【图像处理】MATLAB:图像噪声
噪声模型
模拟噪声的行为和影响的能力是图像复原的核心。
采用函数imnoise来使用噪声污染一幅图像。

噪声应用
高斯噪声在诸如低照明水平图像传感器操作等情况下被用作一种近似。
椒盐噪声由不完善的开关设备产生。
照相乳剂中的银粒大小是用对数正态分布描述的随机变量。
瑞利噪声产生于波段成像。
指数和厄兰噪声在描述激光成像中的噪声方面是很有用的。
相关函数
A = rand( M , N ); % 生成M×N的数组,元素在区间(0,1)均匀分布。
A = randn( M , N ); % 生成M×N的数组,元素是零均值、单位方差的正态(高斯)数。
I = find(A); % 返回I中所有数组A的索引,没找到则返回一个空矩阵。
[r,c] = find(A); % 返回矩阵A的非零元素的行和列索引。
[r,c,v] = find(A); % 除了返回行索引和列索引,还以列向量v返回A的非零值。
I = find(A<128); % 示例1
A(I)=0; % 寻找图像中值小于128的像素并把它们置零。
I = find(A>=64&A<=192); % 示例2
A(I) = 128; % 将闭区间[64,192]的所有像素置为128。使用指定的分布产生空间随机噪声(函数imnoise2)
该函数生成一个大小为M×N的噪声数组R,不以任何形式缩放。imnoise输出一个有噪声的图像,而imnoise2产生噪声模式本身。
function R = imnoise2(type, M, N, a, b)
%IMNOISE2 Generates an array of random numbers with specified PDF.
% R = IMNOISE2(TYPE, M, N, A, B) generates an array, R, of size
% M-by-N, whose elements are random numbers of the specified TYPE
% with parameters A and B. If only TYPE is included in the
% input argument list, a single random number of the specified
% TYPE and default parameters shown below is generated. If only
% TYPE, M, and N are provided, the default parameters shown below
% are used. If M = N = 1, IMNOISE2 generates a single random
% number of the specified TYPE and parameters A and B.
%
% Valid values for TYPE and parameters A and B are:
%
% 'uniform' Uniform random numbers in the interval (A, B).
% The default values are (0, 1).
% 'gaussian' Gaussian random numbers with mean A and standard
% deviation B. The default values are A = 0, B = 1.
% 'salt & pepper' Salt and pepper numbers of amplitude 0 with
% probability Pa = A, and amplitude 1 with
% probability Pb = B. The default values are Pa =
% Pb = A = B = 0.05. Note that the noise has
% values 0 (with probability Pa = A) and 1 (with
% probability Pb = B), so scaling is necessary if
% values other than 0 and 1 are required. The noise
% matrix R is assigned three values. If R(x, y) =
% 0, the noise at (x, y) is pepper (black). If
% R(x, y) = 1, the noise at (x, y) is salt
% (white). If R(x, y) = 0.5, there is no noise
% assigned to coordinates (x, y).
% 'lognormal' Lognormal numbers with offset A and shape
% parameter B. The defaults are A = 1 and B =
% 0.25.
% 'rayleigh' Rayleigh noise with parameters A and B. The
% default values are A = 0 and B = 1.
% 'exponential' Exponential random numbers with parameter A. The
% default is A = 1.
% 'erlang' Erlang (gamma) random numbers with parameters A
% and B. B must be a positive integer. The
% defaults are A = 2 and B = 5. Erlang random
% numbers are approximated as the sum of B
% exponential random numbers.
% Copyright 2002-2004 R. C. Gonzalez, R. E. Woods, & S. L. Eddins
% Digital Image Processing Using MATLAB, Prentice-Hall, 2004
% $Revision: 1.5 $ $Date: 2003/10/12 23:37:29 $
% Set default values.
if nargin == 1
a = 0; b = 1;
M = 1; N = 1;
elseif nargin == 3
a = 0; b = 1;
end
% Begin processing. Use lower(type) to protect against input being
% capitalized.
switch lower(type)
case 'uniform'
R = a + (b - a)*rand(M, N);
case 'gaussian'
R = a + b*randn(M, N);
case 'salt & pepper'
if nargin <= 3
a = 0.05; b = 0.05;
end
% Check to make sure that Pa + Pb is not > 1.
if (a + b) > 1
error('The sum Pa + Pb must not exceed 1.')
end
R(1:M, 1:N) = 0.5;
% Generate an M-by-N array of uniformly-distributed random numbers
% in the range (0, 1). Then, Pa*(M*N) of them will have values <=
% a. The coordinates of these points we call 0 (pepper
% noise). Similarly, Pb*(M*N) points will have values in the range
% > a & <= (a + b). These we call 1 (salt noise).
X = rand(M, N);
c = find(X <= a);
R(c) = 0;
u = a + b;
c = find(X > a & X <= u);
R(c) = 1;
case 'lognormal'
if nargin <= 3
a = 1; b = 0.25;
end
R = a*exp(b*randn(M, N));
case 'rayleigh'
R = a + (-b*log(1 - rand(M, N))).^0.5;
case 'exponential'
if nargin <= 3
a = 1;
end
if a <= 0
error('Parameter a must be positive for exponential type.')
end
k = -1/a;
R = k*log(1 - rand(M, N));
case 'erlang'
if nargin <= 3
a = 2; b = 5;
end
if (b ~= round(b) | b <= 0)
error('Param b must be a positive integer for Erlang.')
end
k = -1/a;
R = zeros(M, N);
for j = 1:b
R = R + k*log(1 - rand(M, N));
end
otherwise
error('Unknown distribution type.')
end代码示例
r = imnoise2('gaussian',100000,1,0,1);
hist(r,50);运行结果

