一、简介
Ehcache是一个用Java实现的使用简单,高速,实现线程安全的缓存管理类库,ehcache提供了用内存,磁盘文件存储,以及分布式存储方式等多种灵活的cache管理方案。同时ehcache作为开放源代码项目,采用限制比较宽松的Apache License V2.0作为授权方式,被广泛地用于Hibernate, Spring,Cocoon等其他开源系统。Ehcache 从 Hibernate 发展而来,逐渐涵盖了 Cahce 界的全部功能,是目前发展势头最好的一个项目。具有快速,简单,低消耗,依赖性小,扩展性强,支持对象或序列化缓存,支持缓存或元素的失效,提供 LRU、LFU 和 FIFO 缓存策略,支持内存缓存和磁盘缓存,分布式缓存机制等等特点。
备注:为了方便大家了最新版本的Ehcache,本文中1-6节采用的最新的Ehcache3.0的特性和使用介绍,从第7节开始采用的是Ehcache2.10.2版本来与Spring相结合来做案例介绍,包括后面的源码分析也将采用这个版本
二、主要特性
快速;
简单;
多种缓存策略;
缓存数据有两级:内存和磁盘,因此无需担心容量问题;
缓存数据会在虚拟机重启的过程中写入磁盘;
可以通过 RMI、可插入 API 等方式进行分布式缓存;
具有缓存和缓存管理器的侦听接口;
支持多缓存管理器实例,以及一个实例的多个缓存区域;
提供 Hibernate 的缓存实现;
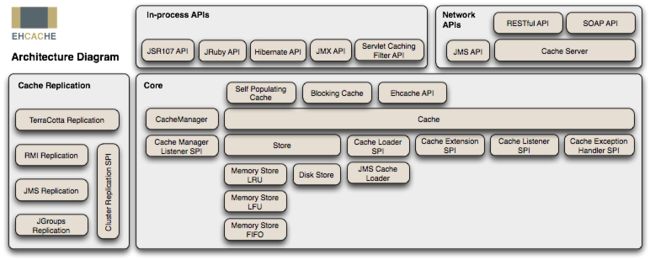
三、Ehcache的架构设计图
说明
CacheManager:是缓存管理器,可以通过单例或者多例的方式创建,也是Ehcache的入口类。
Cache:每个CacheManager可以管理多个Cache,每个Cache可以采用hash的方式管理多个Element。
Element:用于存放真正缓存内容的。
结构图如下所示:
四、Ehcache的缓存数据淘汰策略
FIFO:先进先出
LFU:最少被使用,缓存的元素有一个hit属性,hit值最小的将会被清出缓存。
LRU:最近最少使用,缓存的元素有一个时间戳,当缓存容量满了,而又需要腾出地方来缓存新的元素的时候,那么现有缓存元素中时间戳离当前时间最远的元素将被清出缓存。
五、Ehcache的缓存数据过期策略
Ehcache采用的是懒淘汰机制,每次往缓存放入数据的时候,都会存一个时间,在读取的时候要和设置的时间做TTL比较来判断是否过期。
六、Ehcache缓存的使用介绍
6.1、目前最新的Ehcache是3.0版本,我们也就使用3.0版本来介绍它的使用介绍,看如下代码:
注:这段代码介绍了Ehcache3.0的缓存使用生命周期的一个过程。
1、静态方法CacheManagerBuilder.newCacheManagerBuilder将返回一个新的org.ehcache.config.builders.CacheManagerBuilder的实例。
2、当我们要构建一个缓存管理器的时候,使用CacheManagerBuilder来创建一个预配置(pre-configured)缓存。
- 第一个参数是一个别名,用于Cache和Cachemanager进行配合。
- 第二个参数是org.ehcache.config.CacheConfiguration主要用来配置Cache。我们使用org.ehcache.config.builders.CacheConfigurationBuilder的静态方法newCacheConfigurationBuilder来创建一个默认配置实例。
3、最后调用.build方法返回一个完整的实例,当然我们也能使用CacheManager来初始化。
4、在你开始使用CacheManager的时候,需要使用init()方法进行初始化。
5、我们能取回在第二步中设定的pre-configured别名,我们对于key和要传递的值类型,要求是类型安全的,否则将抛出ClassCastException异常。
6、可以根据需求,通过CacheManager创建出新的Cache。实例化和完整实例化的Cache将通过CacheManager.getCache API返回。
7、使用put方法存储数据。
8、使用get方法获取数据。
9、我们可以通过CacheManager.removeCache方法来获取Cache,但是Cache取出来以后CacheManager将会删除自身保存的Cache实例。
10、close方法将释放CacheManager所管理的缓存资源。
6.2、关于磁盘持久化
注:如果您想使用持久化机制,就需要提供一个磁盘存储的位置给CacheManagerBuilder.persistence这个方法,另外在使用的过程中,你还需要定义一个磁盘使用的资源池。
上面的例子其实是分配了非常少的磁盘存储量,不过我们需要注意的是由于存储在磁盘上我们需要做序列化和反序列化,以及读和写的操作。它的速度肯定比内存要慢的多。
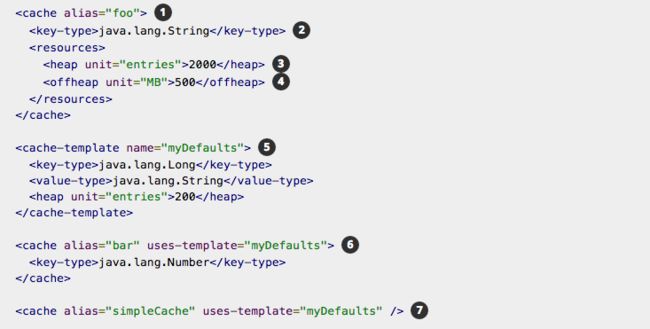
6.3、通过xml配置文件创建CacheManager
注:
1、描述缓存的别名。
2、foo的key的类型指定为String类型,而value并没有指定类型,默认就是Object类型。
3、可以在堆中为foo创建2000个实体。
4、在开始淘汰过期缓存项之前,可以分配多达500M的堆内存。
5、cache-template可以实现一个配置抽象,以便在未来可以进行扩展。
6、bar使用了cache-template模板myDefaults,并且覆盖了key-type类型,myDefaults的key-type是Long类型,覆盖后成了Number类型。
