DBUtils工具类的使用方法详解
DBUtils使用方法详解
目录
-
- DBUtils使用方法详解
-
-
- 一、前言
- 二、JDBC介绍
-
- 1.基本概念
- 2.JDBC访问数据库的流程
- 三、DBUtils介绍
-
- 1.基本概念
- 2.配置文件
- 3.创建JDBCUtils类
- 4.实现对数据表的增删改查
- 四、对以上代码的说明
- 五、总结
-
一、前言
本文是关于DBUtils使用方法的介绍,但在介绍DBUtils之前,首先介绍一些JDBC的基础知识,有不足之处欢迎大家指正!
二、JDBC介绍
1.基本概念
JDBC,英文名为:Java DataBase Connectivity它是Java和数据库之间的桥梁,是一个独立于特定数据库管理系统、通用的SQL数据库存取和操作的公共接口(一组API),定义了用来访问数据库的标准Java类库(java.sql,javax.sql)使用这些类库可以以一种标准的方法,方便的访问数据库资源。
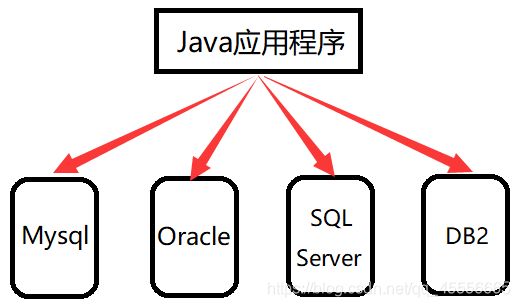
它最大的优点是为访问不同的数据库提供了一种统一的途径。接下来用两张图形象的说明这一特点。
- 没有JDBC时,Java程序访问数据库时:
- 有了JDBC,Java程序访问数据库时:
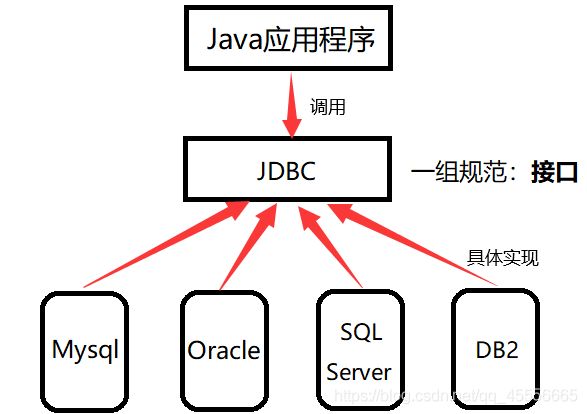
本文中的代码都是针对于MySql数据库实现的,并且所有代码都经过测试,各位放心食用。
2.JDBC访问数据库的流程
- 加载驱动(DriverManager)
- 获取连接(DriverManager,Connection)
- 获取执行SQL对象(Statement,PrepareStatement)
- 解析结果集(ReslutSet)
- 释放资源(close())
以上五个步骤每写一个操作数据库的类都是需要的,例如加载驱动、获取数据库连接、释放资源这三个步骤都要写到。为了简化代码,让程序的可移植性和观赏性更高,更加灵活的应对各种变化,需要编写一个工具类来处理这些重复的步骤,这样就引出了DBUtils工具类。
三、DBUtils介绍
1.基本概念
DBUtils:它是Apache组织提供的一个对JDBC进行简单封装的开源工具类,使用它能简化JDBC应用程序的开发,提高代码的可移植性和观赏性,同时也不会影响程序的性能。
2.配置文件
首先需要在项目(Project)的src目录下创建一个"jdbc.properties"的配置文件,在创建文件时要注意是在src目录下,否则会有错误。
配置文件内容为:
//用户名和密码
user=root
password=root
//数据库路径
url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/test?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&userSSL=false&serverTimezone=GMT%2B8
//数据库驱动
driverClass=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
配置文件的好处是:
- 实现数据和代码分离,实现了解耦;
- 如果需要修改配置文件信息,可以避免程序重新打包;
- 数据库路径、用户名、密码或者驱动发生变更时,无需改动代码,直接修改配置文件,大大提高了生产效率;
出现的问题:
配置数据库路径开始设置url为:
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test";
运行后出现java.sql.SQLException异常, 并显示 The server time zone value '�й���ʱ��' is unrecognized or represents more than one time zone. You must configure either the server or JDBC driver (via the 'serverTimezone' configuration property) to use a more specifc time zone value if you want to utilize time zone support.
