记住我的时间3600秒即1小时
private int rememberMeSeconds = 3600;
}
2.4 配置TokenRepository
@Autowired
//springboot会根据yml文件中的spring:datasource将数据源注入到spring容器
//所以这里直接通过 @Autowired就可以拿到数据源
private DataSource dataSource;
@Bean
public PersistentTokenRepository persistentTokenRepository() {
JdbcTokenRepositoryImpl tokenRepository = new JdbcTokenRepositoryImpl();
tokenRepository.setDataSource(dataSource);
// 第一次启动的时候自动建表(建议不用这句话,因为第二次启动会报错)
// 建表语句可在JdbcTokenRepositoryImpl源码中找到
// tokenRepository.setCreateTableOnStartup(true);
return tokenRepository;
}
2.5 Remember相关配置
//Remember相关配置
.rememberMe()
.tokenRepository(persistentTokenRepository())//指定使用的tokenRepository
.tokenValiditySeconds(securityProperties.getBrowser().getRememberMeSeconds())//指定记住我的时间(秒)
.userDetailsService(NRSCDetailsService)//指定进行登陆认证的UserDetailsService
2.4和2.5其实写在了一个配置类里,里面有很多前面文章的信息,这里也贴一下
package com.nrsc.security.browser.config;
import com.nrsc.security.core.properties.SecurityProperties;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.password.PasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.security.web.authentication.AuthenticationFailureHandler;
import org.springframework.security.web.authentication.AuthenticationSuccessHandler;
import org.springframework.security.web.authentication.rememberme.JdbcTokenRepositoryImpl;
import org.springframework.security.web.authentication.rememberme.PersistentTokenRepository;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
@Configuration
public class BrowserSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Bean
public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
@Autowired
private AuthenticationSuccessHandler NRSCAuthenticationSuccessHandler;
@Autowired
private AuthenticationFailureHandler NRSCAuthenticationFailureHandler;
@Autowired
private SecurityProperties securityProperties;
@Autowired
private UserDetailsService NRSCDetailsService;
@Autowired
//springboot会根据yml文件中的spring:datasource将数据源注入到spring容器
//所以这里直接通过 @Autowired就可以拿到数据源
private DataSource dataSource;
@Bean
public PersistentTokenRepository persistentTokenRepository() {
JdbcTokenRepositoryImpl tokenRepository = new JdbcTokenRepositoryImpl();
tokenRepository.setDataSource(dataSource);
// 第一次启动的时候自动建表(建议不用这句话,因为第二次启动会报错)
// 建表语句可在JdbcTokenRepositoryImpl源码中找到
// tokenRepository.setCreateTableOnStartup(true);
return tokenRepository;
}
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.formLogin()
.loginPage("/authentication/require")//登陆时进入的url-->相当于进入登陆页面
.loginProcessingUrl("/nrsc/signIn")//告诉spring-security点击登陆时访问的url为/nrsc/signIn
// ---->当spring-security接收到此url的请求后,会自动调用
//com.nrsc.security.browser.action.NRSCDetailsService中的loadUserByUsername
//进行登陆校验
.successHandler(NRSCAuthenticationSuccessHandler)//指定使用NRSCAuthenticationSuccessHandler处理登陆成功后的行为
.failureHandler(NRSCAuthenticationFailureHandler)//指定使用NNRSCAuthenticationFailureHandler处理登陆失败后的行为
.and()
//Remember相关配置
.rememberMe()
.tokenRepository(persistentTokenRepository())//指定使用的tokenRepository
.tokenValiditySeconds(securityProperties.getBrowser().getRememberMeSeconds())//指定记住我的时间(秒)
.userDetailsService(NRSCDetailsService)//指定进行登陆认证的UserDetailsService
.and()
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/authentication/require", securityProperties.getBrowser().getLoginPage())//指定不校验的url
.permitAll()
.anyRequest()
.authenticated()
.and()
.csrf().disable(); //关闭csrf
// http.httpBasic()
// .and()
// .authorizeRequests()
// .anyRequest()
// .authenticated();
}
}
3 源码解析—以表单登陆认证方式为例(http.formLogin()…)
3.1 登陆认证时
3.1.1登陆认证成功后
会在执行登陆成功后的逻辑之前走 rememberMeServices.loginSuccess(request, response, authResult); 方法
protected void successfulAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain, Authentication authResult)
