博客作者:凌逆战
博客地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/LXP-Never/p/13404523.html
音频时域波形具有以下特征:音调,响度,质量。我们在进行数据增强时,最好只做一些小改动,使得增强数据和源数据存在较小差异即可,切记不能改变原有数据的结构,不然将产生“脏数据”,通过对音频数据进行数据增强,能有助于我们的模型避免过度拟合并变得更加通用。
我发现对声波的以下改变是有用的:Noise addition(增加噪音)、增加混响、Time shifting(时移)、Pitch shifting(改变音调)和Time stretching(时间拉伸)。
本章需要使用的python库:
- matplotlib:绘制图像
- librosa:音频数据处理
- numpy:矩阵数据处理
使用先画出原始语音数据的语谱图和波形图
import librosa import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] # 用来正常显示中文标签 plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 用来正常显示符号 fs = 16000 wav_data, _ = librosa.load("./p225_001.wav", sr=fs, mono=True) # ########### 画图 plt.subplot(2, 2, 1) plt.title("语谱图", fontsize=15) plt.specgram(wav_data, Fs=16000, scale_by_freq=True, sides='default', cmap="jet") plt.xlabel('秒/s', fontsize=15) plt.ylabel('频率/Hz', fontsize=15) plt.subplot(2, 2, 2) plt.title("波形图", fontsize=15) time = np.arange(0, len(wav_data)) * (1.0 / fs) plt.plot(time, wav_data) plt.xlabel('秒/s', fontsize=15) plt.ylabel('振幅', fontsize=15) plt.tight_layout() plt.show()
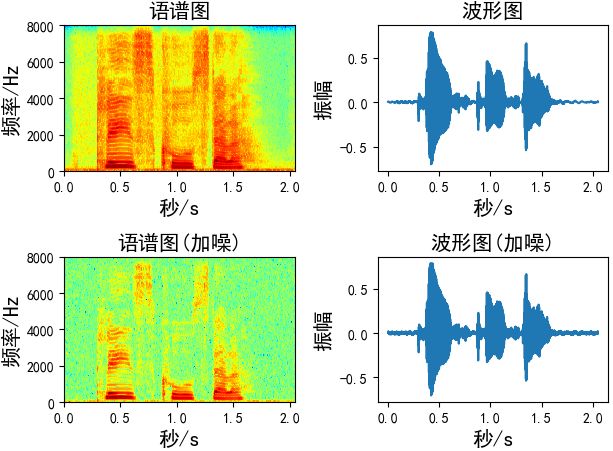
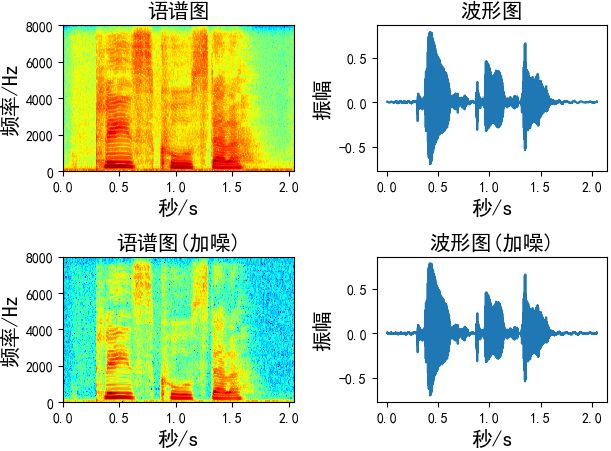
加噪
添加的噪声为均值为0,标准差为1的高斯白噪声,有两种方法对数据进行加噪
第一种:控制噪声因子
def add_noise1(x, w=0.004): # w:噪声因子 output = x + w * np.random.normal(loc=0, scale=1, size=len(x)) return output Augmentation = add_noise1(x=wav_data, w=0.004)
第二种:控制信噪比
通过信噪比的公式推导出噪声。
$$SNR=10*log_{10}(\frac{S^2}{N^2})$$
$$N=\sqrt{\frac{S^2}{10^{\frac{SNR}{10}}}}$$
