数据压缩实验报告3 LZW编解码
写在前面:本次实验由老师写好了LZW编码的代码,先理解了已有代码之后,自己再写解码代码时比较容易。下面给出完整的代码以及实验结果
bitio.h(全部由老师给出,自己写了一些注释)
/*
* Declaration for bitwise IO
*
* vim: ts=4 sw=4 cindent
*/
#ifndef __BITIO__
#define __BITIO__
#include bitio.cpp(全部由老师给出)
/*
* Definitions for bitwise IO
*
* vim: ts=4 sw=4 cindent
*/
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include lzw_E.cpp(解码部分由自己编写,其他部分由老师给出,自己写了一部分注释)
/*
* Definition for LZW coding
*
* vim: ts=4 sw=4 cindent nowrap
*/
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include \n" , argv[0]);
fprintf( stdout, "\t: E or D reffers encode or decode\n" );
fprintf( stdout, "\t: input file name\n" );
fprintf( stdout, "\t: output file name\n" );
return -1;
}
if( 'E' == argv[1][0]){
// do encoding
fp = fopen( argv[2], "rb");
bf = OpenBitFileOutput( argv[3]);
if( NULL!=fp && NULL!=bf){
LZWEncode( fp, bf);
fclose( fp);
CloseBitFileOutput( bf);
fprintf( stdout, "encoding done\n");
}
}else if( 'D' == argv[1][0]){
// do decoding
bf = OpenBitFileInput( argv[2]);
fp = fopen( argv[3], "wb");
if( NULL!=fp && NULL!=bf){
LZWDecode( bf, fp);
fclose( fp);
CloseBitFileInput( bf);
fprintf( stdout, "decoding done\n");
}
}else{
// otherwise
fprintf( stderr, "not supported operation\n");
}
return 0;
}
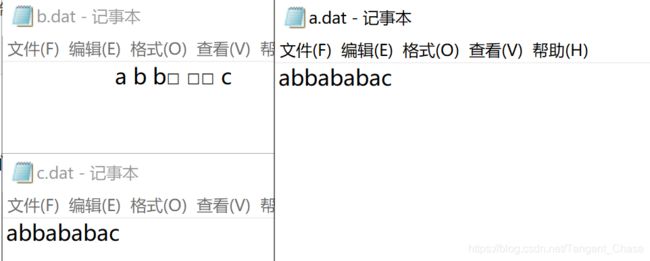
测试代码:先写一个a.dat,将abbababac写入其中。经过LZW编码后生成b.dat,解码后生成c.dat,可见编码再解码后的文件与原文件一致。
选择10种不同格式的文件进行LZW编码并比较压缩效率:
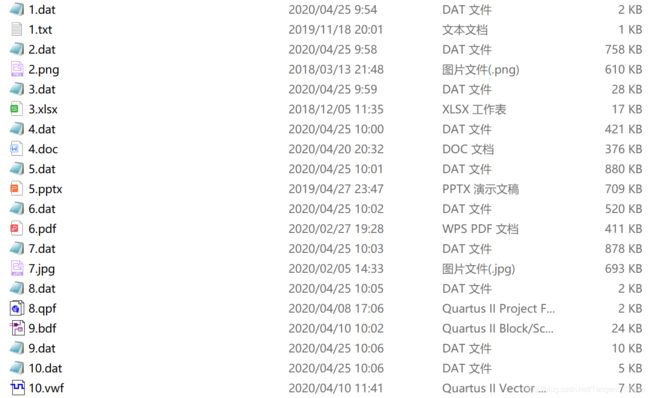
除了bdf(Quartus II原理图文件)和vwf(Quartus II仿真波形文件)之外,其他文件在进行LZW编码后大小反而增加了。