通过查看资料,将url修改为:
String url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/test?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&userSSL=false&serverTimezone=GMT%2B8
解决了问题,在连接字符串后面加上?useUnicode=true& characterEncoding =UTF-8目的是为了解决中文乱码输入问题;加上userSSL=false是为了符合不使用SSL的现有应用程序,通过设置userSSL=false显示禁用SSL;serverTimezone=GMT%2B8作用是统一标准世界时间。
3.创建JDBCUtils类
里面包含了获取数据库的连接、加载驱动方法和释放资源方法
获取数据库的连接、加载驱动方法:
public static Connection getConnection() throws Exception {
/**
* 获取数据库的连接
*/
//1.读取配置文件的4个基本信息
InputStream is = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties");
Properties pros = new Properties();
pros.load(is);
String user = pros.getProperty("user");
String password = pros.getProperty("password");
String url = pros.getProperty("url");
String driverClass = pros.getProperty("driverClass");
//2.加载驱动
Class.forName(driverClass);
//3.获取连接
Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection(url,user,password);
System.out.println(con);
return con;
}
说明:
- 首先通过InputStream读取配置文件的4个基本信息,利用ClassLoader调用getSystemClassLoader()方法实际上相当ConnectionTest.class.getClassLoader()的作用,但使用前者的好处是避免了出现第三方API;
- 定义4个String类型的字符串接收获取到的基本信息;
- 此处省略了注册驱动操作,是因为在mysql的Driver实现类中,声明如下操作,故在实际的代码编写中不需要在重新进行注册驱动。
static {
try {
java.sql.DriverManager.registerDriver(new Driver());
} catch (SQLException E) {
throw new RuntimeException("Can't register driver!");
}
}
非查询类释放资源方法:
/**
* 关闭连接和Statement
* @param con
* @param ps
*/
public static void closeResource(Connection con,Statement ps) {
//资源关闭
try {
if(ps != null)
ps.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if(con != null)
con.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
说明: 非查询类释放资源过程中只需要关闭连接Connection和Statement,通过判断Statement的对象ps和Connection的对象con是否非空即可执行资源关闭。
查询类释放资源方法:
/**
* 关闭连接、Statement和ResultSet
* @param con
* @param ps
*/
public static void closeResource(Connection con,Statement ps,ResultSet rs) {
//资源关闭
try {
if(ps != null)
ps.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if(con != null)
con.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if(rs != null)
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
说明: 查询类释放资源过程中不仅仅要关闭连接Connection和Statement,还需要关闭查询过程中得到的结果集ResultSet。
4.实现对数据表的增删改查
(1)向student表中插入一条数据
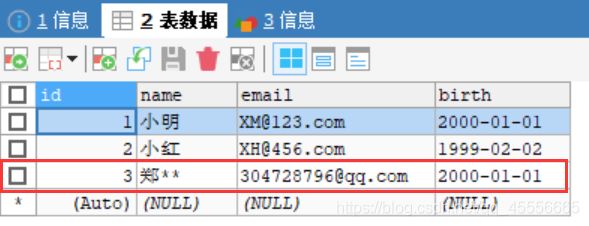
说明: 预期目的是为了将(“郑**”,“[email protected]”,“2000-01-01”)数据插入到数据库中,运行后结果如图所示。
@Test
//向student表中插入一条数据
public void testInsert(){
Connection con = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
try {
//1.读取配置文件的4个基本信息
InputStream is = ConnectionTest.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties");
Properties pros = new Properties();
pros.load(is);
String user = pros.getProperty("user");
String password = pros.getProperty("password");
String url = pros.getProperty("url");
String driverClass = pros.getProperty("driverClass");
//2.加载驱动
Class.forName(driverClass);
//3.获取连接
con = DriverManager.getConnection(url,user,password);
System.out.println(con);
//4.预编译SQL语句,返回PreparedStatement的实例
String sql = "insert into student(name,email,birth)values(?,?,?)";//?:占位符
ps = con.prepareStatement(sql);
//5.填充占位符
ps.setString(1, "郑**");
ps.setString(2, "[email protected]");
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
java.util.Date date = sdf.parse("2000-01-01");
ps.setDate(3,new Date(date.getTime()));
//6.执行SQL
ps.execute();