七、UserManagerCache介绍
7.1 什么是UserManagerCache,它能做什么?
UserManagerCache这是在Ehcache3.0中引入的新的概念,它将直接创建缓存而不需要使用CacheManager来进行管理。所以这也就是UserManagerCache名称的由来。
由于没有CacheManager的管理,用户就必须要手动配置所需要的服务,当然如果你发现要使用大量的服务,那么CacheManager则是更好的选择。
7.2 使用示例
1、基本示例
UserManagedCache userManagedCache =
UserManagedCacheBuilder.newUserManagedCacheBuilder(Long.class, String.class)
.build(false);
userManagedCache.init();
userManagedCache.put(1L, "da one!");
userManagedCache.close(); 2、持久化示例
LocalPersistenceService persistenceService = new DefaultLocalPersistenceService(new DefaultPersistenceConfiguration(new File(getStoragePath(), "myUserData")));
PersistentUserManagedCache cache = UserManagedCacheBuilder.newUserManagedCacheBuilder(Long.class, String.class)
.with(new UserManagedPersistenceContext("cache-name", persistenceService))
.withResourcePools(ResourcePoolsBuilder.newResourcePoolsBuilder()
.heap(10L, EntryUnit.ENTRIES)
.disk(10L, MemoryUnit.MB, true))
.build(true);
// Work with the cache
cache.put(42L, "The Answer!");
assertThat(cache.get(42L), is("The Answer!"));
cache.close();
cache.destroy(); 3、读写缓存示例
UserManagedCache cache = UserManagedCacheBuilder.newUserManagedCacheBuilder(Long.class, String.class)
.withLoaderWriter(new SampleLoaderWriter())
.build(true);
// Work with the cache
cache.put(42L, "The Answer!");
assertThat(cache.get(42L), is("The Answer!"));
cache.close(); 注:
如果你希望频繁的读和写缓存,则可以使用CacheLoaderWriter。
4、缓存淘汰策略示例
UserManagedCache cache = UserManagedCacheBuilder.newUserManagedCacheBuilder(Long.class, String.class)
.withEvictionAdvisor(new OddKeysEvictionAdvisor())
.withResourcePools(ResourcePoolsBuilder.newResourcePoolsBuilder()
.heap(2L, EntryUnit.ENTRIES))
.build(true);
// Work with the cache
cache.put(42L, "The Answer!");
cache.put(41L, "The wrong Answer!");
cache.put(39L, "The other wrong Answer!");
cache.close(); 注:
如果你想使用缓存淘汰算法来淘汰数据,则要使用EvictionAdvisor这个类。
5、按字节设定的缓存示例
UserManagedCache cache = UserManagedCacheBuilder.newUserManagedCacheBuilder(Long.class, String.class)
.withSizeOfMaxObjectSize(500, MemoryUnit.B)
.withSizeOfMaxObjectGraph(1000)
.withResourcePools(ResourcePoolsBuilder.newResourcePoolsBuilder()
.heap(3, MemoryUnit.MB))
.build(true);
cache.put(1L, "Put");
cache.put(1L, "Update");
assertThat(cache.get(1L), is("Update"));
cache.close(); 注:
withSizeOfMaxObjectGraph这个主要是调整可以设置多少字节对象。
.heap方法主要是设置每个对象最大可以设置多大。
八、缓存的使用模式
使用缓存时有几种常见的访问模式:
1、预留缓存(Cache-Aside)