throws IOException, ServletException {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Authentication success. Updating SecurityContextHolder to contain: "
+ authResult);
}
//将认证后的结果放入到SecurityContextHolder中的SecurityContext中
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(authResult);
//走记住我相关的逻辑
rememberMeServices.loginSuccess(request, response, authResult);
// Fire event----还没具体研究是干什么的
if (this.eventPublisher != null) {
eventPublisher.publishEvent(new InteractiveAuthenticationSuccessEvent(
authResult, this.getClass()));
}
//执行登陆成功后的逻辑-----即实现了AuthenticationSuccessHandler接口的类中定义的逻辑
successHandler.onAuthenticationSuccess(request, response, authResult);
}
3.1.2 追踪rememberMeServices.loginSuccess方法
发现会走到onLoginSuccess方法,并在该方法内tokenRepository将认证成功的用户信息(Token)写入到数据库,同时将这个Token写入到浏览器的Cookie
protected void onLoginSuccess(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, Authentication successfulAuthentication) {
String username = successfulAuthentication.getName();
logger.debug("Creating new persistent login for user " + username);
PersistentRememberMeToken persistentToken = new PersistentRememberMeToken(
username, generateSeriesData(), generateTokenData(), new Date());
try {
//tokenRepository会将token存入到数据库
tokenRepository.createNewToken(persistentToken);
//将token写入到Cookie
addCookie(persistentToken, request, response);
}
catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("Failed to save persistent token ", e);
}
}
3.2 用户在规定的时间以内(这里一般指session已经超时或者重启会话时)再次访问我们的服务时
会穿过RememberMeAuthenticationFilter,并在该Filter里进行认证,认证成功后会将认证信息写入SecurityContextHolder,然后再跳转到引发认证的请求上去,其关键代码如下:
public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) req;
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) res;
//如果从SecurityContextHolder拿不到用户信息--session已经超时或者重启会话
if (SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication() == null) {
//就调用下面的方法尝试拿用户信息
Authentication rememberMeAuth = rememberMeServices.autoLogin(request,
response);
if (rememberMeAuth != null) {
// Attempt authenticaton via AuthenticationManager
try {
//在表单登陆认证原理源码解析那篇文章里讲过,这句话就是尝试进行认证登陆
rememberMeAuth = authenticationManager.authenticate(rememberMeAuth);
// Store to SecurityContextHolder---将认证后的用户信息放入到线程里即SecurityContextHolder里
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(rememberMeAuth);
//走认证成功后的逻辑---追踪源码可以发现它并不走我们自定义的认证成功后的逻辑--我猜它走的逻辑肯定是
//重定向到引发认证的请求上-----下面的代码就不再一一解读了
onSuccessfulAuthentication(request, response, rememberMeAuth);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("SecurityContextHolder populated with remember-me token: '"
+ SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication()
+ "'");
}
// Fire event
if (this.eventPublisher != null) {
eventPublisher
.publishEvent(new InteractiveAuthenticationSuccessEvent(
SecurityContextHolder.getContext()
.getAuthentication(), this.getClass()));
}
if (successHandler != null) {
successHandler.onAuthenticationSuccess(request, response,
rememberMeAuth);
return;
}
}
catch (AuthenticationException authenticationException) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug(
"SecurityContextHolder not populated with remember-me token, as "
+ "AuthenticationManager rejected Authentication returned by RememberMeServices: '"
+ rememberMeAuth
+ "'; invalidating remember-me token",
authenticationException);
}
rememberMeServices.loginFail(request, response);
onUnsuccessfulAuthentication(request, response,
authenticationException);
}
}
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
else {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("SecurityContextHolder not populated with remember-me token, as it already contained: '"
+ SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication() + "'");
}
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
}