def add_noise2(x, snr): # snr:生成的语音信噪比 P_signal = np.sum(abs(x) ** 2) / len(x) # 信号功率 P_noise = P_signal / 10 ** (snr / 10.0) # 噪声功率 return x + np.random.randn(len(x)) * np.sqrt(P_noise) Augmentation = add_noise2(x=wav_data, snr=50)
波形位移
语音波形移动使用numpy.roll函数向右移动shift距离
numpy.roll(a, shift, axis=None)
参数:
- a:数组
- shift:滚动的长度
- axis:滚动的维度。0为垂直滚动,1为水平滚动,参数为None时,会先将数组扁平化,进行滚动操作后,恢复原始形状
x = np.arange(10) # array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]) print(np.roll(x, 2)) # array([8, 9, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7])
波形位移函数:
def time_shift(x, shift): # shift:移动的长度 return np.roll(x, int(shift)) Augmentation = time_shift(wav_data, shift=fs//2)
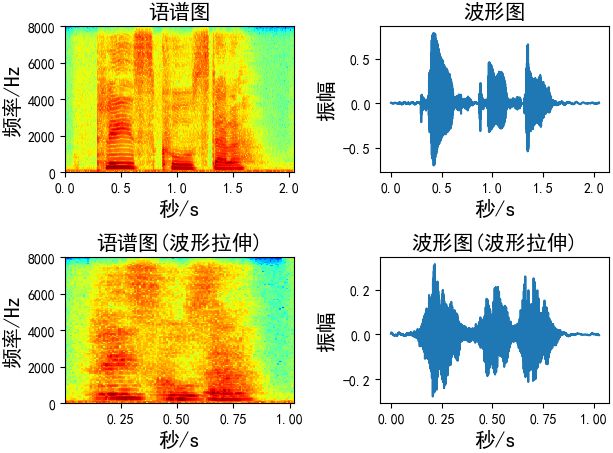
波形拉伸
在不影响音高的情况下改变声音的速度 / 持续时间。这可以使用librosa的time_stretch函数来实现。
def time_stretch(x, rate): # rate:拉伸的尺寸, # rate > 1 加快速度 # rate < 1 放慢速度 return librosa.effects.time_stretch(x, rate) Augmentation = time_stretch(wav_data, rate=2)
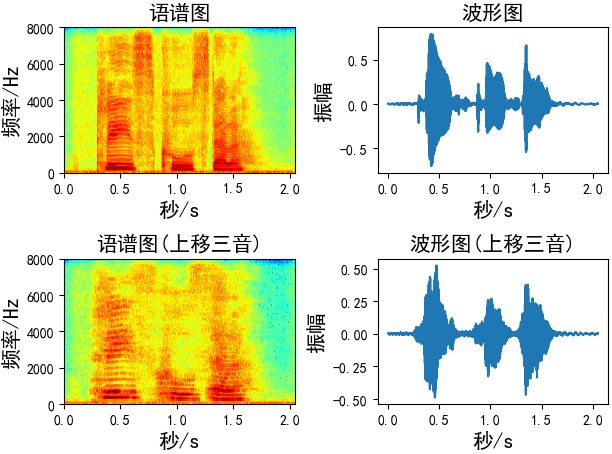
音高修正(Pitch Shifting)
音高修正只改变音高而不影响音速,我发现-5到5之间的步数更合适
def pitch_shifting(x, sr, n_steps, bins_per_octave=12): # sr: 音频采样率 # n_steps: 要移动多少步 # bins_per_octave: 每个八度音阶(半音)多少步 return librosa.effects.pitch_shift(x, sr, n_steps, bins_per_octave=bins_per_octave) # 向上移三音(如果bins_per_octave为12,则六步) Augmentation = pitch_shifting(wav_data, sr=fs, n_steps=6, bins_per_octave=12) # 向上移三音(如果bins_per_octave为24,则3步) Augmentation = pitch_shifting(wav_data, sr=fs, n_steps=3, bins_per_octave=24) # 向下移三音(如果bins_per_octave为12,则六步) Augmentation = pitch_shifting(wav_data, sr=fs, n_steps=-6, bins_per_octave=12)