应用程序在访问数据库之前必须要先访问缓存,如果缓存中包含了该数据则直接返回,不用再经过数据库,否则应用程序必须要从先数据库中取回数据,存储在缓存中并且将数据返回,当有数据要写入的时候,缓存内容必须要和数据库内容保持一致。
示例如下代码分别对应读和写:
v = cache.get(k)
if(v == null) {
v = sor.get(k)
cache.put(k, v)
}
v = newV
sor.put(k, v)
cache.put(k, v)这种方式是将数据库与缓存通过客户端应用程序主动管理来进行同步,这不是很好的使用方式。
2、Read-Through模式
相比上面的由客户端应用程序来管理数据库和缓存同步的方式,这种模式缓存会配有一个缓存中间件,该中间件来负责数据库数据和缓存之间的同步问题。当我们应用要获取缓存数据时,这个缓存中间件要确认缓存中是否有该数据,如果没有,从数据库加载,然后放入缓存,下次以后再访问就可以直接从缓存中获得。
3、Write-Through模式
这种模式就是缓存能够感知数据的变化。
也就是说在更新数据库的同时也要更新缓存,该模式其实也是弱一致性,当数据库更新数据失败的时候,缓存不能继续更新数据,要保持数据库和缓存的最终一致性。
4、Write-behind模式
该模式是以缓存为优先,将缓存更新的数据存放队列中,然后数据库定时批量从队列中取出数据更新数据库。
九、Spring3.2+Ehcache2.10.2的使用
为了使例子更加简单易懂,我没有直接去连接数据库而模拟了一些操作目的主要是演示Spring结合Ehcache的使用。
JavaBean代码如下:
public class User {
public Integer id;
public String name;
public String password;
// 这个需要,不然在实体绑定的时候出错
public User(){}
public User(Integer id, String name, String password) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.password = password;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", password=" + password
+ "]";
}
} UserDAO代码如下:
@Repository("userDao")
public class UserDao {
List userList = initUsers();
public User findById(Integer id) {
for(User user : userList){
if(user.getId().equals(id)){
return user;
}
}
return null;
}
public void removeById(Integer id) {
User delUser = null;
for(User user : userList){
if(user.getId().equals(id)){
delUser = user;
}
}
users.remove(delUser);
}
public void addUser(User user){
users.add(user);
}
public void updateUser(User user){
addUser(user);
}
private List initUsers(){
List users = new ArrayList();
User u1 = new User(1,"张三","123");
User u2 = new User(2,"李四","124");
User u3 = new User(3,"王五","125");
users.add(u1);
users.add(u2);
users.add(u3);
return users;
}
} UserService代码如下:
@Service("userService")
public class UserService {
@Autowired
private UserDao userDao;
// 查询所有数据,不需要key
@Cacheable(value = "serviceCache")
public List getAll(){
printInfo("getAll");
return userDao.users;
}
//根据ID来获取数据,ID可能是主键也可能是唯一键
@Cacheable(value = "serviceCache", key="#id")
public User findById(Integer id){
printInfo(id);
return userDao.findById(id);
}
//通过ID进行删除
@CacheEvict(value = "serviceCache", key="#id")
public void removeById(Integer id){
userDao.removeById(id);
}
//添加数据
public void addUser(User user){
if(user != null && user.getId() != null){
userDao.addUser(user);
}
}
// key 支持条件,包括 属性condition ,可以 id < 20 等等
@CacheEvict(value="serviceCache", key="#u.id")
public void updateUser(User u){