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//7.资源关闭
try {
if(ps != null)
ps.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if(con != null)
con.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
插入之前数据库中原始数据为:

在插入之后数据库中数据为:
(2)修改student表中的数据
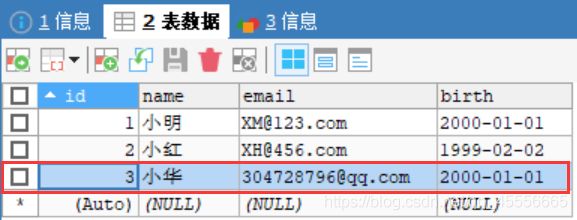
**说明:利用ps.setObject(1, “小华”);ps.setObject(2, 3); 预期目的是为了修改行号为3,列号为2的数据,由"郑"修改为"小华",运行后结果如图所示。
//修改student表的一条记录
@Test
public void testUpdate() {
//1.获取数据库连接
Connection con = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
try {
con = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
//2.预编译SQL语句,返回PraparedStatement的实例
String sql = "update student set name =? where id = ?";
ps = con.prepareStatement(sql);
//3.填充占位符
ps.setObject(1, "小华");
ps.setObject(2, 3);
//4.执行SQL
ps.execute();
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
//5.资源的关闭
JDBCUtils.closeResource(con,ps);
}
}
修改之前数据库中原始数据为:

在修改之后数据库中数据为:
(3)通用的增删改操作数据库
说明:
- 该方法不仅仅适用于该表,其他表也适用;
- 该方法根据testCommonUpdate方法中sql语句的改变而进行不同的操作;可实现增(insert)、删(delete)、改(update)操作;
- update方法中的args为可变参数,sql中的占位符的个数与可变形参长度相同;
- 利用update(sql,2)方法,预期目的是删除行号为2的数据,运行后结果如图所示。
@Test
public void testCommonUpdate() {
String sql = "delete from student where id = ?";
update(sql,2);
}
//通用的增删改操作
public void update(String sql,Object ...args){
//sql中占位符的个数与可变形参长度相同
Connection con = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
try {
//1.获取数据库连接
con = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
//2.预编译SQL语句,返回PraparedStatement的实例
ps = con.prepareStatement(sql);
//3.填充占位符
for(int i=0;i<args.length;i++) {
ps.setObject(i+1, args[i]);//参数声明:列号从1开始
}
//4.执行SQL
ps.execute();
}
catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
//5.资源的关闭
JDBCUtils.closeResource(con,ps);
}
}
删除之前数据库中原始数据为:
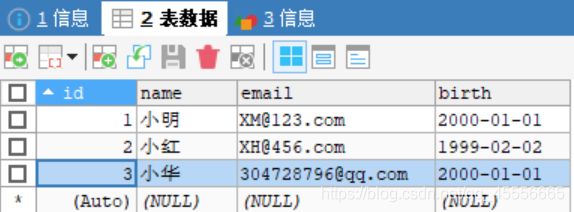
删除之后数据库中数据为:

(4)查询数据库中的数据
package com.javaweb3.preparedstatement;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.Date;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import org.junit.Test;
import com.javaweb4.util.JDBCUtils;
/**
* 针对于student表的查询
* @author 敷衍zgf
*
*/
public class StudentForQuery {
@Test
public void testQuery1(){
Connection con = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
//执行并返回结果集
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
con = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
String sql = "select id,name,email,birth from student where id = ?";
ps = con.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setObject(1, 1);
resultSet = ps.executeQuery();
//处理结果集
if(resultSet.next()) {
//判断结果集的下一条是否有数据,如果有数据返回true,并且指针下移;如果返回false,指针不会下移
//获取当前字条数据的各个字段值
int id = resultSet.getInt(1);
String name = resultSet.getString(2);
String email = resultSet.getString(3);
Date birth = resultSet.getDate(4);
/*处理结果集
* 方式一:
*/
System.out.println("id = "+id+",name = "+name+",email = "+email+",birth = "+birth);
//方式二:
Object[] data = new Object[] {
id,name,email,birth};
for(int i=0;i<data.length;i++) {
System.out.print(data[i]+" ");
}
}
}catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
//关闭资源
JDBCUtils.closeResource(con, ps, resultSet);
}
}
}
四、对以上代码的说明
以上对数据库数据的增删查操作全都是使用PreparedStatement实现的,PreparedStatement是从Statement扩展而来的。不使用Statement是因为它不仅需要拼写sql语句,更严重的是存在SQL注入的问题。PreparedStatement是预编译的,对于批量处理可以大大提高效率。
五、总结
以上就是本人对JDBC和DBUtils工具类的全部认识和简单的运用方法,如有不足之处欢迎大家批评指正!