周期噪声(函数imnoise3)

function [r, R, S] = imnoise3(M, N, C, A, B)
%IMNOISE3 Generates periodic noise.
% [r, R, S] = IMNOISE3(M, N, C, A, B), generates a spatial
% sinusoidal noise pattern, r, of size M-by-N, its Fourier
% transform, R, and spectrum, S. The remaining parameters are:
%
% C is a K-by-2 matrix with K pairs of freq. domain coordinates (u,
% v) that define the locations of impulses in the freq. domain. The
% locations are with respect to the frequency rectangle center at
% (floor(M/2) + 1, floor(N/2) + 1). The impulse locations are spe-
% cified as increments with respect to the center. For ex, if M =
% N = 512, then the center is at (257, 257). To specify an impulse
% at (280, 300) we specify the pair (23, 43); i.e., 257 + 23 = 280,
% and 257 + 43 = 300. Only one pair of coordinates is required for
% each impulse. The conjugate pairs are generated automatically.
%
% A is a 1-by-K vector that contains the amplitude of each of the
% K impulse pairs. If A is not included in the argument, the
% default used is A = ONES(1, K). B is then automatically set to
% its default values (see next paragraph). The value specified
% for A(j) is associated with the coordinates in C(j, 1:2).
%
% B is a K-by-2 matrix containing the Bx and By phase components
% for each impulse pair. The default values for B are B(1:K, 1:2)
% = 0.
% Copyright 2002-2004 R. C. Gonzalez, R. E. Woods, & S. L. Eddins
% Digital Image Processing Using MATLAB, Prentice-Hall, 2004
% $Revision: 1.5 $ $Date: 2004/11/04 22:32:42 $
% Process input parameters.
[K, n] = size(C);
if nargin == 3
A(1:K) = 1.0;
B(1:K, 1:2) = 0;
elseif nargin == 4
B(1:K, 1:2) = 0;
end
% Generate R.
R = zeros(M, N);
for j = 1:K
u1 = M/2 + 1 + C(j, 1); v1 = N/2 + 1 + C(j, 2);
R(u1, v1) = i * (A(j)/2) * exp(i*2*pi*C(j, 1) * B(j, 1)/M);
% Complex conjugate.
u2 = M/2 + 1 - C(j, 1); v2 = N/2 + 1 - C(j, 2);
R(u2, v2) = -i * (A(j)/2) * exp(i*2*pi*C(j, 2) * B(j, 2)/N);
end
% Compute spectrum and spatial sinusoidal pattern.
S = abs(R);
r = real(ifft2(ifftshift(R)));
代码示例
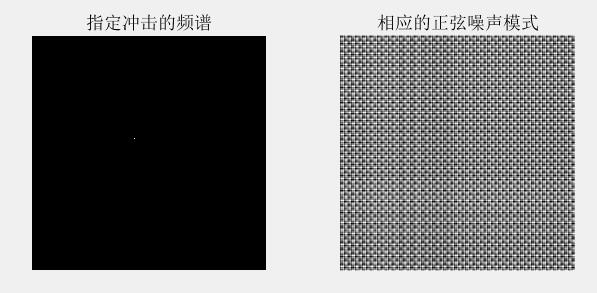
C = [0 64;0 128;32 32;64 0;128 0;-32 32];
[r,R,S] = imnoise3(512,512,C);
subplot(1,2,1);imshow(S,[ ]);title('指定冲击的频谱');
subplot(1,2,2);imshow(r,[ ]);title('相应的正弦噪声模式');运行结果
估计噪声参数


function [p, npix] = histroi(f, c, r)
% 用于计算一幅图像在多边形区域内的直方图,多边形的顶点由c和r指定,通过函数roipoly复制所定义的多边形区域
% Generate the binary mask image.
B = roipoly(f, c, r);
% Compute the histogram of the pixels in the ROI.
p = imhist(f(B));
% Obtain the number of pixels in the ROI if requested in the output.
if nargout > 1
npix = sum(B(:));
end代码示例
f = imread('noisy_image.tif');
figure,imshow(f);
[B,c,r] = roipoly(f);
[p,npix] = histroi(f,c,r);
figure,bar(p,1);
X = imnoise2('gaussian',npix,1,147,20);
figure,hist(X,130);
axis([0 300 0 140]);运行结果
(运行出了些问题…所以贴了书上的图…待以后回来修改,也许…)