removeById(u.getId());
userDao.updateUser(u);
}
// allEntries 表示调用之后,清空缓存,默认false,
// 还有个beforeInvocation 属性,表示先清空缓存,再进行查询
@CacheEvict(value="serviceCache",allEntries=true)
public void removeAll(){
System.out.println("清除所有缓存");
}
private void printInfo(Object str){
System.out.println("非缓存查询----------findById"+str);
}
} ehcache配置文件内容如下
Spring配置文件内容如下:
十、Spring3.2+Ehcache2.10.2分布式缓存的使用
10.1 Ehcache集群简介
从Ehcache1.2版本开始,Ehcache就可以使用分布式的缓存了,从 1.7版本开始,开始支持共五种集群方案,分别是:
- Terracotta
- RMI
- JMS
- JGroups
- EhCache Server
其中有三种上最为常用集群方式,分别是 RMI、JGroups 以及 EhCache Server 。
其实我们在使用Ehcache分布式缓存的过程中,主要是以缓存插件的方式使用,如果我们想根据自己的需要使用分布式缓存那就需要自己开发来定制化,在后面我们会发现其实Ehcache提供的分布式缓存并不是非常好用,有不少问题存在,所以对缓存数据一致性比较高的情况下,使用集中式缓存更合适,比如Redis、Memcached等。
10.2 Ehcache集群的基本概念
1、成员发现(Peer Discovery)
Ehcache集群概念中有一个cache组,每个cache都是另一个cache的peer,并不像Redis或者其他分布式组件一样有一个主的存在,Ehcache并没有主Cache,可是那如何知道集群中的其他缓存都有谁呢?这个就是成员发现。
Ehcache提供了二种机制来实现成员发现功能,分别是手动发现和自动发现。
- 手动发现
在Ehcache的配置文件中指定cacheManagerPeerProviderFactory元素的class属性为
net.sf.ehcache.distribution.RMICacheManagerPeerProviderFactory。这就需要自己去配置IP地址和端口号。- 自动发现
自动的发现方式用TCP广播机制来确定和维持一个广播组。它只需要一个简单的配置可以自动的在组中添加和移除成员。在集群中也不需要什么优化服务器的知识,这是默认推荐的。
成员每秒向群组发送一个“心跳”。如果一个成员 5秒种都没有发出信号它将被群组移除。如果一个新的成员发送了一个“心跳”它将被添加进群组。
任何一个用这个配置安装了复制功能的cache都将被其他的成员发现并标识为可用状态。
要设置自动的成员发现,需要指定ehcache配置文件中
cacheManagerPeerProviderFactory元素的properties属性,就像下面这样:
peerDiscovery=automatic
multicastGroupAddress=multicast address | multicast host name
multicastGroupPort=port
timeToLive=0-255 (timeToLive属性详见常见问题部分的描述)10.3 结合Spring看示例
先看Spring配置文件:
Ehcache配置文件内容如下:
以上配置其实就是使用RMI方式在集群的环境进行缓存数据的复制。
十一、Ehcache的使用场景
11.1、Ehcache使用的注意点
1、比较少的更新数据表的情况
2、对并发要求不是很严格的情况
多台应用服务器中的缓存是不能进行实时同步的。3、对一致性要求不高的情况下
因为Ehcache本地缓存的特性,目前无法很好的解决不同服务器间缓存同步的问题,所以我们在一致性要求非常高的场合下,尽量使用Redis、Memcached等集中式缓存。
11.2、Ehcache在集群、分布式的情况下表现如何
在分布式情况下有二种同步方式:
1、RMI组播方式
原理:当缓存改变时,ehcache会向组播IP地址和端口号发送RMI UDP组播包。
缺陷:Ehcache的组播做得比较初级,功能只是基本实现(比如简单的一个HUB,接两台单网卡的服务器,互相之间组播同步就没问题),对一些复杂的环境(比如多台服务器,每台服务器上多地址,尤其是集群,存在一个集群地址带多个物理机,每台物理机又带多个虚拟站的子地址),就容易出现问题。
2、P2P方式
原理:P2P要求每个节点的Ehcache都要指向其他的N-1个节点。
3、JMS消息模式
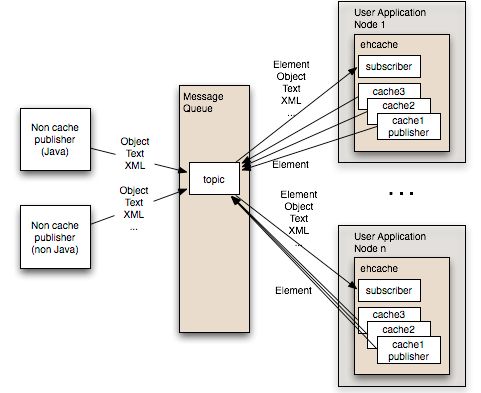
原理:这种模式的核心就是一个消息队列,每个应用节点都订阅预先定义好的主题,同时,节点有元素更新时,也会发布更新元素到主题中去。各个应用服务器节点通过侦听MQ获取到最新的数据,然后分别更新自己的Ehcache缓存,Ehcache默认支持ActiveMQ,我们也可以通过自定义组件的方式实现类似Kafka,RabbitMQ。
4、Cache Server模式
原理:这种模式会存在主从节点。
缺陷:缓存容易出现数据不一致的问题,
11.3、使用Ehcache的瓶颈是什么
1、缓存漂移(Cache Drift):每个应用节点只管理自己的缓存,在更新某个节点的时候,不会影响到其他的节点,这样数据之间可能就不同步了。
2、数据库瓶颈(Database Bottlenecks ):对于单实例的应用来说,缓存可以保护数据库的读风暴;但是,在集群的环境下,每一个应用节点都要定期保持数据最新,节点越多,要维持这样的情况对数据库的开销也越大。
11.4、实际工作中如何使用Ehcache
在实际工作中,我更多是将Ehcache作为与Redis配合的二级缓存。
第一种方式:
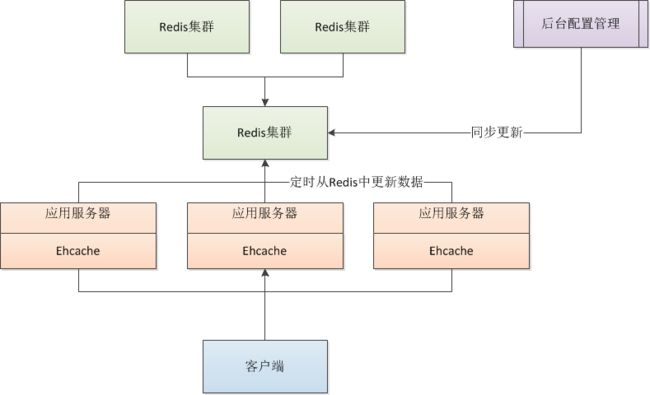
注:
这种方式通过应用服务器的Ehcache定时轮询Redis缓存服务器更同步更新本地缓存,缺点是因为每台服务器定时Ehcache的时间不一样,那么不同服务器刷新最新缓存的时间也不一样,会产生数据不一致问题,对一致性要求不高可以使用。
第二种方式:
注:
通过引入了MQ队列,使每台应用服务器的Ehcache同步侦听MQ消息,这样在一定程度上可以达到准同步更新数据,通过MQ推送或者拉取的方式,但是因为不同服务器之间的网络速度的原因,所以也不能完全达到强一致性。基于此原理使用Zookeeper等分布式协调通知组件也是如此。
总结:
1、使用二级缓存的好处是减少缓存数据的网络传输开销,当集中式缓存出现故障的时候,Ehcache等本地缓存依然能够支撑应用程序正常使用,增加了程序的健壮性。另外使用二级缓存策略可以在一定程度上阻止缓存穿透问题。
2、根据CAP原理我们可以知道,如果要使用强一致性缓存(根据自身业务决定),集中式缓存是最佳选择,如(Redis,Memcached等)。
十二、Ehcache2.10.2源码分析
12.1 源码淘汰策略解析
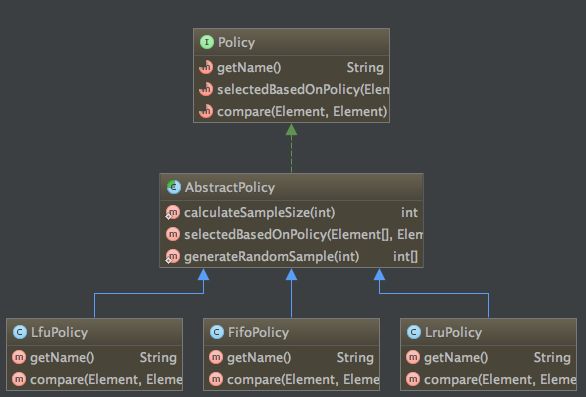
首先看一下类结构图:
从类结构图上看一共有三种缓存淘汰策略分别是:LFU,LRU,FIFO。关于这三个概念在前面都已经有过解释,我们直接这三个的源码:
1、LRUPolicy代码如下:
public class LruPolicy extends AbstractPolicy {
/**
* The name of this policy as a string literal
*/
public static final String NAME = "LRU";
/**
* @return the name of the Policy. Inbuilt examples are LRU, LFU and FIFO.
*/
public String getName() {
return NAME;
}
/**
* Compares the desirableness for eviction of two elements
*
* Compares hit counts. If both zero,
*
* @param element1 the element to compare against
* @param element2 the element to compare
* @return true if the second element is preferable to the first element for ths policy
*/
public boolean compare(Element element1, Element element2) {
return element2.getLastAccessTime() < element1.getLastAccessTime();
}注:
accessTime小的缓存淘汰。
2、LFUPolicy代码如下:
public class LfuPolicy extends AbstractPolicy {
/**
* The name of this policy as a string literal
*/
public static final String NAME = "LFU";
/**
* @return the name of the Policy. Inbuilt examples are LRU, LFU and FIFO.
*/
public String getName() {
return NAME;
}
/**
* Compares the desirableness for eviction of two elements
*
* Compares hit counts. If both zero,
*
* @param element1 the element to compare against
* @param element2 the element to compare
* @return true if the second element is preferable to the first element for ths policy
*/
public boolean compare(Element element1, Element element2) {
return element2.getHitCount() < element1.getHitCount();
}
}注:
hit值小的缓存淘汰。
3、FIFOPolicy代码如下:
public class FifoPolicy extends AbstractPolicy {
/**
* The name of this policy as a string literal
*/
public static final String NAME = "FIFO";
/**
* @return the name of the Policy. Inbuilt examples are LRU, LFU and FIFO.
*/
public String getName() {
return NAME;
}
/**
* Compares the desirableness for eviction of two elements
*
* Compares hit counts. If both zero,
*
* @param element1 the element to compare against
* @param element2 the element to compare
* @return true if the second element is preferable to the first element for ths policy
*/
public boolean compare(Element element1, Element element2) {
return element2.getLatestOfCreationAndUpdateTime() < element1.getLatestOfCreationAndUpdateTime();
}
}注:
以creationAndUpdateTime最新或者最近的缓存淘汰。
4、这三个策略类统一继承AbstractPolicy抽类
最关键的就是下面这个方法:
public Element selectedBasedOnPolicy(Element[] sampledElements, Element justAdded) {
//edge condition when Memory Store configured to size 0
if (sampledElements.length == 1) {
return sampledElements[0];
}
Element lowestElement = null;
for (Element element : sampledElements) {
if (element == null) {
continue;
}
if (lowestElement == null) {
if (!element.equals(justAdded)) {
lowestElement = element;
}
} else if (compare(lowestElement, element) && !element.equals(justAdded)) {
lowestElement = element;
}
}
return lowestElement;
}注:
1、这个方法主要是从取样节点中查找需要淘汰的缓存。
2、最关键的就是调用compare这个方法其实就是调用的上面那三个策略实现的方法来找个可以淘汰的缓存节点。
那么接下来我们看一下淘汰缓存的生命周期流程是怎么样的。
12.2 EhcacheManager类解析
这个类是2.10.2版本的最核心类,初始化、创建缓存、获取缓存都会用到这个类,这个类里面有几十个方法非常多,我们会按照类别分别进行介绍,先看其构造方法吧。
先看方法CacheManager()默认的情况代码如下:
public CacheManager() throws CacheException {
// default config will be done
status = Status.STATUS_UNINITIALISED;
init(null, null, null, null);
}Status.STATUS_UNINITIALISED这句的意思是缓存未被初始化,在构造方法里面要设定一个初始状态。
我们接着看init方法,这个方法是有别于其他构造方法的,因为默认的情况下这个方法的参数全传null值,这就意味着使用ehcache自己默认的配置了。
代码如下:
protected synchronized void init(Configuration initialConfiguration, String configurationFileName, URL configurationURL,
InputStream configurationInputStream) {
Configuration configuration;
if (initialConfiguration == null) {
configuration = parseConfiguration(configurationFileName, configurationURL, configurationInputStream);
} else {
configuration = initialConfiguration;
}
assertManagementRESTServiceConfigurationIsCorrect(configuration);
assertNoCacheManagerExistsWithSameName(configuration);
try {
doInit(configuration);
} catch (Throwable t) {
if (terracottaClient != null) {
terracottaClient.shutdown();
}
if (statisticsExecutor != null) {
statisticsExecutor.shutdown();
}
if (featuresManager != null) {
featuresManager.dispose();
}
if (diskStorePathManager != null) {
diskStorePathManager.releaseLock();
}
if (cacheManagerTimer != null) {
cacheManagerTimer.cancel();
cacheManagerTimer.purge();
}
synchronized (CacheManager.class) {
final String name = CACHE_MANAGERS_REVERSE_MAP.remove(this);
CACHE_MANAGERS_MAP.remove(name);
}
ALL_CACHE_MANAGERS.remove(this);
if (t instanceof CacheException) {
throw (CacheException) t;
} else {
throw new CacheException(t);
}
}
}说明
1、首先要判断initialConfiguration这个参数是不是为空,判断的情况下肯定是为就直接调用了parseConfiguration这个方法,这个方法调用classpath默认路径来查找配置文件内容,初始化完configuration以后调用doInit方法。
2、doInit方法主要用来初始化最大的本地堆大小,初始化最大的本地持久化磁盘设置大小,集群模式,事务设置等等。
12.3 Cache类解析
cache的类继承结构如下所示: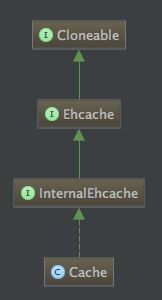
说明:
Ehcache接口是整个缓存的核心接口,该接口提供的方法可以直接操作缓存,比如put,get等方法。由于方法太多我们只单拿出来put和get方法做一个深入分析。
先看put方法源码:
private void putInternal(Element element, boolean doNotNotifyCacheReplicators, boolean useCacheWriter) {
putObserver.begin();
if (useCacheWriter) {
initialiseCacheWriterManager(true);
}
checkStatus();
if (disabled) {
putObserver.end(PutOutcome.IGNORED);
return;
}
if (element == null) {
if (doNotNotifyCacheReplicators) {
LOG.debug("Element from replicated put is null. This happens because the element is a SoftReference" +
" and it has been collected. Increase heap memory on the JVM or set -Xms to be the same as " +
"-Xmx to avoid this problem.");
}
putObserver.end(PutOutcome.IGNORED);
return;
}
if (element.getObjectKey() == null) {
putObserver.end(PutOutcome.IGNORED);
return;
}
element.resetAccessStatistics();
applyDefaultsToElementWithoutLifespanSet(element);
backOffIfDiskSpoolFull();
element.updateUpdateStatistics();
boolean elementExists = false;
if (useCacheWriter) {
boolean notifyListeners = true;
try {
elementExists = !compoundStore.putWithWriter(element, cacheWriterManager);
} catch (StoreUpdateException e) {
elementExists = e.isUpdate();
notifyListeners = configuration.getCacheWriterConfiguration().getNotifyListenersOnException();
RuntimeException cause = e.getCause();
if (cause instanceof CacheWriterManagerException) {
throw ((CacheWriterManagerException)cause).getCause();
}
throw cause;
} finally {
if (notifyListeners) {
notifyPutInternalListeners(element, doNotNotifyCacheReplicators, elementExists);
}
}
} else {
elementExists = !compoundStore.put(element);
notifyPutInternalListeners(element, doNotNotifyCacheReplicators, elementExists);
}
putObserver.end(elementExists ? PutOutcome.UPDATED : PutOutcome.ADDED);
}说明:
1、代码的逻辑其实很简单,我们看一下compoundStore这个类,实际上我们缓存的数据最终都是要到这个类里面进行存储的。
2、代码里面使用了putObserver观察者对象主要是用来做计数统计任务用的。
看一下compoundStore类的继承结构图如下:
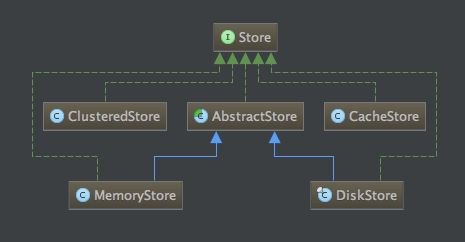
通过图中可以看到所有的存储类都实现Store接口类,大概有以下几种存储方式:
1、集群方式:ClusteredStore
2、缓存方式:CacheStore
3、内存方式:MemoryStore
4、磁盘方式:DiskStore
我们以DiskStore为例深入讲解磁盘的部分源码分析。
writeLock().lock();
try {
// ensure capacity
if (count + 1 > threshold) {
rehash();
}
HashEntry[] tab = table;
int index = hash & (tab.length - 1);
HashEntry first = tab[index];
HashEntry e = first;
while (e != null && (e.hash != hash || !key.equals(e.key))) {
e = e.next;
}
Element oldElement;
if (e != null) {
DiskSubstitute onDiskSubstitute = e.element;
if (!onlyIfAbsent) {
e.element = encoded;
installed = true;
oldElement = decode(onDiskSubstitute);
free(onDiskSubstitute);
final long existingHeapSize = onHeapPoolAccessor.delete(onDiskSubstitute.onHeapSize);
LOG.debug("put updated, deleted {} on heap", existingHeapSize);
if (onDiskSubstitute instanceof DiskStorageFactory.DiskMarker) {
final long existingDiskSize = onDiskPoolAccessor.delete(((DiskStorageFactory.DiskMarker) onDiskSubstitute).getSize());
LOG.debug("put updated, deleted {} on disk", existingDiskSize);
}
e.faulted.set(faulted);
cacheEventNotificationService.notifyElementUpdatedOrdered(oldElement, element);
} else {
oldElement = decode(onDiskSubstitute);
free(encoded);
final long outgoingHeapSize = onHeapPoolAccessor.delete(encoded.onHeapSize);
LOG.debug("put if absent failed, deleted {} on heap", outgoingHeapSize);
}
} else {
oldElement = null;
++modCount;
tab[index] = new HashEntry(key, hash, first, encoded, new AtomicBoolean(faulted));
installed = true;
// write-volatile
count = count + 1;
cacheEventNotificationService.notifyElementPutOrdered(element);
}
return oldElement;
} finally {
writeLock().unlock();
if (installed) {
encoded.installed();
}
}说明:
1、流程采用写锁,先将这段代码锁定。
2、程序中有HashEntry[] tab这样一个桶,每个桶中存储一个链表,首先通过hash & (tab -1) 也就是key的hash值与桶的长度减1取余得出一个桶的index。然后取出链表实体,得到当前链表实体的下一个元素,如果元素为null则直接将元素赋值,否则取出旧的元素用新元素替换,释放旧元素空间,返回旧元素。
十三、Guava Cache的使用与实现
Guava Cache与ConcurrentMap很相似,但也不完全一样。最基本的区别是ConcurrentMap会一直保存所有添加的元素,直到显式地移除。相对地,Guava Cache为了限制内存占用,通常都设定为自动回收元素。在某些场景下,尽管LoadingCache 不回收元素,它也是很有用的,因为它会自动加载缓存。
通常来说,Guava Cache
适用于:
你愿意消耗一些内存空间来提升速度。
你预料到某些键会被查询一次以上。
缓存中存放的数据总量不会超出内存容量。(Guava Cache是单个应用运行时的本地缓存。它不把数据存放到文件或外部服务器。如果这不符合你的需求,请尝试Memcached或者Redis等集中式缓存。
Guava Cache是一个全内存的本地缓存实现,它提供了线程安全的实现机制。
Guava Cache有两种创建方式:
- CacheLoader
- Callable callback
13.1 CacheLoader方式
先看一段示例代码如下:
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
//缓存接口这里是LoadingCache,LoadingCache在缓存项不存在时可以自动加载缓存
LoadingCache strCache
//CacheBuilder的构造函数是私有的,只能通过其静态方法newBuilder()来获得CacheBuilder的实例
= CacheBuilder.newBuilder()
//设置并发级别为8,并发级别是指可以同时写缓存的线程数
.concurrencyLevel(8)
//设置写缓存后8秒钟过期
.expireAfterWrite(8, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
//设置缓存容器的初始容量为10
.initialCapacity(10)
//设置缓存最大容量为100,超过100之后就会按照LRU最近虽少使用算法来移除缓存项
.maximumSize(100)
//设置要统计缓存的命中率
.recordStats()
//设置缓存的移除通知
.removalListener(new RemovalListener() {
public void onRemoval(RemovalNotification notification) {
System.out.println(notification.getKey() + " was removed, cause is " + notification.getCause());
}
})
//build方法中可以指定CacheLoader,在缓存不存在时通过CacheLoader的实现自动加载缓存
.build(
new CacheLoader() {
@Override
public String load(Integer key) throws Exception {
System.out.println("load data: " + key);
String str = key + ":cache-value";
return str;
}
}
);
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
//从缓存中得到数据,由于我们没有设置过缓存,所以需要通过CacheLoader加载缓存数据
String str = strCache.get(1);
System.out.println(str);
//休眠1秒
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
}
System.out.println("cache stats:");
//最后打印缓存的命中率等 情况
System.out.println(strCache.stats().toString());
} 运行结果如下:
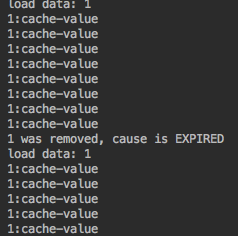
说明:
guava中使用缓存需要先声明一个CacheBuilder对象,并设置缓存的相关参数,然后调用其build方法获得一个Cache接口的实例。
13.2 Callable方式
方法原型如下:get(K, Callable
这个方法返回缓存中相应的值,如果未获取到缓存值则调用Callable方法。这个方法简便地实现了模式"如果有缓存则返回;否则运算、缓存、然后返回"。
看示例代码如下:
Cache cache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder().maximumSize(1000).build();
String resultVal = cache.get("test", new Callable() {
public String call() {
//未根据key查到对应缓存,设置缓存
String strProValue="test-value"
return strProValue;
}
});
System.out.println("return value : " + resultVal);
} 13.3 缓存过期删除
guava的cache数据过期删除的方式有二种,分别是主动删除和被动删除二种。
被动删除三种方式
- 基于条数限制的删除
使用CacheBuilder.maximumSize(long)方法进行设置。
注意点:
1、这个size不是容量大小,而是记录条数。
2、使用CacheLoader方式加载缓存的时候,在并发情况下如果一个key过期删除,正好同时有一个请求获取缓存,有可能会报错。
- 基于过期时间删除
在Guava Cache中提供了二个方法可以基于过期时间删除
1、expireAfterAccess(long, TimeUnit):某个key最后一次访问后,再隔多长时间后删除。
2、expireAfterWrite(long, TimeUnit):某个key被创建后,再隔多长时间后删除。
- 基于引用的删除
通过使用弱引用的键、或弱引用的值、或软引用的值,Guava Cache可以把缓存设置为允许垃圾回收。
主动删除三种方式
- 个别清除:Cache.invalidate(key)
- 批量清除:Cache.invalidateAll(keys)
- 清除所有缓存项:Cache.invalidateAll()
本文由博客群发一文多发等运营工具平台 OpenWrite 发布